
Determine the equation of the circle which touches the line $y=x$ at the origin and bisects the circumference of the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$.
Answer
622.2k+ views
Hint: A circle bisects the circumference of another circle if the common chord of the two circles passes through the centre of the second circle. The common chord of the two circles is found simply by subtracting the two circles.
Let us first plot line $y=x$and the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$
For circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$
Centre \[\equiv \left( -g,-f \right)\] and radius $\text{= }\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-C}$
For the given circle,
Centre $\equiv \left( 0,-1 \right)$
Radius $r=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-\left( -3 \right)}$
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow r=\sqrt{1+3} \\
& \Rightarrow r=\sqrt{4} \\
& \Rightarrow r=2 \\
\end{align}\]
Using this data, we will plot the circle
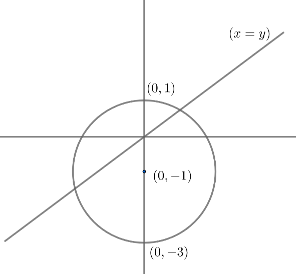
Let us consider a circle having equation
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$
Since, this circle bisect the circumference of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$, the common chord of the two
circles must pass through the centre of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$ i.e., $\left( 0,-1 \right)$
The common chord of the two circles is found out by subtracting the equation of the two circles. Hence
the equation of the common chord of the two circles is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C \right)-\left( {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2gx+2y\left( f-1 \right)+C+3=0 \\
\end{align}$
This chord has $\left( 0,1 \right)$ on it. Substituting $x=0$ and $y=1$ in the common chord, we get 🡪
$\begin{align}
& 2g\left( 0 \right)+2\left( -1 \right)\left( f-1 \right)+C+3=0 \\
& \Rightarrow C-2f+5=0.........(i) \\
\end{align}$
It is given that circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$ touches line $y=x$ at $\left( 0,0 \right)$. Substituting
$x=0$ and $y=0$ in ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$., we get 🡪
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+2g\left( 0 \right)+2f\left( 0 \right)+C=0 \\
& \Rightarrow C=0.........\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Also, in the question, it is given that $y=x$ is tangent to the required circle since it touches the circle.
Substituting \[y=x\] in ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}+2gx+2fx+C=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+2\left( g+f \right)x+C=0.........\left( iii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Since the circle touches the line, there is only a single value of $x$ possible. So the roots of the above quadratic equation in $x$ must be equal. For roots of the quadratic equation to be equal, the discriminant of the quadratic equation must be 0.
For quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+C=0$
Discriminant $D={{b}^{2}}-4ac$
Substituting $a=2,\text{ }b=2\left( g+f \right)\text{ and }C=C$from equation $\left( iii \right)$, we get 🡪
$D={{\left( 2\left( g+f \right) \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( C \right)$
As explained in the above paragraph, $D=0$
$\Rightarrow 4{{\left( g+f \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( C \right)=0........\left( iv \right)$
From equation $\left( ii \right),C=0$
Substituting $C$ in $\left( i \right)$, we get
$\begin{align}
& 0-2f+5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{5}{2}...........\left( v \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting equation $\left( ii \right)$ and $\left( v \right)$ in equation$\left( iv \right)$,
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\left( g+\dfrac{5}{2} \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( 0 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\left( g+\dfrac{5}{2} \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( g+\dfrac{5}{2} \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow g+\dfrac{5}{2}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow g=\dfrac{-5}{2}..........\left( vi \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting $C=0,f=\dfrac{5}{2},g=-\dfrac{5}{2}$ from equation $\left( ii \right),\left( v \right),\left( vi \right)$ in assumed circle i.e. ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$, then required circle is 🡪
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-5x+5y=0$
Note: There is an alternative approach to use the condition that line $y=x$ touches the circle. We can also find the perpendicular distance from the centre of the circle to the line and equate it to the radius of the circle instead of substituting $y=x$ in the circle and making the discriminant of quadratic $=0$.
Let us first plot line $y=x$and the circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$
For circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$
Centre \[\equiv \left( -g,-f \right)\] and radius $\text{= }\sqrt{{{g}^{2}}+{{f}^{2}}-C}$
For the given circle,
Centre $\equiv \left( 0,-1 \right)$
Radius $r=\sqrt{{{0}^{2}}+{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-\left( -3 \right)}$
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow r=\sqrt{1+3} \\
& \Rightarrow r=\sqrt{4} \\
& \Rightarrow r=2 \\
\end{align}\]
Using this data, we will plot the circle

Let us consider a circle having equation
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$
Since, this circle bisect the circumference of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$, the common chord of the two
circles must pass through the centre of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$ i.e., $\left( 0,-1 \right)$
The common chord of the two circles is found out by subtracting the equation of the two circles. Hence
the equation of the common chord of the two circles is,
$\begin{align}
& \left( {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C \right)-\left( {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2gx+2y\left( f-1 \right)+C+3=0 \\
\end{align}$
This chord has $\left( 0,1 \right)$ on it. Substituting $x=0$ and $y=1$ in the common chord, we get 🡪
$\begin{align}
& 2g\left( 0 \right)+2\left( -1 \right)\left( f-1 \right)+C+3=0 \\
& \Rightarrow C-2f+5=0.........(i) \\
\end{align}$
It is given that circle ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2y-3=0$ touches line $y=x$ at $\left( 0,0 \right)$. Substituting
$x=0$ and $y=0$ in ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$., we get 🡪
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0 \right)}^{2}}+2g\left( 0 \right)+2f\left( 0 \right)+C=0 \\
& \Rightarrow C=0.........\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Also, in the question, it is given that $y=x$ is tangent to the required circle since it touches the circle.
Substituting \[y=x\] in ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$,
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}+2gx+2fx+C=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}+2\left( g+f \right)x+C=0.........\left( iii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Since the circle touches the line, there is only a single value of $x$ possible. So the roots of the above quadratic equation in $x$ must be equal. For roots of the quadratic equation to be equal, the discriminant of the quadratic equation must be 0.
For quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+C=0$
Discriminant $D={{b}^{2}}-4ac$
Substituting $a=2,\text{ }b=2\left( g+f \right)\text{ and }C=C$from equation $\left( iii \right)$, we get 🡪
$D={{\left( 2\left( g+f \right) \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( C \right)$
As explained in the above paragraph, $D=0$
$\Rightarrow 4{{\left( g+f \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( C \right)=0........\left( iv \right)$
From equation $\left( ii \right),C=0$
Substituting $C$ in $\left( i \right)$, we get
$\begin{align}
& 0-2f+5=0 \\
& \Rightarrow f=\dfrac{5}{2}...........\left( v \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting equation $\left( ii \right)$ and $\left( v \right)$ in equation$\left( iv \right)$,
$\begin{align}
& 4{{\left( g+\dfrac{5}{2} \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 2 \right)\left( 0 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{\left( g+\dfrac{5}{2} \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( g+\dfrac{5}{2} \right)}^{2}}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow g+\dfrac{5}{2}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow g=\dfrac{-5}{2}..........\left( vi \right) \\
\end{align}$
Substituting $C=0,f=\dfrac{5}{2},g=-\dfrac{5}{2}$ from equation $\left( ii \right),\left( v \right),\left( vi \right)$ in assumed circle i.e. ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2gx+2fy+C=0$, then required circle is 🡪
${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-5x+5y=0$
Note: There is an alternative approach to use the condition that line $y=x$ touches the circle. We can also find the perpendicular distance from the centre of the circle to the line and equate it to the radius of the circle instead of substituting $y=x$ in the circle and making the discriminant of quadratic $=0$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




