
Explain the mechanism of cleaning action of soaps
Answer
601.5k+ views
Hint: In this question, to explain the mechanism first we have to understand the term soap further according to the structure of soap name as micelles we will discuss the cleaning process.
Complete step by step solution:
Soap is a water-soluble compound produced by the reaction from sodium hydroxide to potassium hydroxide with vegetable or animal oil by a process called saponification.
In nature, the majority of dirt is oily, and in water oil is not dissolved. The soap molecule contains long-chain carboxylic acid salts from sodium or potassium. For soap, the carbon chain in oil dissolves and the ionic component of water dissolves. So structures called micelles form the soap molecules. The one end is the droplet of Micelles, and the other end is the liquid ionic faces. It therefore creates an emulsion in water and helps to remove dirt when washing our clothes
Soap is a molecule with different properties on both sides.
• Hydrophilic end
• Hydrophobic end
Diagram of micelles:
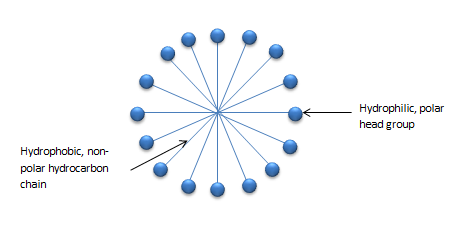
The first is the hydrophilic end that dissolves and attracts water, while the second is the hydrophobic end that is dissolved in hydrocarbons and repulsive. On the water's surface, the soap must interact with the water's surface with the hydrophobic tail and is not water soluble.
The soap molecule is oriented to the water, so that the hydrocarbon portion is kept out of the water. When the molecular clusters are formed, the hydrophobic tail is positioned in the cluster, and the ionic end is on the surface of the cluster and is called a micelle. If the soap is micelle-shaped it will clear up the sticky soil that is deposited in the center of the soap. Such micelles remain colloidal. And the soil is quickly separated from the fabric. The soap solution becomes opaque, since it forms a colloidal, light-dispersing solution.
Note: Synthetic detergents are washing agents. It is like soaps, i.e. it has all the soap-functions. However, they have no soap, their chemical composition is completely different from soap. One of the biggest advantages of soap detergents is their ability. You can work in both natural and rough water. Under rough mud, they do not shape scum. Even in ice cold water some detergents can work while with soap it is not possible to work in both.
Complete step by step solution:
Soap is a water-soluble compound produced by the reaction from sodium hydroxide to potassium hydroxide with vegetable or animal oil by a process called saponification.
In nature, the majority of dirt is oily, and in water oil is not dissolved. The soap molecule contains long-chain carboxylic acid salts from sodium or potassium. For soap, the carbon chain in oil dissolves and the ionic component of water dissolves. So structures called micelles form the soap molecules. The one end is the droplet of Micelles, and the other end is the liquid ionic faces. It therefore creates an emulsion in water and helps to remove dirt when washing our clothes
Soap is a molecule with different properties on both sides.
• Hydrophilic end
• Hydrophobic end
Diagram of micelles:

The first is the hydrophilic end that dissolves and attracts water, while the second is the hydrophobic end that is dissolved in hydrocarbons and repulsive. On the water's surface, the soap must interact with the water's surface with the hydrophobic tail and is not water soluble.
The soap molecule is oriented to the water, so that the hydrocarbon portion is kept out of the water. When the molecular clusters are formed, the hydrophobic tail is positioned in the cluster, and the ionic end is on the surface of the cluster and is called a micelle. If the soap is micelle-shaped it will clear up the sticky soil that is deposited in the center of the soap. Such micelles remain colloidal. And the soil is quickly separated from the fabric. The soap solution becomes opaque, since it forms a colloidal, light-dispersing solution.
Note: Synthetic detergents are washing agents. It is like soaps, i.e. it has all the soap-functions. However, they have no soap, their chemical composition is completely different from soap. One of the biggest advantages of soap detergents is their ability. You can work in both natural and rough water. Under rough mud, they do not shape scum. Even in ice cold water some detergents can work while with soap it is not possible to work in both.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




