




How to Identify Corresponding Sides in Geometry
In Geometry, the three-sided polygon is a triangle that has three edges and three vertices. The most noteworthy property of a triangle is that the total sum of the interior angles of a triangle equals 180 degrees.
A triangle is a two-dimensional shape/ figure constituting three sides, three angles, and three vertices. The total sum of all internal angles of a triangle is invariably $180^{\circ}$ whether it is an isosceles, equilateral, or scalene triangle. The Sum of angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degrees. The external angles of a triangle always add up to 360 degrees.
A fun cartoon of triangles
What Is a True Triangle?
A true triangle is a shape that has three sides and three angles. The lengths of two of the sides must add up to a number greater than the third side, and the three angles must add up to $180^{\circ}$
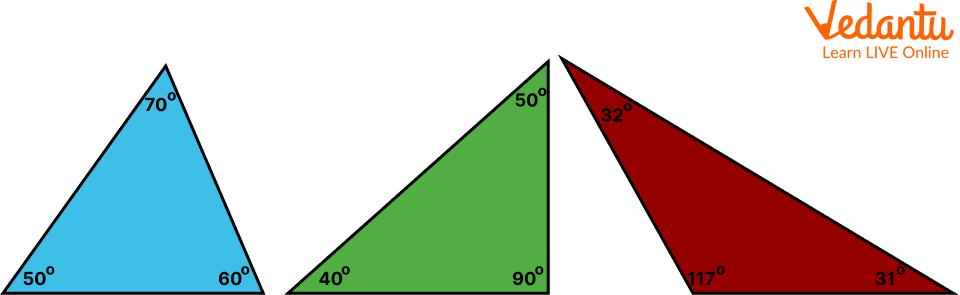
The three angles of any above triangle will add up to $180^{\circ}$
What Is the Formula for the Triangle?
The basic formula for the area of a triangle is equal to half the product of its base and height, i.e., $A = \frac{1}{2} \times b \times h$. This formula is applicable to all types of triangles, whether it is a scalene triangle, an isosceles triangle, or an equilateral triangle.
The angle sum property of a triangle states that the angles of a triangle always add up to $180^{\circ}$
$\angle \mathrm{A}+\angle \mathrm{B}+\angle \mathrm{C}=180^{\circ}$
Triangle ABC
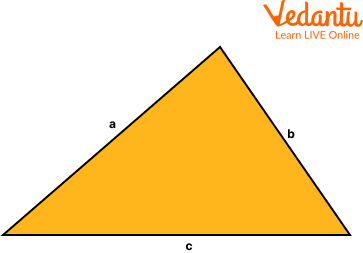
$S = \frac{a+b+c}{2}$
Here, S is the semi perimeter and a, b and c are the sides of the triangle.
$\text { Area of Triangle }=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
Corresponding Angles in Triangle and Its Sides
What is the meaning of the corresponding sides?
Corresponding sides and angles are a pair of matching angles or sides that are in the same spot in two different shapes.
Corresponding parts of congruent triangles or cpct tell us that corresponding sides and corresponding angles of the two triangles which are congruent are equal.
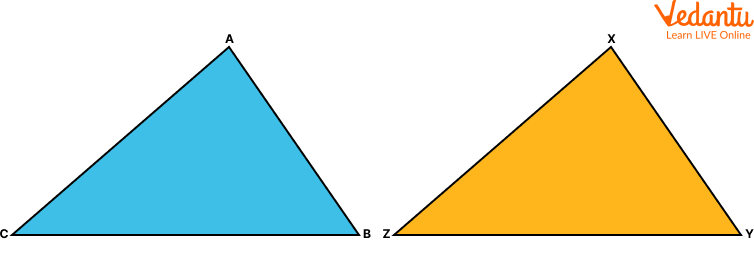
Triangle ABC = Triangle XYZ
What is the example of the corresponding side?
For example, look at the above triangle ABC and XYZ.
Corresponding Angles
$\angle A \longleftrightarrow \angle X$
$\angle C \longleftrightarrow \angle Z$
$\angle B \longleftrightarrow \angle Y$
Corresponding sides
$\overline{A B} \longleftrightarrow \overline{XY}$
$\overline{B C} \longleftrightarrow \overline{YZ}$
$\overline{A C} \longleftrightarrow \overline{XZ}$
Note: Similar triangles have corresponding angles and corresponding sides.
What is the Congruent Triangle?
Meaning of Congruent
If two figures can be placed precisely over each other, they are said to be 'congruent' figures. If you place one slice of bread over the other, you will find that both the slices are of equal shape and size. The term “congruent” means exactly equal shape and size.
Below are the congruent triangles examples.

Congruent triangles
How do you know if triangles are congruent?
If two sides and the included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and angle of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
Congruence in Triangles
Congruence in two or more triangles depends on the measurements of their sides and angles. The three sides of a triangle determine its size and the three angles of a triangle determine its shape. Two triangles are said to be congruent if pairs of their corresponding sides and their corresponding angles are equal. They are of the same shape and size.
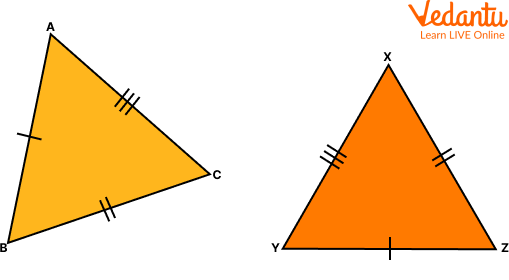
Congruence in Triangles ABC and XYZ
Naming Similar Triangles
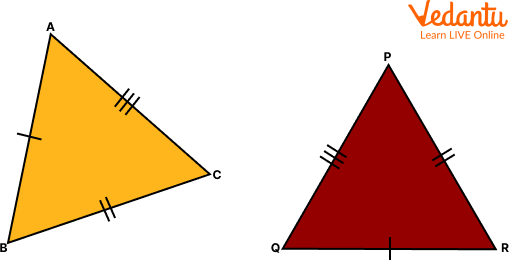
Congruence in Triangles ABC and PQR
In the above figure, $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}$ and $\triangle \mathrm{PQR}$ are congruent triangles. This means,
Vertices: A and P, B and Q, and C and R are the same.
Sides: $A B=P Q, Q R=B C$ and $A C=P R$;
Angles: $\angle \mathrm{A}=\angle \mathrm{P}, \angle \mathrm{B}=\angle \mathrm{Q}$, and $\angle \mathrm{C}=\angle \mathrm{R}$.
Congruent triangles are triangles having corresponding sides and angles to be equal. The perimeter denotes congruence.
Solved Questions
Q 1. In a $\triangle A B C$, if $A B=A C$ and $\angle B=70^{\circ}$, find $\angle A$.
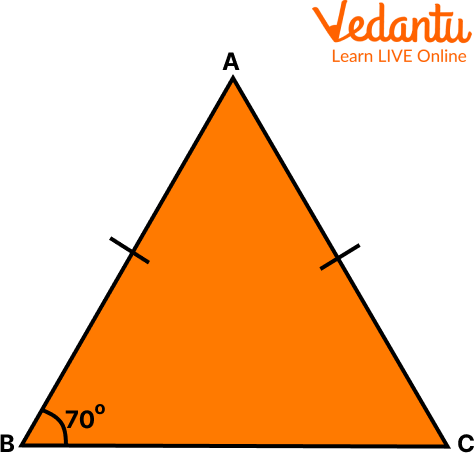
Triangle ABC
Ans: Given: In a $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}, \mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{AC}$ and $\angle \mathrm{B}=70^{\circ}$
$\angle B=\angle C$ [Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal]
Therefore, $\angle \mathrm{B}=\angle \mathrm{C}=70^{\circ}$
Sum of angles in a triangle $=180^{\circ}$
$\angle \mathrm{A}+\angle \mathrm{B}+\angle \mathrm{C}=180^{\circ}$
$\angle \mathrm{A}+70^{\circ}+70^{\circ}=180^{\circ}$
$\angle \mathrm{A}=180^{\circ}-140^{\circ}$
$\angle \mathrm{A}=40^{\circ}$
Q 2. In a $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}$, if
$\mathrm{AB}^2=\mathrm{BC}^2+\mathrm{AC}^2$, then the right angle is at:
Ans: By Pythagoras theorem,
$(\text { hypotenuse })^2=(\text { perpendicular })^2+(\text { base })^2$
Clearly, $\mathrm{AB}$ is hypotenuse, $\mathrm{BC}$ and $\mathrm{AC}$ are either base or perpendicular.
Since, $A B$ is hypotenuse, therefore neither A nor $B$ is right angle.
Therefore, $C$ is the right angle.
Practice Questions
Q 1. If $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}$ and $\triangle U Y T$ are similar triangles, then what sides/angles correspond with:
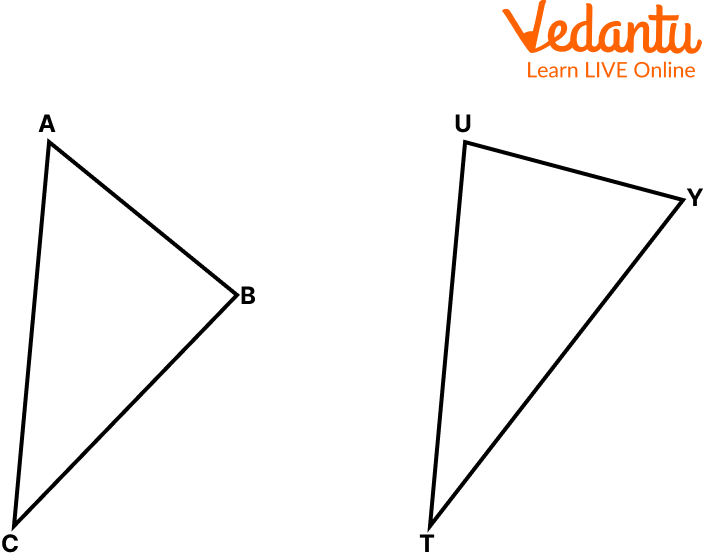

Triangle ABC and UYT
(a) TU?
Ans: CA
(b) $\angle T U Y$?
Ans: $\angle C A B$
Q 2. Recognize congruent triangles
Decide whether this pair of triangles are congruent. If they are congruent, state why:

Picture in reference to the question
(a) Check the corresponding angles and corresponding sides.?
Ans: Triangles have sides of 6.3cm,8.1cm, and 10.2cm.
(b) Decide if the shapes are congruent or not.
Ans: The triangles are the same shape and the same size – they are congruent.
Summary
There are six types of triangles– Isosceles, Scalene, Equilateral, Oblique, Acute, and Right. Based on the type according to internal angles, there are three types – Equilateral, Scalene, and Isosceles. Whereas, the kinds of a triangle are classified according to the length of their sides which are Right, Acute, and Oblique.
The Properties of a Triangle Are:
A triangle contains three sides, three angles, and three vertices.
The totality of all interior angles of a triangle is equal to $180^{\circ}$. This is known as the angle sum of a triangle.
The total sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the length of its third side.
The side which is opposite the largest angle of a triangle is its largest side.
FAQs on What Are Corresponding Sides in Maths?
1. What are corresponding sides in Maths?
In geometry, corresponding sides are the matching sides between two or more shapes that are in the same relative position. When you compare two polygons, such as triangles or quadrilaterals, that are either congruent or similar, the sides that hold the same spot in each shape are considered corresponding.
2. Can you give an example of corresponding sides in two triangles?
Certainly. Imagine two triangles, ΔABC and ΔPQR, where ΔABC is similar to ΔPQR. The side AB would correspond to side PQ, side BC corresponds to side QR, and side AC corresponds to side PR. These matching pairs are identified based on their positions relative to the corresponding angles in each triangle.
3. How can I identify the corresponding sides of two shapes?
To identify corresponding sides, especially in triangles, you can use these methods:
- Look at the angles: The side opposite a specific angle in one triangle corresponds to the side opposite the matching angle in the other triangle.
- Compare side lengths: In similar or congruent shapes, the longest side of one shape corresponds to the longest side of the other. The same logic applies to the shortest and middle-length sides.
- Use the similarity statement: If it is given that ΔABC ~ ΔPQR, the order of the letters directly tells you the pairs: AB corresponds to PQ, BC to QR, and AC to PR.
4. What is the main difference between corresponding sides in congruent versus similar figures?
The primary difference is their measurement.
- In congruent figures, corresponding sides are always equal in length. If two triangles are congruent, their matching sides have the exact same length.
- In similar figures, corresponding sides are proportional, meaning their lengths share a constant ratio. They are not necessarily equal. For example, if one triangle's sides are all twice as long as the corresponding sides of another triangle, they are similar.
5. Why is it important to understand corresponding sides in geometry?
Understanding corresponding sides is fundamental for proving whether two shapes are congruent (identical in shape and size) or similar (same shape, different size). This principle is essential for solving problems in geometry and has practical applications in fields like architecture for creating scale models, in engineering for design, and in art for maintaining perspective.
6. Do corresponding sides have to be in the same orientation or parallel?
No, corresponding sides do not need to be in the same orientation or parallel. One figure can be rotated, reflected (flipped), or translated (moved) relative to the other. Correspondence is determined by the relative position within each figure (e.g., the side between the 60° and 90° angles), not by its orientation on the page.
7. Does the concept of corresponding sides apply only to triangles?
No, the concept of corresponding sides applies to all types of polygons, not just triangles. This includes quadrilaterals (like squares and rectangles), pentagons, hexagons, and so on. Whenever you compare two polygons that are either congruent or similar, you can identify their corresponding sides and angles based on their matching positions.

















