
From a solid cylinder of height \[7\text{ cm}\] and a base diameter \[12\text{ cm}\], a conical cavity of same height and same base diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid.\[\left[ \text{Use }\pi =\dfrac{22}{7} \right]\].
Answer
627k+ views
First assume that radius of cylinder $=r$ and height of the cylinder $=h$ , then in the right circular cone, assume its slant height $=l$. Calculate $l$ by using Pythagoras Theorem. Then calculate, total Surface Area of a solid cylinder $=2\pi rh+2\pi {{r}^{2}}$, Lateral Surface Area of a cylinder $=2\pi rh$, Total Surface Area of a solid cone $=\pi rl+\pi {{r}^{2}}$, Lateral Surface Area of a cone $=\pi rl$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Radius of cylinder be $r=\dfrac{d}{2}=\dfrac{12}{2}=6\text{ cm}$ where $d=$ diameter of the cylinder.
And, the height of the cylinder is $h=7\text{ cm}$.
Now, we have given that the radii and heights of both the cone and cylinder are the same.
When we remove the portion of cone from the solid cylinder we have to imagine how the remaining portion will look. We observe that the lateral surface area of the cylinder is visible and one of the circular bases is also remaining. Now, the lateral surface of the cone is also visible while one of the base circles of the cylinder is cut out. Therefore, the required total surface area of the remaining solid is given by the sum of lateral surface area of cylinder, lateral surface area of cone and the area of the remaining circular base of cylinder.
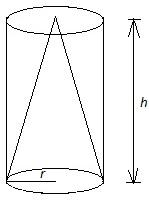
$\text{Required area = }2\pi rh+\pi rl+\pi {{r}^{2}}.............................(i)$
Where, \[l=\] slant height of cone.
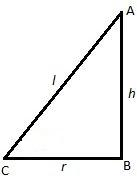
In the right circular cone, we use Pythagoras theorem to determine slant height \[l\].
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle ABC whose hypotenuse is \[c\]and other two sides are \[a\] and \[b\] then ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$.
Therefore considering \[c=l\], \[a=h\] and $b=r$ we get;
$\begin{align}
& {{l}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}} \\
& \therefore l=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting values of $l,h,r$ in equation \[\left( i \right)\], we get
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Required Area = }\left( \text{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 6\times 7 \right)+\left( \dfrac{22}{7}\times 6\times \sqrt{{{7}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}} \right)+\left( \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{6}^{2}} \right) \\
& \text{ = 264+173}\text{.85+113}\text{.14} \\
& \text{ }\approx 551\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: One may get confused in imagining the required figure, therefore it is better to draw the figure somewhere and then solve the question. One should memorize the formulas of areas of different shapes to solve the problem in time.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Radius of cylinder be $r=\dfrac{d}{2}=\dfrac{12}{2}=6\text{ cm}$ where $d=$ diameter of the cylinder.
And, the height of the cylinder is $h=7\text{ cm}$.
Now, we have given that the radii and heights of both the cone and cylinder are the same.
When we remove the portion of cone from the solid cylinder we have to imagine how the remaining portion will look. We observe that the lateral surface area of the cylinder is visible and one of the circular bases is also remaining. Now, the lateral surface of the cone is also visible while one of the base circles of the cylinder is cut out. Therefore, the required total surface area of the remaining solid is given by the sum of lateral surface area of cylinder, lateral surface area of cone and the area of the remaining circular base of cylinder.


$\text{Required area = }2\pi rh+\pi rl+\pi {{r}^{2}}.............................(i)$
Where, \[l=\] slant height of cone.
In the right circular cone, we use Pythagoras theorem to determine slant height \[l\].
Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle ABC whose hypotenuse is \[c\]and other two sides are \[a\] and \[b\] then ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}={{c}^{2}}$.
Therefore considering \[c=l\], \[a=h\] and $b=r$ we get;
$\begin{align}
& {{l}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}} \\
& \therefore l=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{r}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Now substituting values of $l,h,r$ in equation \[\left( i \right)\], we get
\[\begin{align}
& \text{Required Area = }\left( \text{2}\times \dfrac{22}{7}\times 6\times 7 \right)+\left( \dfrac{22}{7}\times 6\times \sqrt{{{7}^{2}}+{{6}^{2}}} \right)+\left( \dfrac{22}{7}\times {{6}^{2}} \right) \\
& \text{ = 264+173}\text{.85+113}\text{.14} \\
& \text{ }\approx 551\text{ c}{{\text{m}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Note: One may get confused in imagining the required figure, therefore it is better to draw the figure somewhere and then solve the question. One should memorize the formulas of areas of different shapes to solve the problem in time.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




