
Find the locus of the circumcenters of the triangle whose two sides are along the coordinate axes and the third side passes through the point of intersection of the lines \[ax + by + c = 0\]and\[lx + my + n = 0\].
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Locus of a point is the set of all points that have the same property or we can say the set of points which behaves in the same way. Circumcenters of the triangle refers to the point in a triangle where all perpendicular bisector of the triangle intersects.
In this question, we have asked to determine the locus of the circumcentre of the triangle such that its two sides are along the coordinate axes and the third side passes through the point of intersection of the lines \[ax + by + c = 0\]and\[lx + my + n = 0\].
Complete step by step answer:
Given that two lines pass through the coordinate axis, hence we can draw the figure as
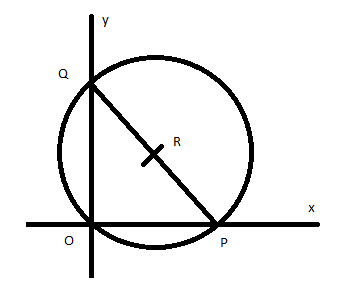
The two lines are perpendicular to each other and the third line passes through the point of intersection of line hence the triangle\[\Delta OPQ\]formed is a right-angle triangle, we know that the circumcenters of a right triangle is the midpoint \[R\left( {h,k} \right)\] of its hypotenuses which is the midpoint of the line PQ, hence
\[
R\left( {h,k} \right) = \dfrac{{p + 0}}{2},\dfrac{{0 + q}}{2} \\
= \left( {\dfrac{p}{2},\dfrac{q}{2}} \right) \\
\]
We can write \[p = 2h\]and\[q = 2k\]
We know the equation of the hypotenuses PQ is\[\dfrac{x}{p} + \dfrac{y}{q} = 1\], hence we can write
\[
\dfrac{x}{p} + \dfrac{y}{q} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{{2h}} + \dfrac{y}{{2k}} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{h} + \dfrac{y}{k} = 2 - - - (i) \\
\]
Given that the hypotenuses passes through the intersecting lines \[ax + by + c = 0\]and\[lx + my + n = 0\]
Now solve both the given equations
\[ax + by + c = 0 - - - - (ii)\]
\[lx + my + n = 0 - - - - (iii)\]
By multiplying (ii) by l and (iii) by a,
\[
ax + by + c = 0\left. {} \right\} \times l \\
lx + my + n = 0\left. {} \right\} \times a \\
\]
We get
\[
\underline
alx + bly + cl = 0 \\
alx\mathop + \limits_ - amy\mathop + \limits_ - an = 0 \\
\\
bly - amy + cl - an = 0 \\
\\
y\left( {bl - am} \right) = an - cl \\
y = \dfrac{{an - cl}}{{bl - am}} \\
\]
Now multiply (ii) by m and (iii) by b
\[
ax + by + c = 0\left. {} \right\} \times m \\
lx + my + n = 0\left. {} \right\} \times b \\
\]
We get
\[
\underline
+ amx + bmy + cm = 0 \\
\mathop + \limits_ - blx\mathop + \limits_ - bmy\mathop + \limits_ - bn = 0 \\
\\
amx - blx + cm - bn = 0 \\
\\
x\left( {am - bl} \right) = bn - cm \\
x = \dfrac{{an - cl}}{{am - bl}} \\
\]
Now put the value of x and y in equation (i), we get
\[
\dfrac{x}{h} + \dfrac{y}{k} = 2 \\
\dfrac{1}{h}\left( {\dfrac{{an - cl}}{{am - bl}}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{k}\left( {\dfrac{{an - cl}}{{bl - am}}} \right) = 2 \\
\\
\\
\dfrac{{k\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + h\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right)}}{{hk\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right)}} = 2 \\
k\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + h\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right) = 2\left\{ {hk\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right)} \right\} \\
y\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + x\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right) = 2xy\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) \\
\\
\]
Hence\[y\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + x\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right) = 2xy\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right)\] is the equation for the locus of the circumcenter of the circle.
Note: Locus can be a set of points, lines, line segments, curve, and surface which satisfy one or more properties. In the case of a right-angled triangle, the circumcenter of the triangle is always the midpoint of hypotenuses of that triangle.
In this question, we have asked to determine the locus of the circumcentre of the triangle such that its two sides are along the coordinate axes and the third side passes through the point of intersection of the lines \[ax + by + c = 0\]and\[lx + my + n = 0\].
Complete step by step answer:
Given that two lines pass through the coordinate axis, hence we can draw the figure as

The two lines are perpendicular to each other and the third line passes through the point of intersection of line hence the triangle\[\Delta OPQ\]formed is a right-angle triangle, we know that the circumcenters of a right triangle is the midpoint \[R\left( {h,k} \right)\] of its hypotenuses which is the midpoint of the line PQ, hence
\[
R\left( {h,k} \right) = \dfrac{{p + 0}}{2},\dfrac{{0 + q}}{2} \\
= \left( {\dfrac{p}{2},\dfrac{q}{2}} \right) \\
\]
We can write \[p = 2h\]and\[q = 2k\]
We know the equation of the hypotenuses PQ is\[\dfrac{x}{p} + \dfrac{y}{q} = 1\], hence we can write
\[
\dfrac{x}{p} + \dfrac{y}{q} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{{2h}} + \dfrac{y}{{2k}} = 1 \\
\dfrac{x}{h} + \dfrac{y}{k} = 2 - - - (i) \\
\]
Given that the hypotenuses passes through the intersecting lines \[ax + by + c = 0\]and\[lx + my + n = 0\]
Now solve both the given equations
\[ax + by + c = 0 - - - - (ii)\]
\[lx + my + n = 0 - - - - (iii)\]
By multiplying (ii) by l and (iii) by a,
\[
ax + by + c = 0\left. {} \right\} \times l \\
lx + my + n = 0\left. {} \right\} \times a \\
\]
We get
\[
\underline
alx + bly + cl = 0 \\
alx\mathop + \limits_ - amy\mathop + \limits_ - an = 0 \\
\\
bly - amy + cl - an = 0 \\
\\
y\left( {bl - am} \right) = an - cl \\
y = \dfrac{{an - cl}}{{bl - am}} \\
\]
Now multiply (ii) by m and (iii) by b
\[
ax + by + c = 0\left. {} \right\} \times m \\
lx + my + n = 0\left. {} \right\} \times b \\
\]
We get
\[
\underline
+ amx + bmy + cm = 0 \\
\mathop + \limits_ - blx\mathop + \limits_ - bmy\mathop + \limits_ - bn = 0 \\
\\
amx - blx + cm - bn = 0 \\
\\
x\left( {am - bl} \right) = bn - cm \\
x = \dfrac{{an - cl}}{{am - bl}} \\
\]
Now put the value of x and y in equation (i), we get
\[
\dfrac{x}{h} + \dfrac{y}{k} = 2 \\
\dfrac{1}{h}\left( {\dfrac{{an - cl}}{{am - bl}}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{k}\left( {\dfrac{{an - cl}}{{bl - am}}} \right) = 2 \\
\\
\\
\dfrac{{k\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + h\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right)}}{{hk\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right)}} = 2 \\
k\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + h\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right) = 2\left\{ {hk\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right)} \right\} \\
y\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + x\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right) = 2xy\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) \\
\\
\]
Hence\[y\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right) + x\left( {an - cl} \right)\left( {am - bl} \right) = 2xy\left( {am - bl} \right)\left( {bl - am} \right)\] is the equation for the locus of the circumcenter of the circle.
Note: Locus can be a set of points, lines, line segments, curve, and surface which satisfy one or more properties. In the case of a right-angled triangle, the circumcenter of the triangle is always the midpoint of hypotenuses of that triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




