
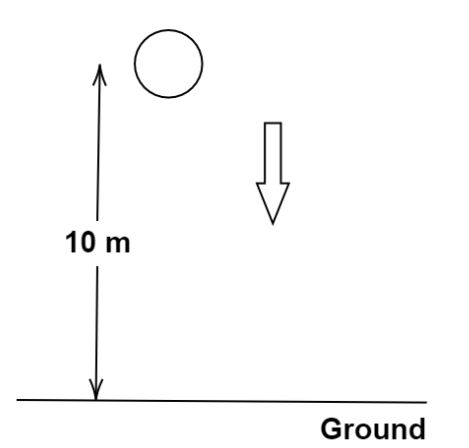
A child drops a ball from a height of \[10\,m\] . Assume that its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of \[10\,m/{s^2}\] . Find the velocity with which the ball strikes the ground and the time taken by the ball to reach the ground.
Answer
478.8k+ views
Hint: We are asked to find the velocity with which the ball strikes the ground and the time taken by the ball to reach the ground. We can easily find both of these quantities by the direct substitution in the equations of motion that gives us the relation between the distance traveled and time taken.
Formulas used:
The formula to find the value of final velocity is given by,
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS\]
The formula to find the distance travelled is given by,
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Where \[u\] is the initial velocity of motion, \[a\] is the acceleration of the body and \[t\] is the time taken for the motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by noting down the values given in the question. The initial velocity of the ball can be taken as Zero as the child just drops the ball.
The value of acceleration is given as \[a = 10\,m/{s^2}\]
The distance from which the ball is dropped is given as \[S = 10\,m\]
Now that we have written down the values given in the question, we can move onto finding the final velocity or the velocity with which the ball hits the ground using the formula,
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS\]
We can substitute the values and get \[{v^2} = 2 \times 10 \times 10 = 200\]
Taking the square root, we get the value of final velocity as \[v = 10\sqrt 2 m/s\]
Now that we have found the value of final velocity, we can move onto finding the value of time taken for the fall.We use the formula,
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
The value of time can be isolated and be found out as \[t = \sqrt {2\dfrac{S}{a}} \].
We can substitute the values and get,
\[t = \sqrt {2\dfrac{S}{a}} \\
\Rightarrow t = \sqrt {2 \times \dfrac{{10}}{{10}}} \\
\therefore t = \sqrt 2 s\]
Therefore, the time taken for the fall is \[\sqrt 2 s\] and the velocity with which the ball hits the ground will be \[10\sqrt 2 m/s\].
Note:The value of time taken can also be found out using the formula of acceleration. That is, acceleration is given by the formula, \[a = \dfrac{{v - u}}{t}\].We can substitute the values of acceleration and final velocity and get the value as the same answer which is,
\[t = \dfrac{v}{a} \\
\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{10\sqrt 2 }}{{10}} \\
\therefore t = \sqrt 2 s\]
Formulas used:
The formula to find the value of final velocity is given by,
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS\]
The formula to find the distance travelled is given by,
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
Where \[u\] is the initial velocity of motion, \[a\] is the acceleration of the body and \[t\] is the time taken for the motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us start by noting down the values given in the question. The initial velocity of the ball can be taken as Zero as the child just drops the ball.
The value of acceleration is given as \[a = 10\,m/{s^2}\]
The distance from which the ball is dropped is given as \[S = 10\,m\]

Now that we have written down the values given in the question, we can move onto finding the final velocity or the velocity with which the ball hits the ground using the formula,
\[{v^2} = {u^2} + 2aS\]
We can substitute the values and get \[{v^2} = 2 \times 10 \times 10 = 200\]
Taking the square root, we get the value of final velocity as \[v = 10\sqrt 2 m/s\]
Now that we have found the value of final velocity, we can move onto finding the value of time taken for the fall.We use the formula,
\[S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
The value of time can be isolated and be found out as \[t = \sqrt {2\dfrac{S}{a}} \].
We can substitute the values and get,
\[t = \sqrt {2\dfrac{S}{a}} \\
\Rightarrow t = \sqrt {2 \times \dfrac{{10}}{{10}}} \\
\therefore t = \sqrt 2 s\]
Therefore, the time taken for the fall is \[\sqrt 2 s\] and the velocity with which the ball hits the ground will be \[10\sqrt 2 m/s\].
Note:The value of time taken can also be found out using the formula of acceleration. That is, acceleration is given by the formula, \[a = \dfrac{{v - u}}{t}\].We can substitute the values of acceleration and final velocity and get the value as the same answer which is,
\[t = \dfrac{v}{a} \\
\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{10\sqrt 2 }}{{10}} \\
\therefore t = \sqrt 2 s\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




