
What happens when lactic acid is treated with ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ ? Write the equation.
Answer
570k+ views
Hint: First we will draw the structure of lactic acid and see the reactivity of the attached groups in it. ${\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{5}}}$ mainly releases the chloride ion as a nucleophile. This chloride nucleophile will attack the reactive site in the compound.
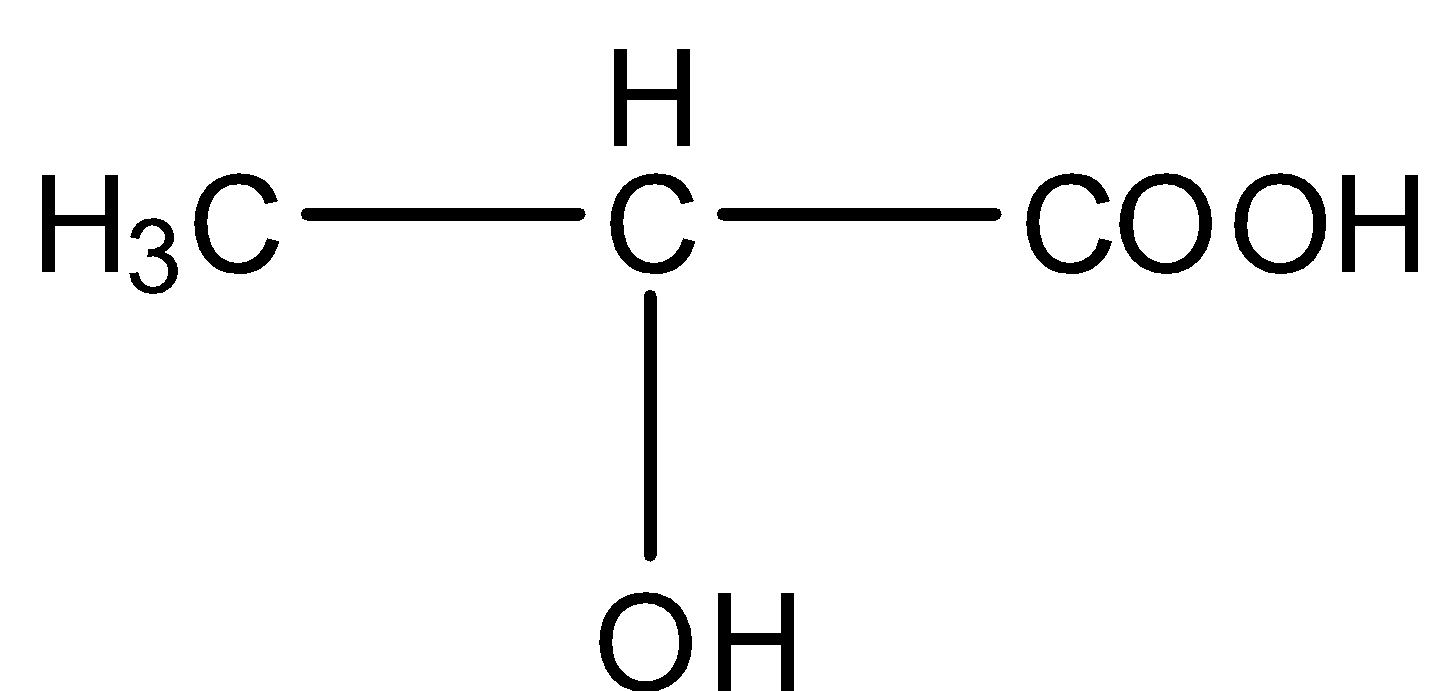
Complete step by step answer:
The formula of lactic acid is . It is a white crystalline solid and soluble in water. When in aqueous state it is a colorless solution. It is also called alpha-hydroxy acid because of the presence of the hydroxyl group in the adjacent carboxyl group. It is an ionizable molecule which dissociates in carboxylate ions and a proton. It is more acidic than acetic acid because of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl group and carboxyl group. Lactic acid is a chiral molecule which has two enantiomers. D and L enantiomers are there and also can be present as racemic mixture.
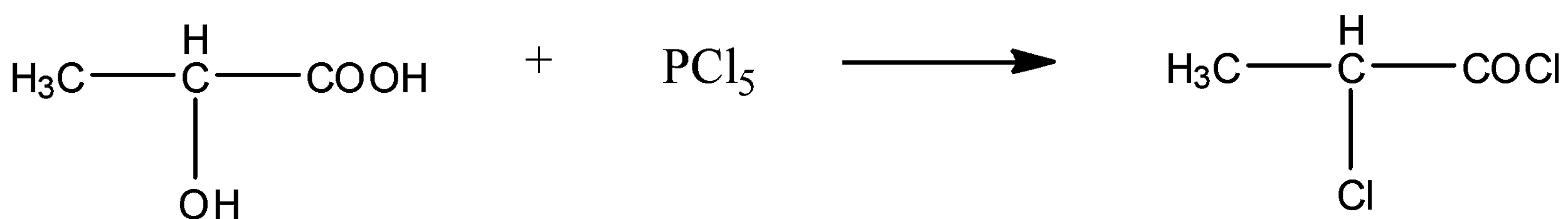
$\text{ Lactic acid
Phosphorus pentachloride
Lactyl chloride.}$
From the substrate i.e. lactic acid we see that it has carbonyl carbon the nucleophile chloride will attack on the carbonyl carbon because it is electrophilic in nature. Due to the presence of electron withdrawing group carboxylic acid the hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon also becomes acidic and becomes a good leaving group.
Note: Lactic acid can be fermented by the lactic acid bacteria. These bacteria can convert carbohydrates like glucose, sucrose into lactic acid. These bacteria are also present in the mouth and responsible for the tooth decay.
Lactic acid is made on a huge industrial scale with the help of bacterial fermentation of different types of carbohydrate. Most reliable and production method of the production of lactic acid is by the process of fermentation only.

Complete step by step answer:
The formula of lactic acid is . It is a white crystalline solid and soluble in water. When in aqueous state it is a colorless solution. It is also called alpha-hydroxy acid because of the presence of the hydroxyl group in the adjacent carboxyl group. It is an ionizable molecule which dissociates in carboxylate ions and a proton. It is more acidic than acetic acid because of the intramolecular hydrogen bonding between hydroxyl group and carboxyl group. Lactic acid is a chiral molecule which has two enantiomers. D and L enantiomers are there and also can be present as racemic mixture.
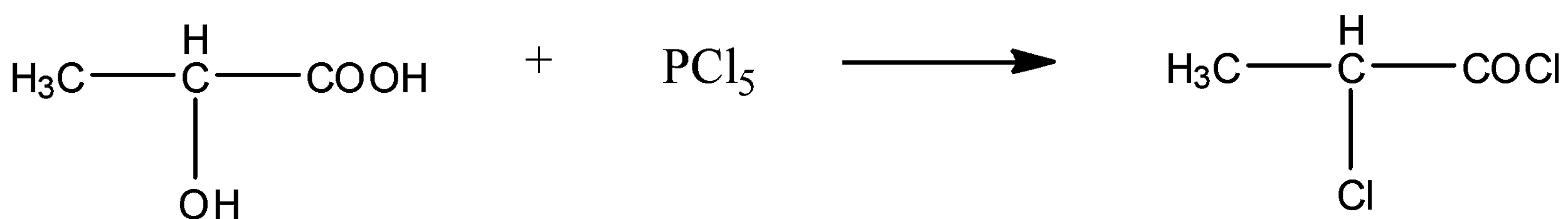
$\text{ Lactic acid
Phosphorus pentachloride
Lactyl chloride.}$
From the substrate i.e. lactic acid we see that it has carbonyl carbon the nucleophile chloride will attack on the carbonyl carbon because it is electrophilic in nature. Due to the presence of electron withdrawing group carboxylic acid the hydroxyl group on the adjacent carbon also becomes acidic and becomes a good leaving group.
Note: Lactic acid can be fermented by the lactic acid bacteria. These bacteria can convert carbohydrates like glucose, sucrose into lactic acid. These bacteria are also present in the mouth and responsible for the tooth decay.
Lactic acid is made on a huge industrial scale with the help of bacterial fermentation of different types of carbohydrate. Most reliable and production method of the production of lactic acid is by the process of fermentation only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




