
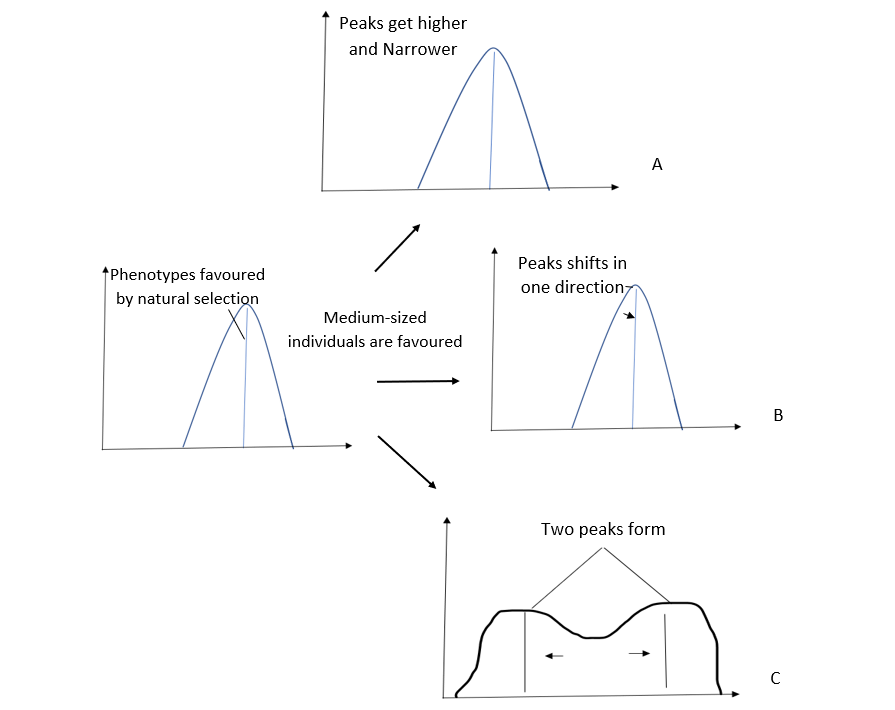
Following is the diagrammatic representation of the operation of natural selection of different traits. Which of the following options correctly identifies all three graphs A, B, and C.
A.
A B C Directional Stabilising Disruptive
B.
Stabilising Directional Disruptive
C.
Disruptive Stabilising Directional
D.
Directional Disruptive Stabilising

| A | B | C |
| Directional | Stabilising | Disruptive |
| Stabilising | Directional | Disruptive |
| Disruptive | Stabilising | Directional |
| Directional | Disruptive | Stabilising |
Answer
374.1k+ views
Hint: Natural selection is the process by which populations of living organisms change and adapt. Individuals in the general population are inherently variable, which means they are all different in certain ways. This variation means that certain individuals have characteristics more suited to the environment than others.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Graph A, B, and C show stabilising, directional and disruptive traits of natural selection.
In stabilizing selection, the median phenotype is chosen at the time of natural selection and does not tilt the bell curve in any manner. Instead, this makes the peak of the bell curve even greater than what would be considered normal.
Directional selection of natural selection is named after the shape of an approximate bell curve that is formed when all individual traits are plotted. Rather than the bell curve falling directly in the middle of the axes on which they are drawn, it tilts either to the right or the left by different degrees. Consequently, it has moved in one direction or another.
In disruptive selection rather than the bell curve that has one peak in the middle, it has two peaks with one valley in the middle of them.
Therefore the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Stabilizing selection leads to a reduction of a population‘s genetic variance when natural selection favours an average phenotype and chooses as opposed to extreme variations. In directional selection, a population’s genetic variance moves toward a new phenotype when subjected to changes in the environment. Diversifying or disruptive selection raises genetic variance when natural selection chooses two or more extreme phenotypes that everyone has particular advantages.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Graph A, B, and C show stabilising, directional and disruptive traits of natural selection.
In stabilizing selection, the median phenotype is chosen at the time of natural selection and does not tilt the bell curve in any manner. Instead, this makes the peak of the bell curve even greater than what would be considered normal.
Directional selection of natural selection is named after the shape of an approximate bell curve that is formed when all individual traits are plotted. Rather than the bell curve falling directly in the middle of the axes on which they are drawn, it tilts either to the right or the left by different degrees. Consequently, it has moved in one direction or another.
In disruptive selection rather than the bell curve that has one peak in the middle, it has two peaks with one valley in the middle of them.
Therefore the correct answer is Option B.
Note: Stabilizing selection leads to a reduction of a population‘s genetic variance when natural selection favours an average phenotype and chooses as opposed to extreme variations. In directional selection, a population’s genetic variance moves toward a new phenotype when subjected to changes in the environment. Diversifying or disruptive selection raises genetic variance when natural selection chooses two or more extreme phenotypes that everyone has particular advantages.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




