
Calculate the total number of optical isomers of the following compounds respectively:
Tartaric acid, lactic acid, fumaric acid, cinnamic acid.
(A) 3,2,0,2
(B) 3,2,0,1
(C) 2,2,0,0
(D) 3,2,0,0
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: Optical isomers have the same chemical formula and vary in their orientation. The pair of isomers bend a beam of plane polarised light in different directions(left or right) and that is how we identify a pair of optical isomers. Draw the structure of compounds given and find the number of chiral carbon atoms and the optical activity to calculate the number of optical isomers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formula but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their respective orientations of the atoms belonging to the compound in a 3D space.
The types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
Optical isomers are two compounds having same molecular formula but differ in their spatial arrangements of atoms, which have non-superimposable mirror images.
We will now draw the structure of the above-mentioned compounds and identify the number of optical isomers.
Tartaric acid:
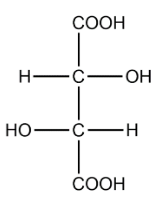
In the structure of tartaric we can identify 2 chiral carbons. The optical isomers are :
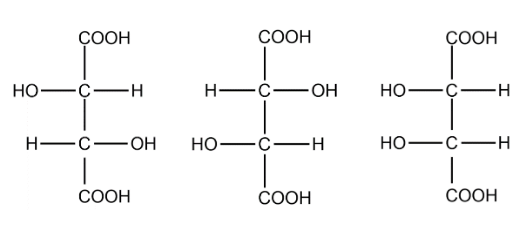
The total number of optical isomers for tartaric acid are 3.
Lactic acid:
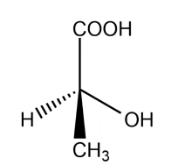
Lactic acid one chiral carbon, the optical isomers are :
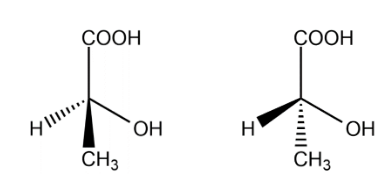
The total number of isomers for lactic acid is 2.
Fumaric acid:
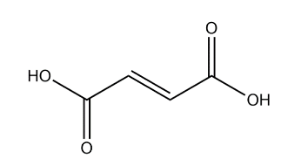
In the above structure of fumaric acid we observe that there is no chiral carbon present. So, the number of optical isomers is 0.
Cinnamic acid:
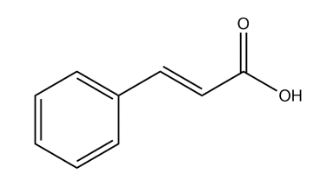
In the above structure of cinnamic acid we observe that there is no chiral carbon present. So, the number of optical isomers is 0.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: In general, we get a pair of optical isomers that deflects the incoming beam of plane polarized light. However, in the case of tartaric acid, we obtained only 3 isomers. This is because the third structure of tartaric acid is a meso compound. The mirror image of the meso compound superimposes on the original image. This compound is optically active about the chiral carbon atoms but the molecule as a whole does not show optical activity.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formula but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their respective orientations of the atoms belonging to the compound in a 3D space.
The types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
Optical isomers are two compounds having same molecular formula but differ in their spatial arrangements of atoms, which have non-superimposable mirror images.
We will now draw the structure of the above-mentioned compounds and identify the number of optical isomers.
Tartaric acid:

In the structure of tartaric we can identify 2 chiral carbons. The optical isomers are :

The total number of optical isomers for tartaric acid are 3.
Lactic acid:

Lactic acid one chiral carbon, the optical isomers are :

The total number of isomers for lactic acid is 2.
Fumaric acid:

In the above structure of fumaric acid we observe that there is no chiral carbon present. So, the number of optical isomers is 0.
Cinnamic acid:

In the above structure of cinnamic acid we observe that there is no chiral carbon present. So, the number of optical isomers is 0.
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: In general, we get a pair of optical isomers that deflects the incoming beam of plane polarized light. However, in the case of tartaric acid, we obtained only 3 isomers. This is because the third structure of tartaric acid is a meso compound. The mirror image of the meso compound superimposes on the original image. This compound is optically active about the chiral carbon atoms but the molecule as a whole does not show optical activity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




