
A circular railway track of radius r is banked at angle so that a train moving with speed v can safely go round the track. A student writes: $tan\theta = \dfrac{{rg}}{{{v^2}}}$. Why is this relation not correct?
(i) Equality of dimension does not guarantee correctness of the relation
(ii) Dimension correct relation may not be numerically correct
(iii) The relation is dimensionally incorrect.
A.) (i) and (ii)
B.) (ii) and (iii)
C.) (iii) and (i)
D.) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: In dimensional analysis, the presence or absence of constants, ratios, trigonometric identities cannot be determined. They are dimensionless. That means the dimension is ${M^0}{L^0}{T^0}$. Therefore adding or removing them does not affect the equation.
Formula used: Centripetal Force : \[{F_c} = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}\] \[\]
Complete step by step solution:
The car moving on a normal road does not experience any forces other than its weight, normal reaction and friction. In this question the frictional force is not considered.
So we have its weight $mg$ acting downwards and its normal reaction $N$ acting upwards.
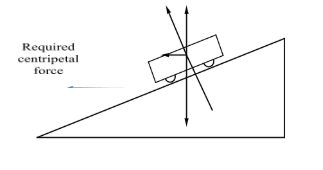
Car on a banked road with no friction
Here we can see that due to banking of the road the normal reaction is not straight up.
It is normal to the banked road which makes an angle of $\theta $ with the horizontal surface.
Taking components of the normal reaction in parallel and perpendicular directions with respect to horizontal surface, we can come to these conclusions that (see fig 2)
(i) The $\cos \theta $ component of N(normal reaction) balances the weight of the car.
(ii) The $\sin \theta $ component of N(normal reaction) provides the necessary centripetal force for the car.
$Ncos\theta = mg$
$N = \dfrac{{m \times g}}{{cos\theta }}$
Similarly
$Nsin\theta = \dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r}$
${F_{centripetal}} = \dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r}$ (And this is balanced by $Nsin\theta $)
Substituting value of $N$, we get
$\dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r} = \left( {\dfrac{{m \times g}}{{cos\theta }}} \right) \times sin\theta = mgtan\theta $
$mgtan\theta = \dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r}$
Rearranging, $tan\theta = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{{rg}}$
This shows that even though the equation is dimensionally correct, the answer is wrong.
Therefore (i) and (ii) are the correct options
Note: Unlike other inclined plane problems we took the components of normal in horizontal and vertical direction since the acceleration is along these directions. Usually in inclined problems the components of mass $mg$ are taken parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane.But here taking components of the normal force in the horizontal and vertical direction makes it simpler to understand.
Formula used: Centripetal Force : \[{F_c} = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{r}\] \[\]
Complete step by step solution:
The car moving on a normal road does not experience any forces other than its weight, normal reaction and friction. In this question the frictional force is not considered.
So we have its weight $mg$ acting downwards and its normal reaction $N$ acting upwards.

Car on a banked road with no friction
Here we can see that due to banking of the road the normal reaction is not straight up.
It is normal to the banked road which makes an angle of $\theta $ with the horizontal surface.
Taking components of the normal reaction in parallel and perpendicular directions with respect to horizontal surface, we can come to these conclusions that (see fig 2)
(i) The $\cos \theta $ component of N(normal reaction) balances the weight of the car.
(ii) The $\sin \theta $ component of N(normal reaction) provides the necessary centripetal force for the car.
$Ncos\theta = mg$
$N = \dfrac{{m \times g}}{{cos\theta }}$
Similarly
$Nsin\theta = \dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r}$
${F_{centripetal}} = \dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r}$ (And this is balanced by $Nsin\theta $)
Substituting value of $N$, we get
$\dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r} = \left( {\dfrac{{m \times g}}{{cos\theta }}} \right) \times sin\theta = mgtan\theta $
$mgtan\theta = \dfrac{{m \times {v^2}}}{r}$
Rearranging, $tan\theta = \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{{rg}}$
This shows that even though the equation is dimensionally correct, the answer is wrong.
Therefore (i) and (ii) are the correct options
Note: Unlike other inclined plane problems we took the components of normal in horizontal and vertical direction since the acceleration is along these directions. Usually in inclined problems the components of mass $mg$ are taken parallel and perpendicular to the inclined plane.But here taking components of the normal force in the horizontal and vertical direction makes it simpler to understand.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




