
Given diagram showing a typical agarose gel electrophoresis showing migration of DNA fragments. The undigested DNA fragment will be present in the lane
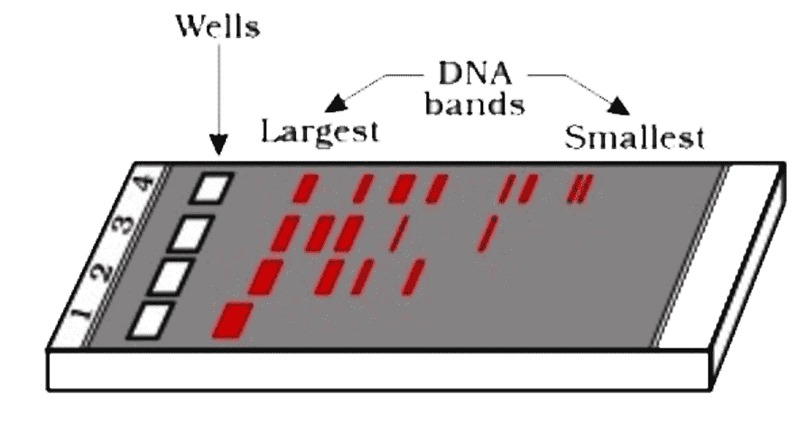
A. 4
B. 3
C. 2
D. 1

Answer
351.3k+ views
Hint:
Gel electrophoresis is a technique that uses electricity to transport tiny molecules across a gel material according to their charge density. Molecules with a larger or more pronounced electric charge go farther and quicker than those with a lower electric charge. Based on the size of its pores or mesh, the type of gel utilized also affects how the molecules flow.
Complete step by step solution:
By using gel electrophoresis, different tiny molecules can be divided according to their size and charge. The rationale behind gel electrophoresis is that different molecules have different electric charges. A gel medium must first be made, which might be either agarose or polyacrylamide. We need a semi-solid gel medium because the molecules must travel through it while remaining in the well column. A gel/semi-solid medium will allow the molecules to migrate while being partially dispersed. Because acrylamide has a higher resolving power than agarose but a wider range of separation, it is used to separate proteins, whereas agarose is used to separate DNA molecules because it has a narrower range of separation but a higher range of separation. Typically, a buffer solution is used to prepare the gel in order to allow the molecules to pass through it. The equipment required for gel electrophoresis techniques allows for power connections and well combs. Since we know that DNA molecules are negatively charged, the piece that is closest to the well is the positive terminal, and the portion that is furthest from the well is the negative terminal. Because the DNA is negatively charged, it moves from the positive terminal to the negative terminal when a current is run through the gel. Larger DNA/protein fragments move more quickly and over longer distances because they are negatively charged. And using this theory, we may distinguish between and determine the molecular weight of DNA and/or proteins.
Therefore, we can say that the bigger the DNA fragment it will move slow on the agarose gel.
Hence, the correct option is 1
Option ‘D’ is correct
Note:
Small biomolecules like DNA or proteins can be separated via a method called gel electrophoresis. Agarose DNA Electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) are the two names for the gel electrophoresis methods used for DNA and proteins, respectively.
Gel electrophoresis is a technique that uses electricity to transport tiny molecules across a gel material according to their charge density. Molecules with a larger or more pronounced electric charge go farther and quicker than those with a lower electric charge. Based on the size of its pores or mesh, the type of gel utilized also affects how the molecules flow.
Complete step by step solution:
By using gel electrophoresis, different tiny molecules can be divided according to their size and charge. The rationale behind gel electrophoresis is that different molecules have different electric charges. A gel medium must first be made, which might be either agarose or polyacrylamide. We need a semi-solid gel medium because the molecules must travel through it while remaining in the well column. A gel/semi-solid medium will allow the molecules to migrate while being partially dispersed. Because acrylamide has a higher resolving power than agarose but a wider range of separation, it is used to separate proteins, whereas agarose is used to separate DNA molecules because it has a narrower range of separation but a higher range of separation. Typically, a buffer solution is used to prepare the gel in order to allow the molecules to pass through it. The equipment required for gel electrophoresis techniques allows for power connections and well combs. Since we know that DNA molecules are negatively charged, the piece that is closest to the well is the positive terminal, and the portion that is furthest from the well is the negative terminal. Because the DNA is negatively charged, it moves from the positive terminal to the negative terminal when a current is run through the gel. Larger DNA/protein fragments move more quickly and over longer distances because they are negatively charged. And using this theory, we may distinguish between and determine the molecular weight of DNA and/or proteins.
Therefore, we can say that the bigger the DNA fragment it will move slow on the agarose gel.
Hence, the correct option is 1
Option ‘D’ is correct
Note:
Small biomolecules like DNA or proteins can be separated via a method called gel electrophoresis. Agarose DNA Electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) are the two names for the gel electrophoresis methods used for DNA and proteins, respectively.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




