
An aeroplane can carry a maximum load of 200 passengers. Baggage allowed to the first class ticket holder is 30 kg and for the economy class ticket holder is 20 kg. Maximum capacity of the aeroplane to carry the baggage is 4500 kg. The profit on each first class ticket is Rs.500 and on each economy class ticket is Rs.300. Formulate the problem, as L.P.P to maximize the profit.
Answer
626.7k+ views
Hint: For solving this problem, we should be aware about the basic concepts concerning Linear Programming problems. We will formulate the above problem in terms of two variables (x and y) to represent the above given problem. Here, x represents the number of first class ticket holders and y represents the number of economy class ticket holders. These equations are then plotted on a graph and then we get the required points where value of cost is evaluated.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, to solve the problem, we try to represent the constraints given in the problem using x and y, where x represents the number of first class ticket holders and y represents the number of economy class ticket holders. Thus, the first condition is that aeroplane can carry a maximum load of 200 passengers. We have,
x+y $\le $ 200 -- (1)
Now, we have the capacity for the first class ticket holder is 30 kg and for the economy class ticket holder is 20 kg. Further, the maximum capacity is given as 4500 kg. Thus, we have,
30x + 20y $\le $ 4500
3x + 2y $\le $ 450 -- (2)
Apart from these, we also know that x and y should be positive quantities. Thus, we have,
x $\ge $ 0 -- (3)
y $\ge $ 0 -- (4)
Now, to maximize profit, it is given that profit on each first class ticket is Rs.500 and on each economy class ticket is Rs.300. Thus, we have to maximize,
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y -- (A)
Now, we represent (1), (2), (3) and (4) on the graph, we have,
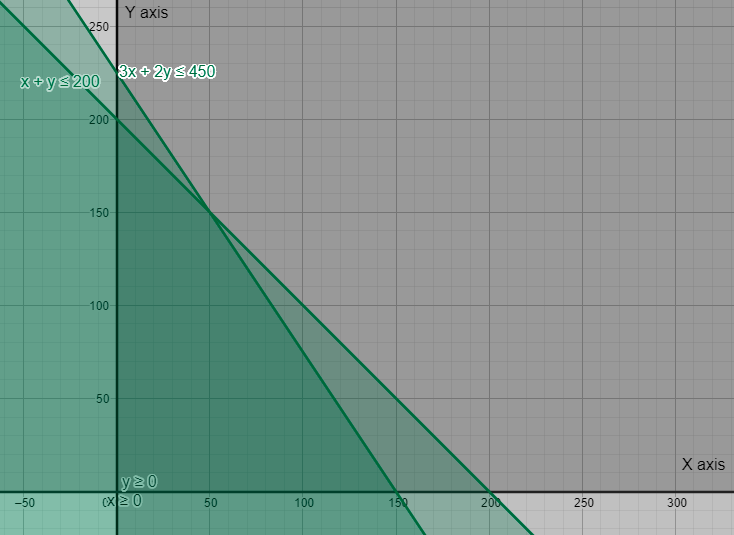
Now, to get the maximum profit, by finding the value of profit at the close bounded figure obtained by representing these equations on the graph. Then, we find the value of the profit at the vertices of the intersection figure formed. These vertices are (0,200), (0,0), (150,0) and intersection point of lines (1) and (2). We find the intersections of the lines (1) and (2). We get,
(solving x+y = 200 and 3x + 2y = 450) –
x = 50 and y = 150.
Now, we find profit at all these vertices. Thus, we have,
Case 1: (0,200)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 0 + 300 $\times $ 200
f(0,200) = 60000
Case 2: (0,0)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 0 + 300 $\times $ 0
f(0,200) = 0
Case 3: (150,0)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 150 + 300 $\times $ 0
f(0,200) = 75000
Case 4: (50,150)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 50 + 300 $\times $ 150
f(0,200) = 70000
Thus, the maximum profit is Rs 75000 for the case where 150 passengers are first class ticket holders and 0 passengers are economy class ticket holders.
Note: While solving LPP (Linear Programming Problems), it is always important not to forget the trivial cases (like in this problem, we had x $\ge $ 0 and y $\ge $ 0). Another, key point to note is that the graphical method can only be effectively used for solving problems concerning two variables. Suppose, we had a third constraint concerning another variable (say z), then, it becomes a 3-dimensional problem making it much more tedious to solve by graph. In such cases, generally we use a software like Matlab to solve these types of problems.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, to solve the problem, we try to represent the constraints given in the problem using x and y, where x represents the number of first class ticket holders and y represents the number of economy class ticket holders. Thus, the first condition is that aeroplane can carry a maximum load of 200 passengers. We have,
x+y $\le $ 200 -- (1)
Now, we have the capacity for the first class ticket holder is 30 kg and for the economy class ticket holder is 20 kg. Further, the maximum capacity is given as 4500 kg. Thus, we have,
30x + 20y $\le $ 4500
3x + 2y $\le $ 450 -- (2)
Apart from these, we also know that x and y should be positive quantities. Thus, we have,
x $\ge $ 0 -- (3)
y $\ge $ 0 -- (4)
Now, to maximize profit, it is given that profit on each first class ticket is Rs.500 and on each economy class ticket is Rs.300. Thus, we have to maximize,
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y -- (A)
Now, we represent (1), (2), (3) and (4) on the graph, we have,

Now, to get the maximum profit, by finding the value of profit at the close bounded figure obtained by representing these equations on the graph. Then, we find the value of the profit at the vertices of the intersection figure formed. These vertices are (0,200), (0,0), (150,0) and intersection point of lines (1) and (2). We find the intersections of the lines (1) and (2). We get,
(solving x+y = 200 and 3x + 2y = 450) –
x = 50 and y = 150.
Now, we find profit at all these vertices. Thus, we have,
Case 1: (0,200)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 0 + 300 $\times $ 200
f(0,200) = 60000
Case 2: (0,0)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 0 + 300 $\times $ 0
f(0,200) = 0
Case 3: (150,0)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 150 + 300 $\times $ 0
f(0,200) = 75000
Case 4: (50,150)
f(x,y) = 500x + 300y
f(0,200) = 500 $\times $ 50 + 300 $\times $ 150
f(0,200) = 70000
Thus, the maximum profit is Rs 75000 for the case where 150 passengers are first class ticket holders and 0 passengers are economy class ticket holders.
Note: While solving LPP (Linear Programming Problems), it is always important not to forget the trivial cases (like in this problem, we had x $\ge $ 0 and y $\ge $ 0). Another, key point to note is that the graphical method can only be effectively used for solving problems concerning two variables. Suppose, we had a third constraint concerning another variable (say z), then, it becomes a 3-dimensional problem making it much more tedious to solve by graph. In such cases, generally we use a software like Matlab to solve these types of problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?

Draw the diagram of the sectional view of the human class 10 biology CBSE




