
ABCD is a rectangle with sides 36cm and 90cm. P is a point on BC which is one of the longer sides such that PA=2PD. The length of PB is
A) 80 cm
B) 76 cm
C) 72 cm
D) 64 cm
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint:
First draw a suitable diagram of the rectangle. Then, take a pint on BC. Take both right angled triangles and apply Pythagoras theorems. Compare both expressions together as $PA= 2 PD$. Solve the quadratic equation, thus obtained. Suitable root of it will be the result.
Complete step by step solution:
Draw the rectangle ABCD as below.
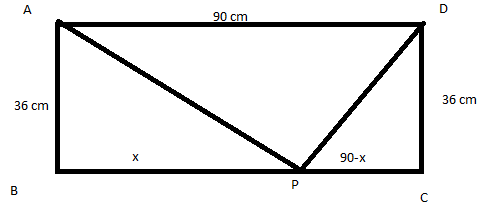
Sides AB and DC are equal and 36 cm.
Also, sided AC and AD are 90 cm.
Let us assume that P is appointed somewhere on side BC.
It is given that ,
PA = 2 PD …(1)
Now let us assume that length of BP is x cm,
So, the PC will be (90-x) cm.
In right angled triangle ABP, we apply the Pythagoras theorem, and hence we get,
$P{A^2} = A{B^2} + B{P^2}$
Substituting the values in above equation, we have
$P{A^2} = {36^2} + {x^2}$ …(2)
Similarly in right angled triangle CPD, we apply the Pythagoras theorem, and hence we get,
$P{D^2} = P{C^2} + D{C^2}$
Substituting the values in above equation, we have
$P{D^2} = {36^2} + {(90 - x)^2}$ …(3)
Doing square on both sides of equation (1), we get
$P{A^2} = 4P{D^2}$
Now, from equations (2) and (3) in the above equation, we have
${36^2} + {x^2} = 4({36^2} + {(90 - x)^2})$
Further simplification, we get
$
{36^2} + {x^2} = 4({36^2} + {(90 - x)^2}) \\
\Rightarrow {36^2} + {x^2} = 4 \times {36^2} + 4 \times {(90 - x)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = 3 \times {36^2} + 4 \times (8100 + {x^2} - 180x) \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = 3888 + 32400 + 4{x^2} - 720x \\
\Rightarrow 3{x^2} - 720x + 36288 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 240x + 12096 = 0 \\
$
Thus we have a quadratic equation. Two factors of 12096 are 168 and 72. Thus doing factorization of above equation we get,
$(x-168) (x-72) = 0$
Thus values of $x = 168$ and $72$.
Since $168 > 90$, which is not possible for point P.
Thus a suitable value of $x = 72$.
$\therefore $ The length of PB will be 72 cm.
So, the correct option is C.
Note:
This question is a direct application of Pythagoras theorem. Also, solving the quadratic equation is an important part of such problems. In this way, we can solve a geometrical problem with the help of algebraic computations.
First draw a suitable diagram of the rectangle. Then, take a pint on BC. Take both right angled triangles and apply Pythagoras theorems. Compare both expressions together as $PA= 2 PD$. Solve the quadratic equation, thus obtained. Suitable root of it will be the result.
Complete step by step solution:
Draw the rectangle ABCD as below.

Sides AB and DC are equal and 36 cm.
Also, sided AC and AD are 90 cm.
Let us assume that P is appointed somewhere on side BC.
It is given that ,
PA = 2 PD …(1)
Now let us assume that length of BP is x cm,
So, the PC will be (90-x) cm.
In right angled triangle ABP, we apply the Pythagoras theorem, and hence we get,
$P{A^2} = A{B^2} + B{P^2}$
Substituting the values in above equation, we have
$P{A^2} = {36^2} + {x^2}$ …(2)
Similarly in right angled triangle CPD, we apply the Pythagoras theorem, and hence we get,
$P{D^2} = P{C^2} + D{C^2}$
Substituting the values in above equation, we have
$P{D^2} = {36^2} + {(90 - x)^2}$ …(3)
Doing square on both sides of equation (1), we get
$P{A^2} = 4P{D^2}$
Now, from equations (2) and (3) in the above equation, we have
${36^2} + {x^2} = 4({36^2} + {(90 - x)^2})$
Further simplification, we get
$
{36^2} + {x^2} = 4({36^2} + {(90 - x)^2}) \\
\Rightarrow {36^2} + {x^2} = 4 \times {36^2} + 4 \times {(90 - x)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = 3 \times {36^2} + 4 \times (8100 + {x^2} - 180x) \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} = 3888 + 32400 + 4{x^2} - 720x \\
\Rightarrow 3{x^2} - 720x + 36288 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} - 240x + 12096 = 0 \\
$
Thus we have a quadratic equation. Two factors of 12096 are 168 and 72. Thus doing factorization of above equation we get,
$(x-168) (x-72) = 0$
Thus values of $x = 168$ and $72$.
Since $168 > 90$, which is not possible for point P.
Thus a suitable value of $x = 72$.
$\therefore $ The length of PB will be 72 cm.
So, the correct option is C.
Note:
This question is a direct application of Pythagoras theorem. Also, solving the quadratic equation is an important part of such problems. In this way, we can solve a geometrical problem with the help of algebraic computations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




