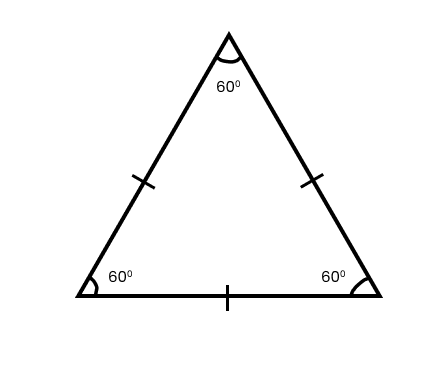
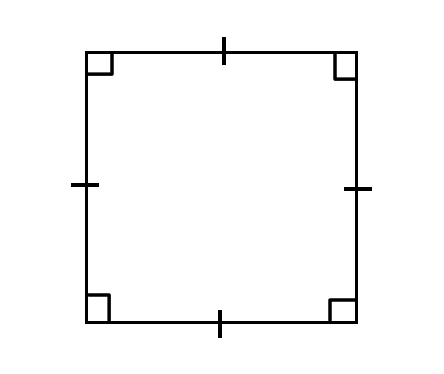
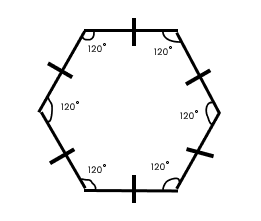
Understanding Quadrilaterals Class 8 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
Recently Updated Pages
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 15 Exercise 15.1: Free PDF 2024-25

NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 12 "Mineral Nutrition".

NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 "Hydrocarbons".

Class 10 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections

Chapter 8 Organic Chemistry Class 11 NCERT Solutions FREE PDF Download

NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability.

Trending pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Light - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Social Science - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 8 English Honeydew Chapter 1 The Best Christmas Present In The World - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Sound - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Hindi Vasant Chapter 12 Pani Ki Kahani - 2025-26

Other Pages
Important Days in February 2026 – Check All National & International Events List

Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Biography

Republic Day Essay 2026: Samples and Writing Guide for Students

What is the Full Form of AM and PM?

India vs Pakistan

Farewell Speech for Students: Express Your Appreciation and Inspire Success