
Find the nature of the roots of the following quadratic equation. If the real roots exist, find them.
$2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$
A) x = 0 and x = -2
B) x = 3, x = -6
C) No real root
D) None of these
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: The nature of the roots depends on the value of the discriminant of the quadratic equation.
$a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
Find the Discriminant, $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ , of the given quadratic equation, and check the sign (i.e. positive or negative or zero) to know if there are two solutions or one solution or no solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Given the quadratic equation:
$2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$
On comparing with standard quadratic equation: $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
a = 2, b = -3, c = 5
Step 2: Find discriminant:
$D = {b^2} - 4ac$
$D = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} - 4 \times 2 \times 5$
$
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = 9 - 40 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = - 31 \\
$
Step 3: Check the sign of discriminant:
$D < 0$
Hence, the roots are imaginary.
Final answer: The roots of $2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$ are not real. Thus the correct option is (C).
Additional Information:
Roots of the quadratic equation is given by:
Quadratic equation: $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
Roots: \[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}\]
The imaginary roots of the given quadratic equation are:
$2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$
D = -31
\[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}\]
$
{\text{ }}x = \dfrac{{ - \left( { - 3} \right) \pm \sqrt {\left( { - 31} \right)} }}{{2\left( 2 \right)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = \dfrac{{3 \pm {\text{i}}\sqrt {31} }}{4} \\
$
Note: For quadratic equation: $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
Let $y = f\left( x \right) = a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$
Discriminant, $D = {b^2} - 4ac$
A discriminant of zero indicates that the quadratic has a repeated real number solution.
i.e. $D = 0$ , roots are real and equal.
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - 4ac = 0$
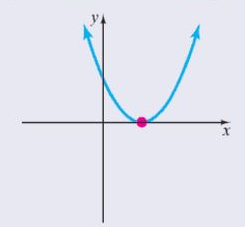
A positive discriminant indicates that the quadratic has two distinct real number solutions.
i.e. $D > 0$ , roots are real and unequal.
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - 4ac > 0$
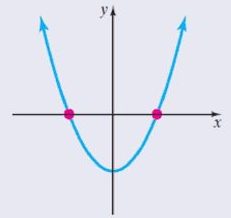
A negative discriminant indicates that neither of the solutions is real numbers.
And if D < 0, as in the case of the given question, roots are imaginary.
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - 4ac < 0$
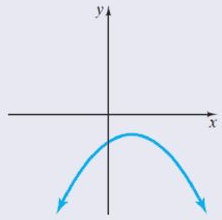
$a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
Find the Discriminant, $D = {b^2} - 4ac$ , of the given quadratic equation, and check the sign (i.e. positive or negative or zero) to know if there are two solutions or one solution or no solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Given the quadratic equation:
$2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$
On comparing with standard quadratic equation: $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
a = 2, b = -3, c = 5
Step 2: Find discriminant:
$D = {b^2} - 4ac$
$D = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} - 4 \times 2 \times 5$
$
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = 9 - 40 \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = - 31 \\
$
Step 3: Check the sign of discriminant:
$D < 0$
Hence, the roots are imaginary.
Final answer: The roots of $2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$ are not real. Thus the correct option is (C).
Additional Information:
Roots of the quadratic equation is given by:
Quadratic equation: $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
Roots: \[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}\]
The imaginary roots of the given quadratic equation are:
$2{x^2} - 3x + 5 = 0$
D = -31
\[x = \dfrac{{ - b \pm \sqrt D }}{{2a}}\]
$
{\text{ }}x = \dfrac{{ - \left( { - 3} \right) \pm \sqrt {\left( { - 31} \right)} }}{{2\left( 2 \right)}} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{ }} = \dfrac{{3 \pm {\text{i}}\sqrt {31} }}{4} \\
$
Note: For quadratic equation: $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$, where $a \ne 0$
Let $y = f\left( x \right) = a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$
Discriminant, $D = {b^2} - 4ac$
A discriminant of zero indicates that the quadratic has a repeated real number solution.
i.e. $D = 0$ , roots are real and equal.
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - 4ac = 0$

A positive discriminant indicates that the quadratic has two distinct real number solutions.
i.e. $D > 0$ , roots are real and unequal.
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - 4ac > 0$

A negative discriminant indicates that neither of the solutions is real numbers.
And if D < 0, as in the case of the given question, roots are imaginary.
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} - 4ac < 0$

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




