
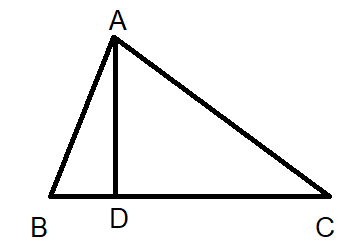
Given that for the following image $AD\bot BC$. Show that $A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.

Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint: We first take $AD\bot BC$ which gives $\angle ADB=\angle ADC={{90}^{\circ }}$. We then apply Pythagoras’ theorem for the right-angle triangles $\Delta ADB$ and $\Delta ADC$. We get two equations and we equate them with $A{{D}^{2}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
For the given image we have that $AD\bot BC$. This means $\angle ADB=\angle ADC={{90}^{\circ }}$.
We can now apply the Pythagoras’ theorem for the right-angle triangles.
We got two right-angle triangles $\Delta ADB$ and $\Delta ADC$.
The theorem for the right-angle triangle gives that $heigh{{t}^{2}}+bas{{e}^{2}}=hypotenus{{e}^{2}}$.
For $\Delta ADB$, $height=AD,base=BD,hypotenuse=AB$.
So, $A{{D}^{2}}+B{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}$ which gives $A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}$.
For $\Delta ADC$, $height=AD,base=CD,hypotenuse=AC$.
So, $A{{D}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$ which gives $A{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.
We got two equations being equal to $A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.
Thus, proved $A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.
Note: Pythagoras theorem is basically used to find the length of an unknown side and angle of a triangle. By this theorem, we can derive base, perpendicular and hypotenuse formula. The theorem can be generalised in various ways in higher-dimensional spaces, to spaces that are not Euclidean, to objects that are not right triangles.
Complete step-by-step solution:
For the given image we have that $AD\bot BC$. This means $\angle ADB=\angle ADC={{90}^{\circ }}$.
We can now apply the Pythagoras’ theorem for the right-angle triangles.
We got two right-angle triangles $\Delta ADB$ and $\Delta ADC$.
The theorem for the right-angle triangle gives that $heigh{{t}^{2}}+bas{{e}^{2}}=hypotenus{{e}^{2}}$.
For $\Delta ADB$, $height=AD,base=BD,hypotenuse=AB$.
So, $A{{D}^{2}}+B{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}$ which gives $A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}$.
For $\Delta ADC$, $height=AD,base=CD,hypotenuse=AC$.
So, $A{{D}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}$ which gives $A{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.
We got two equations being equal to $A{{D}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.
Thus, proved $A{{B}^{2}}-B{{D}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}-C{{D}^{2}}$.
Note: Pythagoras theorem is basically used to find the length of an unknown side and angle of a triangle. By this theorem, we can derive base, perpendicular and hypotenuse formula. The theorem can be generalised in various ways in higher-dimensional spaces, to spaces that are not Euclidean, to objects that are not right triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





