
ABCD is a rectangle in which diagonal AC bisects $\angle $${\text{A}}$ as well as $\angle $${\text{C}}$.
Show that,
(i) ABCD is square
(ii) diagonal BD bisects $\angle $${\text{B}}$ as well as $\angle $${\text{D}}$.
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: To solve this question we need to know the basic theory related to the rectangle. We learned that a rectangle has four-sided and all the internal angles are equal to 90 degrees. The length of the opposite sides of the rectangle is always equal to each other. The length of the opposite sides of the rectangle is always equal to each other. If all the sides are equal then it is square.
Complete step-by-step solution:
(i) we need to prove ABCD is square.
Given in question,
ABCD is a rectangle, in which diagonal AC bisect $\angle $${\text{A}}$ as well as $\angle $${\text{C}}$.
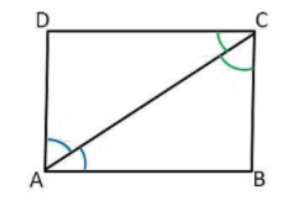
Therefore,
$\angle $${\text{DAC}}$=$\angle $${\text{CAB}}$……………… (1)
$\angle $${\text{DCA}}$=$\angle $${\text{BCA}}$………………. (2)
A square is a rectangle when all sides are equal. Now,
AD$\parallel $BC & AC is transversal, therefore
$\angle$${\text{DAC}}$=$\angle$${\text{BCA}}$ [Alternate angles]
From (1),
$\angle $${\text{CAB}}$=$\angle $${\text{BCA}}$……………….. (3)
In $\vartriangle $ABC,
$\angle $${\text{CAB}}$=$\angle $${\text{BCA}}$, therefore
BC=AB………………….. (4) [sides opposite to equal angles]
But BC=AD & AB=DC………………….. (5) [Opposite sides of rectangle]
Therefore from (4) & (5),
AB=BC=CD=AD
Hence, ABCD is a square.
(ii) we need to prove that diagonal BD bisects $\angle $${\text{B}}$ as well as $\angle $${\text{D}}$.
Now, As we discussed in the previous part.
ABCD is a square and we know that diagonals of a square bisect its angles.
Hence, BD bisects ∠B as well as ∠D.
Note: Here we use various properties of a rectangle. Always remember that the diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other and also the sides in a rectangle are always equal to each other.
Complete step-by-step solution:
(i) we need to prove ABCD is square.
Given in question,
ABCD is a rectangle, in which diagonal AC bisect $\angle $${\text{A}}$ as well as $\angle $${\text{C}}$.

Therefore,
$\angle $${\text{DAC}}$=$\angle $${\text{CAB}}$……………… (1)
$\angle $${\text{DCA}}$=$\angle $${\text{BCA}}$………………. (2)
A square is a rectangle when all sides are equal. Now,
AD$\parallel $BC & AC is transversal, therefore
$\angle$${\text{DAC}}$=$\angle$${\text{BCA}}$ [Alternate angles]
From (1),
$\angle $${\text{CAB}}$=$\angle $${\text{BCA}}$……………….. (3)
In $\vartriangle $ABC,
$\angle $${\text{CAB}}$=$\angle $${\text{BCA}}$, therefore
BC=AB………………….. (4) [sides opposite to equal angles]
But BC=AD & AB=DC………………….. (5) [Opposite sides of rectangle]
Therefore from (4) & (5),
AB=BC=CD=AD
Hence, ABCD is a square.
(ii) we need to prove that diagonal BD bisects $\angle $${\text{B}}$ as well as $\angle $${\text{D}}$.
Now, As we discussed in the previous part.
ABCD is a square and we know that diagonals of a square bisect its angles.
Hence, BD bisects ∠B as well as ∠D.
Note: Here we use various properties of a rectangle. Always remember that the diagonals of a rectangle bisect each other and also the sides in a rectangle are always equal to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




