
If a flag-staff of 6m height placed on top of a tower throws a shadow of $2\sqrt 3 m$ along the ground, then what is the angle that the sun makes with the ground?
$(a){\text{ 6}}{{\text{0}}^0}$
$(b){\text{ 4}}{{\text{5}}^0}$
$(c){\text{ 3}}{{\text{0}}^0}$
$(d){\text{ 1}}{{\text{5}}^0}$
Answer
630.6k+ views
Hint- By the data provided in the question we can easily form a triangle and implementation of trigonometric ratios to this triangle will help to reach the answer.
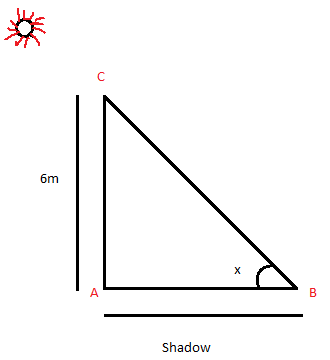
Let us take the angle of elevation made by the point B on the ground with the sun as x degree.
Now length of shadow that is AB =$2\sqrt 3 m$, given in question.
The length of tower AC =6m, given in question.
$\operatorname{Tan} \theta = \dfrac{{height}}{{base}}$……………………………….. (1)
Now in $\vartriangle ABC$
Using equation (1) we can say that
$\operatorname{Tan} x = \dfrac{{AC}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{6}{{2\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Now let’s rationalize the denominator part by multiplying $\sqrt 3 $ in both the numerator and denominator part.
$\tan x = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 3 }} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{3} = \sqrt 3 $
Now
$
\tan x = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow x = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{3} = {60^0} \\
$
Hence the required angle is 60 degrees.
Note- Whenever we come across this type of question the basic concept that we need to recall is that of trigonometric ratios, example$\operatorname{Tan} \theta = \dfrac{{height}}{{base}}$, similarly all other trigonometric ratios have a default implementation formula. Having a good grasp over them helps to reach the right answer.

Let us take the angle of elevation made by the point B on the ground with the sun as x degree.
Now length of shadow that is AB =$2\sqrt 3 m$, given in question.
The length of tower AC =6m, given in question.
$\operatorname{Tan} \theta = \dfrac{{height}}{{base}}$……………………………….. (1)
Now in $\vartriangle ABC$
Using equation (1) we can say that
$\operatorname{Tan} x = \dfrac{{AC}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{6}{{2\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
Now let’s rationalize the denominator part by multiplying $\sqrt 3 $ in both the numerator and denominator part.
$\tan x = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 3 }} \times \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{3} = \sqrt 3 $
Now
$
\tan x = \sqrt 3 \\
\Rightarrow x = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 3 } \right) = \dfrac{\pi }{3} = {60^0} \\
$
Hence the required angle is 60 degrees.
Note- Whenever we come across this type of question the basic concept that we need to recall is that of trigonometric ratios, example$\operatorname{Tan} \theta = \dfrac{{height}}{{base}}$, similarly all other trigonometric ratios have a default implementation formula. Having a good grasp over them helps to reach the right answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




