
From a window 15 meters height above the ground in a street, the angles of elevation and depression of the top and the foot of another house on the opposite side of the street are \[{{30}^{{}^\circ }}\] and \[{{45}^{{}^\circ }}\]respectively, show that the height of the opposite house is 23.66 meters. (Take \[\sqrt{3}=1.732\]).
Answer
621.9k+ views
Hint: First, construct an appropriate diagram with the given information. Assume the height of the building that you have to find as ‘4’. Finally, determine the expression for \[tan\theta \] from the two triangles and obtain the value of ‘h’ accordingly.
It was given that the angles of elevation and depression of the top and foot of a different house on the opposite side of the street are \[30{}^\circ \]and \[45{}^\circ \]respectively from a height of 15m above the ground.
First, let us understand the basic difference between the angle of elevation and angle of depression.
For suppose, if you were looking at something above the horizon, then the angle made by the horizontal and your line of right is the angle of elevation. Similarly, if you were looking at something that is below the horizon, then we are looking at something that is below the horizon, then we are looking at something that is below the horizon, then the angle made by the horizontal and your line of sight is the angle of depression.
Now let us construct the diagram with information we have:
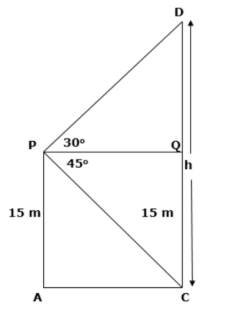
We have assumed the height of another building is ’h’, now from \[\Delta PQC\], we have:
\[tan\theta \]= opposite side / hypotenuse
\[tan{{45}^{{}^\circ }}=\dfrac{QC}{PQ}\]
From figure we have QC = PA = 15 and substituting the value of ‘tan’, we get
\[1=\dfrac{15}{PQ}\]
\[PQ=15m\]
Now, in \[\Delta PQC\], we have:
QD = CD – QC
Substituting the values from the figure, we get
\[QD=\left( h-15 \right)m.......(i)\]
Now as we know, \[tan\theta \]= opposite side / hypotenuse
\[\Rightarrow tan{{30}^{{}^\circ }}=\dfrac{QD}{PQ}\]
Substituting the value of ‘tan’ and value from equation (i), we get
\[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h-15}{15}\]
\[h-15=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{3}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& h=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{3}}+15 \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{(5\times 3)\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}\times \sqrt{3}}+15 \\
\end{align}\]
Solving further we get:
\[h=5\sqrt{3}+15\]
Taking ‘5’ common, we have:
\[h=5\left( \sqrt{3}+5 \right)\]
Substituting \[\sqrt{3}=1.732\] in the above equation, we get:
\[h=5\left( 3+1.732 \right)\]
\[h=5\left( 4.732 \right)\]
\[h=23.66\] Meters
Hence, we have proved that the height of the opposite house is \[h=23.66\] meters.
Note: Constructing a proper diagram is mandatory for these questions. You may also go ahead by considering the expressions of \[\sin \theta \] and \[\cos \theta \] from the triangle, but it would require extra effort to solve.
It was given that the angles of elevation and depression of the top and foot of a different house on the opposite side of the street are \[30{}^\circ \]and \[45{}^\circ \]respectively from a height of 15m above the ground.
First, let us understand the basic difference between the angle of elevation and angle of depression.
For suppose, if you were looking at something above the horizon, then the angle made by the horizontal and your line of right is the angle of elevation. Similarly, if you were looking at something that is below the horizon, then we are looking at something that is below the horizon, then we are looking at something that is below the horizon, then the angle made by the horizontal and your line of sight is the angle of depression.
Now let us construct the diagram with information we have:

We have assumed the height of another building is ’h’, now from \[\Delta PQC\], we have:
\[tan\theta \]= opposite side / hypotenuse
\[tan{{45}^{{}^\circ }}=\dfrac{QC}{PQ}\]
From figure we have QC = PA = 15 and substituting the value of ‘tan’, we get
\[1=\dfrac{15}{PQ}\]
\[PQ=15m\]
Now, in \[\Delta PQC\], we have:
QD = CD – QC
Substituting the values from the figure, we get
\[QD=\left( h-15 \right)m.......(i)\]
Now as we know, \[tan\theta \]= opposite side / hypotenuse
\[\Rightarrow tan{{30}^{{}^\circ }}=\dfrac{QD}{PQ}\]
Substituting the value of ‘tan’ and value from equation (i), we get
\[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{h-15}{15}\]
\[h-15=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{3}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& h=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{3}}+15 \\
& \Rightarrow h=\dfrac{(5\times 3)\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}\times \sqrt{3}}+15 \\
\end{align}\]
Solving further we get:
\[h=5\sqrt{3}+15\]
Taking ‘5’ common, we have:
\[h=5\left( \sqrt{3}+5 \right)\]
Substituting \[\sqrt{3}=1.732\] in the above equation, we get:
\[h=5\left( 3+1.732 \right)\]
\[h=5\left( 4.732 \right)\]
\[h=23.66\] Meters
Hence, we have proved that the height of the opposite house is \[h=23.66\] meters.
Note: Constructing a proper diagram is mandatory for these questions. You may also go ahead by considering the expressions of \[\sin \theta \] and \[\cos \theta \] from the triangle, but it would require extra effort to solve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




