
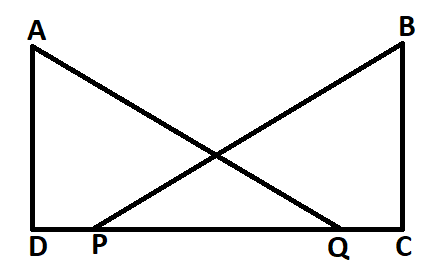
$AD \bot CD$ and $CB \bot CD$. If AQ=BP and DP=CQ , prove that $\angle DAQ = \angle CBP$

Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: Given that, $AD \bot CD$ and $CB \bot CD$. Now we have to prove $\angle DAQ = \angle CBP$. Note that both $\vartriangle ADQ$ and $\vartriangle BPC$ are right angled triangles. AQ=BP and DP=CQ, given. Therefore, first we have to show that the triangles are congruent. And lastly, show that $\angle DAQ = \angle CBP$, as they are corresponding parts of congruent triangles.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, $AD \bot CD$ and $CB \bot CD$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADQ = \angle BCP = {90^ \circ }$
Therefore, both $\vartriangle ADQ$ and $\vartriangle BPC$ are right angled triangles.
Also, AQ=BP and DP=CQ
$ \Rightarrow DP + PQ = CQ + PQ$
$ \Rightarrow DQ = CP$
Now, in $\vartriangle ADQ$ and $\vartriangle BPC$,
$\angle ADQ = \angle BCP = {90^ \circ }$
AQ=BP (given)
DQ=CP
Therefore, $\vartriangle ADQ \cong \vartriangle BPC$ (by RHS rule of congruence)
Hence, $\angle DAQ = \angle CBP$ (corresponding parts of congruent triangles)
Note: The four rules of congruency are as follows:
SSS: When three sides of two different triangles are equal in length.
SAS: When two sides are equal, and the angle between them is also the same in measure.
AAS: When any two angles and a side is equal.
RHS: When the hypotenuse and any one side of two right angled triangles are equal in length.
Complete step-by-step solution:
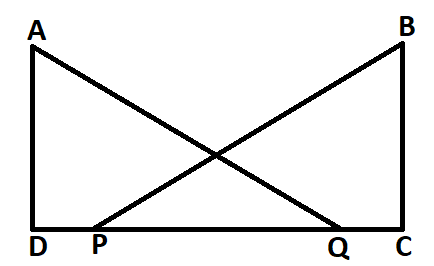
Given, $AD \bot CD$ and $CB \bot CD$.
$ \Rightarrow \angle ADQ = \angle BCP = {90^ \circ }$
Therefore, both $\vartriangle ADQ$ and $\vartriangle BPC$ are right angled triangles.

Also, AQ=BP and DP=CQ
$ \Rightarrow DP + PQ = CQ + PQ$
$ \Rightarrow DQ = CP$
Now, in $\vartriangle ADQ$ and $\vartriangle BPC$,
$\angle ADQ = \angle BCP = {90^ \circ }$
AQ=BP (given)
DQ=CP
Therefore, $\vartriangle ADQ \cong \vartriangle BPC$ (by RHS rule of congruence)
Hence, $\angle DAQ = \angle CBP$ (corresponding parts of congruent triangles)
Note: The four rules of congruency are as follows:
SSS: When three sides of two different triangles are equal in length.
SAS: When two sides are equal, and the angle between them is also the same in measure.
AAS: When any two angles and a side is equal.
RHS: When the hypotenuse and any one side of two right angled triangles are equal in length.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





