
If all sides of a parallelogram touch a circle, show that the parallelogram is a rhombus.
Answer
621.3k+ views
Hint: In this question apply the property of tangent from the external point on the circle which is that the length of tangent drawn from the external point on the circle is equal, so use this concept to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
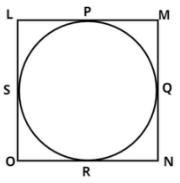
Let LMNO be the quadrilateral that touches a circle at P, Q, R, S respectively. (see figure)
Now we have to prove Parallelogram is a rhombus.
Proof:
For a parallelogram to be a rhombus it is necessary that all the sides of the parallelogram should be equal.
As we know that the tangents drawn from the external point on the circle are equal.
$ \Rightarrow LP = LS...............\left( 1 \right)$ (Tangent from point L)
$ \Rightarrow MP = MQ...............\left( 2 \right)$ (Tangent from point M)
$ \Rightarrow NR = NQ...............\left( 3 \right)$ (Tangent from point N)
$ \Rightarrow OR = OS...............\left( 4 \right)$ (Tangent from point O)
Adding equation (1), (2), (3) and (4) we get.
$LP + MP + NR + OR = LS + MQ + NQ + OS$
$\left( {LP + MP} \right) + \left( {NR + OR} \right) = \left( {OS + LS} \right) + \left( {MQ + NQ} \right)$
Now from figure
$
LP + MP = LM,{\text{ }}NR + OR = NO \\
OS + LS = OL,{\text{ }}MQ + NQ = MN \\
$
Substitute these values in the above equation we have
$\left( {LM} \right) + \left( {NO} \right) = \left( {OL} \right) + \left( {MN} \right)$
Now as we know that in a parallelogram opposite sides are equal.
$ \Rightarrow LM = NO,\;OL = MN$
Therefore above equation becomes,
$
\left( {LM} \right) + \left( {LM} \right) = \left( {OL} \right) + \left( {OL} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 2LM = 2OL \\
\Rightarrow LM = OL................\left( 5 \right) \\
$
But, $\left( {LM = NO{\text{ & }}OL = MN} \right)..............\left( 6 \right)$
Therefore from equation (5) and (6)
$LM = MN = NO = OL$
Therefore all the sides of a parallelogram are equal.
Hence, Parallelogram LMNO is a rhombus.
Hence proved.
Note: In such types of questions the key concept is that always recall the property of tangent from external point on the circle and also remember the property of parallelogram and rhombus which is all stated above, then first use the property of tangent and make equations as above, then add these equation and apply the property of parallelogram as above and simplify, we will get the required result.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let LMNO be the quadrilateral that touches a circle at P, Q, R, S respectively. (see figure)
Now we have to prove Parallelogram is a rhombus.
Proof:
For a parallelogram to be a rhombus it is necessary that all the sides of the parallelogram should be equal.
As we know that the tangents drawn from the external point on the circle are equal.
$ \Rightarrow LP = LS...............\left( 1 \right)$ (Tangent from point L)
$ \Rightarrow MP = MQ...............\left( 2 \right)$ (Tangent from point M)
$ \Rightarrow NR = NQ...............\left( 3 \right)$ (Tangent from point N)
$ \Rightarrow OR = OS...............\left( 4 \right)$ (Tangent from point O)
Adding equation (1), (2), (3) and (4) we get.
$LP + MP + NR + OR = LS + MQ + NQ + OS$
$\left( {LP + MP} \right) + \left( {NR + OR} \right) = \left( {OS + LS} \right) + \left( {MQ + NQ} \right)$
Now from figure
$
LP + MP = LM,{\text{ }}NR + OR = NO \\
OS + LS = OL,{\text{ }}MQ + NQ = MN \\
$
Substitute these values in the above equation we have
$\left( {LM} \right) + \left( {NO} \right) = \left( {OL} \right) + \left( {MN} \right)$
Now as we know that in a parallelogram opposite sides are equal.
$ \Rightarrow LM = NO,\;OL = MN$
Therefore above equation becomes,
$
\left( {LM} \right) + \left( {LM} \right) = \left( {OL} \right) + \left( {OL} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 2LM = 2OL \\
\Rightarrow LM = OL................\left( 5 \right) \\
$
But, $\left( {LM = NO{\text{ & }}OL = MN} \right)..............\left( 6 \right)$
Therefore from equation (5) and (6)
$LM = MN = NO = OL$
Therefore all the sides of a parallelogram are equal.
Hence, Parallelogram LMNO is a rhombus.
Hence proved.
Note: In such types of questions the key concept is that always recall the property of tangent from external point on the circle and also remember the property of parallelogram and rhombus which is all stated above, then first use the property of tangent and make equations as above, then add these equation and apply the property of parallelogram as above and simplify, we will get the required result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




