




How to Identify and Prove Congruence in Plane Figures
Two shapes are said to be congruent if they are equal to each other in all possible ways. In Mathematics, congruent figures are those figures which have the same shape and the same size. The congruence applies to both the 2-D and 3-D figures. But in this article, we shall discuss the congruence of plane figures only.
Congruent figures are those having the same shape and size. The relation used in the two congruent figures is known as congruence. It is denoted by the symbol \[ \cong \].
Congruent Figure
In Mathematics, Congruent figures are those geometric figures that have the same shape and size. If you transform one figure into another figure by a sequence of rotations, and/or reflections, then the two figures are equal to each and hence they are called congruent figures. For more illustration, we take two figures and prove them congruent.
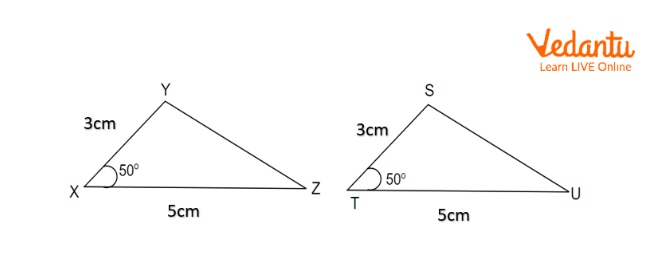
Two Congruent Triangles
In \[\Delta XYZ\] and \[\Delta STU\] here,
\[ \Rightarrow XY = ST = 3cm\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle YXZ = \angle STU = 50^\circ \]
\[ \Rightarrow XZ = TU = 5cm\]
These two triangles are congruent with each by the property S.A.S (Side-Angle-Side).
Therefore, \[\Delta XYZ \cong \Delta STU\].
Congruence of Plane Figures
A plane figure is a geometric figure consisting of no thickness. Line segments, curves or a combination of both line segments and curves are some of the plane figures. The straight or curved lines that make up the plane figures are called their sides.
Plane figures such as line segments, angles and other figures are said to be congruent if they have the same shape and size. The relation used is known as the congruence of plane figures. For example,
Two Congruent Figures
Here, these planes are congruent with each other because both of these figures have the same shape and size.
Congruent Segments Definition
The congruent segment is a set of two line segments that have equal lengths. A line segment is a straight line with specific starting and ending points. As it has specific starting and ending points, its length can be measured. Congruent line segments don’t need to be parallel, perpendicular or at any specific angle to each other, but they can be.
Two Congruent Line Segments
Congruence of Line Segment
A line segment is a primary figure in the geometry that is formed by connecting any two points of the plane figure. The sides of the plane figures are also line segments. If two line segments have the same length, then they are said to be congruent. In other words, if two line segments are congruent, then their lengths are equal.
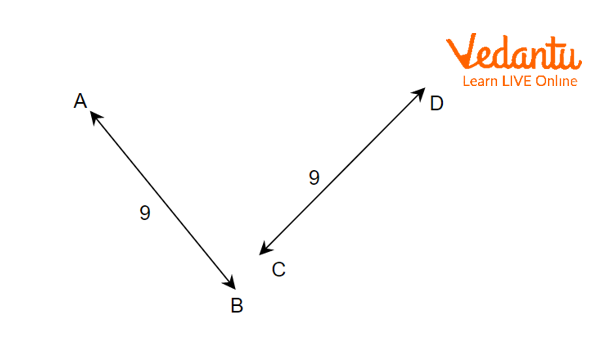
Two Line Segments
In the above figures, two line segments \[\overline {AB} \] and \[\overline {CD} \] have equal lengths of 9 units. Two line segments \[\overline {AB} \] and \[\overline {CD} \] superimpose on each other. So, they are congruent with each other. Hence, the line segments \[\overline {AB} \] and \[\overline {CD} \] are congruent lines.
\[\overline {AB} \cong \overline {CD}\]
Two Line Segments are Congruent
Two line segments are congruent if they have the same length. However, they don't need to be parallel. They can be oriented at any angle or can be at any position. A line segment is defined by the distance between two points.
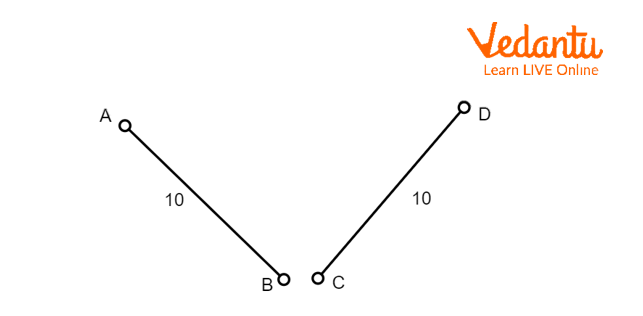
Two Congruent Line Segments
In the figures given above, the line segment has the same length that's why line AB is congruent with line CD. This statement can also be written as \[AB \cong CD\].
Plane Shapes Images
A closed 2-D or flat figure is called a plane shape. Different plane shapes have different properties, such as the number of vertices. A side is a straight line that is included in the shape, and a vertex is where two sides meet each other. Some of the basic plane shapes are triangles, squares, rectangles, ovals, circles and polygons whose figures are given below.
Plane Figures
Interesting Facts
The other name for the plane figure is a paraboloid.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz is the father of congruence.
The hexagon is the strongest plane shape known.
Solved Examples Related to Congruence of Plane Figures
1. If two triangles ABC and PQR are congruent, then find \[\angle PQR\].
Solution: Given that the \[\Delta ABC\] and \[\Delta PQR\] are congruent to each other.
\[\angle BAC = \angle QPR = 40^{\circ}\], \[\angle ACB = \angle PRQ = 60^{\circ} \], and \[\angle CBA = \angle RQP \].
The sum of all angles of a triangle is \[180^{\circ}\].
\[\angle QPR + \angle PRQ + \angle RQP = 180^{\circ}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 40^{\circ} + 40^{\circ}+ \angle RQP = 180^{\circ}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 100^{\circ} + \angle RQP = 180^{\circ}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \angle RQP = 80^{\circ}\]
Therefore \[\angle RQP = 80^{\circ}\].
2. If two shapes are congruent to each other and the perimetre of the first figure is 180 m, then find the perimeter of another shape.
Solution: Since both shapes are congruent to each other, the perimeter of both shapes will be the same. The perimeter of another shape is 180 cm.
Key Features
Two figures are congruent if they possess the same shape and size, or if the figure has the same shape and size as its mirror image, then it is congruent to its mirror image.
Plane figures are those figures which are drawn on a plane or 2-D surface.
A plane in geometry is a flat surface that can extend up to infinity in all directions. As it is extended to infinity, it has infinite width and length, has no thickness and has curvature.
Practice Questions
If two regular pentagons are congruent and the perimeter of one of them is 30 cm, then find the length of one side of another pentagon.
Answer: 5 cm
FAQs on Congruence of Plane Figures: Complete Guide for Students
1. What does it mean for two plane figures to be congruent?
Two plane figures are called congruent if they have the exact same shape and same size. You can think of them as perfect copies of each other. If you could cut one out and place it on top of the other, it would cover it completely without any overlap.
2. What is the main difference between congruent and similar figures?
The key difference lies in their size. Congruent figures have the same shape and the same size. Similar figures have the same shape but can have different sizes. For example, two one-rupee coins are congruent, while a passport-size photo and its enlarged version are similar.
3. What are the rules for proving that two triangles are congruent?
To prove that two triangles are congruent, you don't need to check all six parts (three sides and three angles). You can use any of these four main criteria:
- SSS (Side-Side-Side): If all three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding three sides of another triangle.
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side): If two sides and the angle between them in one triangle are equal to the corresponding parts of another triangle.
- ASA (Angle-Side-Angle): If two angles and the side included between them in one triangle are equal to the corresponding parts of another triangle.
- RHS (Right angle-Hypotenuse-Side): In two right-angled triangles, if the hypotenuse and one side of one triangle are equal to the hypotenuse and corresponding side of the other.
4. Can you give some examples of congruent shapes we see in daily life?
Yes, congruent shapes are all around us! Some common examples include:
- Two pages from the same book.
- Two new coins of the same denomination (e.g., two ₹5 coins).
- The two wings of a butterfly.
- Two identical biscuits from the same packet.
- The floor tiles in a pattern, which are all identical copies.
5. Why are all congruent figures also similar, but not all similar figures are congruent?
This is because congruence is a stricter condition than similarity. To be similar, figures only need to have the same shape. To be congruent, they must have both the same shape and the same size. Since congruent figures already have the same shape, they automatically qualify as similar. However, similar figures might have different sizes, so they are not always congruent.
6. If two triangles are proven congruent, what does that tell us about their parts?
Once you prove two triangles are congruent, it means that all their corresponding parts are also equal. This includes their three corresponding angles and their three corresponding sides. This rule is often called CPCTC, which stands for 'Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent'. It's a very useful tool for solving geometry problems.
7. Does the order of letters matter when writing that two triangles are congruent, like ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR?
Yes, the order is extremely important! The statement ∆ABC ≅ ∆PQR tells you exactly which parts correspond. It means vertex A corresponds to P, B corresponds to Q, and C corresponds to R. This implies that ∠A = ∠P, side AB = side PQ, ∠B = ∠Q, side BC = side QR, and so on. Writing it in the wrong order, like ∆ABC ≅ ∆QRP, would mean something completely different and would be incorrect.























