
Find the locus of the third vertex of a right-angled triangle, the ends of whose hypotenuse are (4,0) and (0,4).
Answer
599.4k+ views
Hint: a locus (Latin word for "place", "location") is a set of all points (commonly, a line, line segment a curve, or a surface) whose location satisfies or is determined by one or more specified conditions. In other words, the set of points that satisfy some property is often called the locus of a point satisfying this property.
The locus of a point P is such that it is equidistant from two given points. A and B i.e. PA=PB. The locus of a point at fixed distance d, from point P, is a circle with given point P as its center and d as its radius. Here in this question, we can use the distance formula for two given points.
Distance formula = \[\sqrt {{{(x_2 - x_1)}^2} + {{(y_2 - y_1)}^2}} \]
Complete step by step answer:
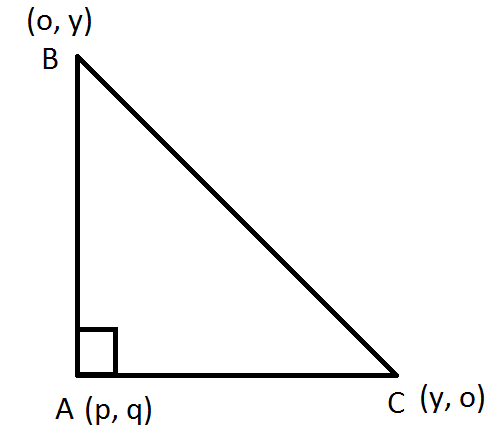
Let the point be \[(p,q)\]
\[B{C^2} = A{B^2} + A{C^2}\](By Pythagoras theorem)
\[{(4 - 0)^2} + {(0 - 4)^2} = {(p - 0)^2} + {(q - 4)^2} + {(p - 4)^2} + {(q - 0)^2}\]
\[16 + 16 = {p^2} + {q^2} + 16 - 8q + {p^2} + 16 - 8p + {q^2}\]
\[32 = 2({p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q) + 32\]
Or \[{p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q = 0\]
Replacing \[p \to x\]and \[q \to y\]
\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 4y = 0\] is the locus of the equation.
Note: we can also find this finding slope of two lines AB as \[m_1 = \dfrac{{y_2 - y_1}}{{x_2 - x_1}}\], and AC as \[m_2 = \dfrac{{y_2 - y_1}}{{x_2 - x_1}}\]
And for perpendicular lines\[{m_1}{m_2} = - 1\]
We get the required locus of the third vertex.
The locus of a point P is such that it is equidistant from two given points. A and B i.e. PA=PB. The locus of a point at fixed distance d, from point P, is a circle with given point P as its center and d as its radius. Here in this question, we can use the distance formula for two given points.
Distance formula = \[\sqrt {{{(x_2 - x_1)}^2} + {{(y_2 - y_1)}^2}} \]
Complete step by step answer:
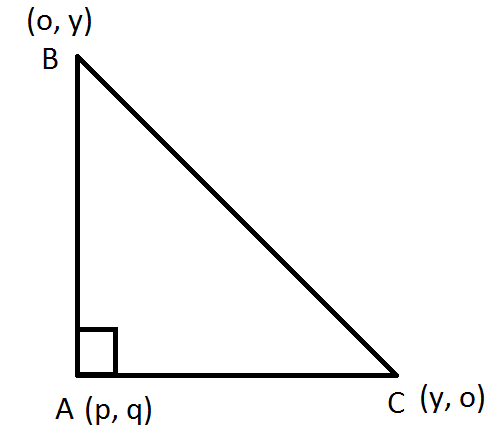
Let the point be \[(p,q)\]
\[B{C^2} = A{B^2} + A{C^2}\](By Pythagoras theorem)
\[{(4 - 0)^2} + {(0 - 4)^2} = {(p - 0)^2} + {(q - 4)^2} + {(p - 4)^2} + {(q - 0)^2}\]
\[16 + 16 = {p^2} + {q^2} + 16 - 8q + {p^2} + 16 - 8p + {q^2}\]
\[32 = 2({p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q) + 32\]
Or \[{p^2} + {q^2} - 4p - 4q = 0\]
Replacing \[p \to x\]and \[q \to y\]
\[{x^2} + {y^2} - 4x - 4y = 0\] is the locus of the equation.
Note: we can also find this finding slope of two lines AB as \[m_1 = \dfrac{{y_2 - y_1}}{{x_2 - x_1}}\], and AC as \[m_2 = \dfrac{{y_2 - y_1}}{{x_2 - x_1}}\]
And for perpendicular lines\[{m_1}{m_2} = - 1\]
We get the required locus of the third vertex.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




