ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 9 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Updated ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 9 - The Excretory system Selina Solutions are provided by Vedantu in a step-by-step method. Selina is the most famous publisher of ICSE textbooks. Studying these solutions by Selina Concise Biology Class 10 Solutions which are explained and solved by our subject matter experts will help you in preparing for ICSE exams. Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions can be easily downloaded in the given PDF format. These solutions for Class 10 ICSE will help you to score good marks in ICSE Exams 2024-25.
The updated solutions for Selina textbooks are created in accordance with the latest syllabus. These are provided by Vedantu in a chapter-wise manner to help the students get a thorough knowledge of all the fundamentals.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 10 Biology Chapter No. 9 - Excretory system
Progress Check
1. Given below is the list of substances- select the ones that need to be eliminated from the body.
Glucose, excess water, amino acids, urea, carbon dioxide, excess common salt, glycogen, uric acid.
Ans: Excess water, Amino Acids, Urea, Excess common salt, Uric acid
Reason of Elimination
Uric acid and urea are the nitrogen waste created by the liver from dead protein present in other cells. Urea is highly poisonous for our body, so can not be stored in our body.
Other remaining by-products of dead proteins called amino acids can be stored in our body.
Excess water removes other soluble excretory products along with it.
Excess common salt needs to be removed from the body to maintain osmolarity of blood.
2. Give two examples of the following.
Nitrogenous waste
Ans: Urea and Uric acid
Bile pigment
Ans: Bilirubin and Biliverdin
Main excretory system
Ans: Kidney and Ureters
Accessory excretory system
Ans: Lungs and Liver
Water-soluble vitamins
Ans: Thiamin and Riboflavin
Progress Check
1. Name the following.
The tube rising from the notch of the kidney on the median side and connecting behind the urinary bladder.
Ans: Ureters
The tube that passes the urine to the outside of the body.
Ans: Urethra
The inner lighter region of the kidney.
Ans: Renal Medulla
Knot like mass of the blood capillary inside the Bowman’s capsule.
Ans: Glomerulus
The structural and function unit of the kidney.
Ans: Nephron
The blood vessel which
Enters the malpighian capsule
Ans: Afferent Arteriole
Leaves the malpighian capsule
Ans: Efferent Arteriole
2. Given is a jumbled list of the parts of a certain body structure- Loop of Henle, Bowman’s capsule, distal convoluted tubule, glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule.
Name the structure to which the listed parts belong.
Ans: Kidney
Rearrange the parts in their proper sequence from the starting point to where they end.
Ans: Proper Sequence of the parts.
Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, Loop of Henle, proximal convoluted tubule, distal convoluted tubule.
Progress Check
1. State if the following statements are true or false.
The blood flows through glomerulus under great pressure.
Ans: True
Explanation: The efferent arteriole is less wider than the afferent arteriole. The blood flowing through afferent arterioles is under great pressure and the resistance to blood flow is less.
Glomerular filtrate consists of many substances such as water, salts, glucose and white blood corpuscles.
Ans: True
Explanation: Glomerular filtrate consists of many substances such as water, salts, glucose and white blood corpuscles for reabsorption (by renal tubules) and it does not contain proteins and fat molecules due to their large size.
Sodium chloride contained in glomerular filtrate is fully reabsorbed in the renal tubule.
Ans: False
Explanation: Sodium chloride contained in glomerular filtrate is not fully reabsorbed in renal tubule. Some amount is excreted in urine.
The blood flowing through the renal artery is oxygenated and contains a lot of nitrogenous waste.
Ans: False
Explanation:Renal artery transports oxygenated blood to the kidney. The oxygenated blood contains nutrients and minerals, and also nitrogenous wastes.
The blood flowing through the renal vein is oxygenated and normally does not contain nitrogenous waste.
Ans: False
Explanation: Deoxygenated blood leaves the kidney by left and right renal vein and renal vein, do not contain nitrogenous waste.
Excessive uric acid may produce kidney stones.
Ans: True
Explanation: When excess uric acid accumulates in the kidney, it crystallizes and settles in different parts of the body such as joints and kidneys. In kidneys, these stones are called Kidney stones.
A. Multiple Choice Type
1. Excretion primarily involves
Removal of all byproducts during catabolism
Removal of byproducts during anabolism
Removal of nitrogenous wastes
Throwing out excess water
Ans: (c) Removal of nitrogenous wastes
Explanation: Excretion is defined as the removal of unwanted and harmful substances from the body to maintain homeostasis. Some unwanted substances are the byproducts of cellular respiration and metabolic reactions such as nitrogenous wastes - Urea, Ammonia and uric acid.
2. Maximum amount of water from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in.
Proximal convoluted tubule
Descending limbs of loop of Henle
Ascending limb of loop Henle
Distal convoluted tubule
Ans: (a) Proximal convoluted tubule
Explanation: Proximal convoluted tubule reabsorbs 70% of glucose and minerals along with water and the remaining amount is reabsorbed in Loop of Henle’s.
3. Which one of the following is not an excretory activity ?
Giving out carbon dioxide
Passing out faecal matter
Sweating
Removal of urea
Ans: (a) Giving out carbon dioxide
Explanation: Carbon dioxide is a byproduct of cellular respiration, not a part of excretory activities. Thus, giving out carbon dioxide is not an excretory activity.
4. In human, urea is formed in the
Ureter
Liver
Spleen
Kidney
Ans: (b) Liver
Explanation: Urea is the nitrogen waste created by the liver from dead protein present in other cells. Urea is highly poisonous for our body, so can not be stored in our body.
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Name the following.
The outer region of the kidney containing the Bowman’s capsule.
Ans: Renal Cortex
The tuft to capillaries inside the Bowman’s capsule
Ans: Glomerulus
The part of kidney tubules where the term urine is first used for the fluid in it.
Ans: Collecting duct
The organ which filters urea.
Ans: Kidneys
The organ through which urea is released outside the body of a human being.
Ans: Ureters
The specific pigment found in urine.
Ans: Urochrome or Urobilin
2. Given below are two sets (a and b) of five terms each. Rewrite the terms in their correct order so as to be in logical sequence.
Afferent arteriole, renal vein, capillary network, glomerulus, efferent arteriole.
Ans: Correct Sequence-
Afferent arteriole, glomerulus, efferent arteriole, capillary network, renal Vein.
Renal artery, urethra, ureter, kidney, urinary bladder.
Ans: Correct Sequence-
Renal artery, kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra.
3. In each of the following sets of body parts or substances or processes, pick out the one item which overall includes the remaining four .
Glomerular filtrate, Bowman’s capsule, ultrafiltration, glomerulus, blood
Plasma.
Ans: ultrafiltration
Explanation: Ultrafiltration is the process of filtration of the liquid part of blood flowing through afferent arteriole into glomerulus due to high hydrostatic pressure because of narrower width of efferent arterioles as compared to afferent arterioles.
During ultrafiltration, blood plasma (including glucose, amino acids, minerals and water) comes out of Bowman’s capsule and enters in renal tubules. This fluid is called glomerular filtrate.
Skin, liver, lungs, kidneys, excretion.
Ans: excretion
Explanation: Excretion is defined as the removal of unwanted and harmful substances from the body to maintain homeostasis. Skin, liver, kidney and lungs are the excretory org
ADH, water, pituitary, osmoregulation, urine.
Ans: osmoregulation
Explanation: Osmoregulation is the process by which amount of water and minerals is maintained to regulate the osmotic pressure of the blood.
When blood volume decreases, it activates the osmotic receptors which in response send signals to the pituitary to initiate the secretion of ADH (Antidiuretic hormone). The ADH act in distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct, responsible for facilitating conditional reabsorption of water, resulting in formation of concentrated urine.
\[CO_{2}\], bile pigments, water, excretion, urea
Ans: Excretion
Explanation: - Excretion is defined as the removal of unwanted and harmful substances from the body. The unwanted substances are the byproducts of cellular respiration and metabolic reactions such as Bile pigments are formed by rapture of dead RBCs, \[CO_{2}\] and water is a byproduct of cellular respiration and Urea is formed when dead proteins are digested.
4. Name the diseases caused due to the following abnormal constituents in urine.
Abnormal constituents Diseases
Blood _________
Glucose _________
Albumin _________
Bile pigments _________
Ans:
Abnormal Constituents Diseases
Blood Haematuria
Glucose Glycosuria
Albumin Albuminuria
Bile pigments Hepatitis
Explanation: The excess amount of urea in blood caused Haematuria.
The excess amount of Glucose in blood causes glycosuria.
The excess amount of albumin in blood causes albuminuria.
The excess amount of bile pigment in blood causes hepatitis .
C. Short Answer Type-
1. Write down the functional activity of the following parts.
Glomerulus
Ans: Glomerulus is a structure primarily involved in the ultrafiltration process. The blood plasma is filtered from the glomerulus.
Collecting duct
Ans: Collecting duct is a twisted tube like structure which concentrates urine when required and collects urine from nephron tubular structure and passes into renal pelvis and ureter.
Ureters
Ans: Ureter is a tube-like structure, carries urine to the urinary bladder for temporary storage.
Vasa recta
Ans: Vasa recta transports nutrients and oxygen to the medullary nephron segments. They also remove the water and solute, maintaining osmolarity of the blood.
Urethra
Ans: Urethra passes the urine out of the body and this process is called Micturition.
2. Match the items in Column I with those in Column II and write down the matching pair.
Column I | Column II |
(a) Bowman’s capsule | (i) Renal Artery |
(b) Contains more \[CO_{2}\] and less urea | (ii) Regulates amount of water excreted |
(c) Antidiuretic Hormone | (iii) Renal Veins |
(d) Contains more urea | (iv) Glomerulus |
Ans:
Column I | Column II |
(a) Bowman’s capsule | (iv) Glomerulus |
(b) Contains more \[CO_{2}\] and less urea | (iii) Renal Veins |
(c) Antidiuretic Hormone | (ii) Regulates amount of water excreted |
(d) Contains more urea | (i) Renal Artery |
3. Fill in the blanks in the following passage to make it a meaningful description.
In a nephron, __________ flows through the ________ under great pressure.
The reason for this great pressure is that _________ (outgoing) ___________ is narrower than the ___________ (incoming). This high pressure causes the _________part of the blood to filter out from the _________ into the ___________ capsule.
Ans: In a nephron, blood flows through the glomerulus under great pressure.
The reason for this great pressure is that the efferent (outgoing) arteriole is narrower than the afferent arteriole (incoming). This high pressure causes the fluid part of the blood to filter out from the glomerulus into the renal capsule.
4. Name the following.
Three nitrogenous wastes of our body.
Ans: Urea, Uric acid and Ammonia
Three organic wastes of our body.
Ans: Creatinine, Urea, Uric acid
Three inorganic wastes of our body.
Ans: Calcium, Ions, Salt (NaCl)
Three main parts of our urinary system.
Ans: Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder
Six main parts of nephrons.
Ans: Glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, Proximal convoluted tubule, Loop of Henle, Distal convoluted tubule, Collecting duct
Three stages of urine formation.
Ans: Ultrafiltration, Reabsorption, Tubular secretion
Three types of fluids in different parts of a nephron.
Ans: Glomerular filtrate, Glomerular filtrate with glucose and Salt, Urine
5. Choose the odd one out in each of the following sets and write the category for the remaining terms.
Kidney, ureter, neuron, urethra, urinary bladder
Ans: The odd one- Neuron
Explanation: Kidney, ureter, urethra and urinary bladder are the part of excretory system, play crucial role in removing excretory substances from our body such as urea, uric acid etc.
Ammonia, urea, excess sodium chloride, uric acid
Ans: The odd one- Excess sodium chloride
Explanation: Ammonia, urea and uric acid are nitrogenous waste whereas sodium chloride is a salt.
Cortex, medulla, loop of Henle, hilum
Ans: The odd one- Loop of Henle
Explanation: Cortex, Medulla and hilum are the part of the kidney whereas Loop of Henle is a tubular part of nephron.
Glomerulus, collecting duct, papilla, Bowman's capsule
Ans: The odd one- Papilla
Explanation: Glomerulus, collecting duct and Bowman's capsule are the part of nephron (Internal functional unit of kidney) whereas papilla is part of kidney.
6. Write full forms of the following abbreviations.
PCT. ……………………….
Ans: PCT- Proximal convoluted tubule
DCT. ……………………….
Ans: DCT- Distal convoluted tubule
ADH. ……………………….
Ans: ADH- Antidiuretic hormone
ORS. ……………………….
Ans: ORS- Oral rehydration solution
7. Write the exact location of each of the following.
Kidney
Ans: Kidney is located on either side of the backbone and protected by the two ribs.
Uriniferous Tubule
Ans: Uriniferous tubules are also called nephrons. These are tubular structures present inside the kidney, known as the structural and functional unit of kidney.
Malpighian Capsule
Ans: Malpighian Capsule is located in the kidney, comprises of Bowman’s capsule and Glomerulus.
Loop of Henle
Ans: Loop of Henle is the tubular part of nephron, found in cortical region of kidney and comes back medullary region extent in convoluted tubular part.
D. Descriptive Questions
1. Define the following terms.
Excretion
Ans: Excretion is the process of removal of waste products such as urea, uric acid and excess salts from the body to maintain the homeostasis.
Kidney
Ans: Kidney is a paired, bean shaped organ located in the backbone and protected by two ribs. It performs major functions in the reabsorption of water and minerals from filtrate and in the formation of urine.
Micturition
Ans: Micturition is the process by which urine is passed out by the urethra to outside of the body.
Osmoregulation
Ans: Osmoregulation is the process which maintains the osmotic concentration of water and salts in the blood.
2. Differentiate between the following pairs of terms.
Bowman's capsule and Malpighian capsule (structure)
Ans:
Bowman's Capsule | Malpighian Capsule |
Bowman’s capsule is a cup-shaped thin walled structure which comprises the tuft of blood vessels to facilitate blood filtration. | Glomerulus (Tuft of blood vessels) along with Bowman’s capsule together known as Malphigian capsule. |
Diuresis and Uremia (cause and problem)
Ans:
Diuresis | Uremia |
Diuresis is defined as the frequently passing out urine. Diuresis occurs due to less secretion of ADH which facilitates reabsorption of water from the tubular region of nephron. | The accumulation of urea in the body is called uremia. Urea is an excretory product, harmful to the body. Uremia is caused due to inability of the kidney to excrete urea from the body. |
Renal cortex and Renal medulla (location and appearance)
Ans:
Renal cortex | Renal medulla |
Renal cortex is the outer darker region of the kidney. | Renal medulla is the inner lighter region of the kidney. |
Renal pelvis and Renal papilla (structure)
Ans:
Renal Pelvis | Renal Papilla |
The front end of the ureter is somewhat extended into the kidney, called renal pelvis (Basin). | The medulla is composed of finely striped substances in several conical pyramids. The apex of these pyramids is called renal papilla, projected into the pelvis of the kidney. |
Urea and Urine
Ans:
Urea | Urine |
Urea is a chief excretory product, produced by liver. | Urine is left out filtrate containing 95% of water and 5% of solid waste. It is produced after reabsorption and tubular secretion from nephron. |
Excretion and secretion (utility)
Ans:
Excretion | Secretion |
Excretion is the removal of the waste product (specially nitrogenous wastes) from the body to maintain homeostasis. | Secretion helps in the passage of substances such as potassium and large numbers of foreign chemicals and drugs in the forming urine. |
3. Give Reason/Explain.
Excretion is a necessary process of our body.
Ans: Excretion is a crucial process by which our body eliminates waste products from the body because the accumulation of waste products causes discomfort and various diseases which disturbs the homeostasis of our body. For example- Bilirubin and Biliverdin are the byproducts of ruptured RBCs. The accumulation of Bilirubin and Biliverdin causes Jaundice.
If we donate one kidney to a needy patient, would it cause any harm to us?
Ans: Kidney is a paired bean shaped structure, located on the dorsal surface of the abdominal cavity. It filters our blood and forms urine. Thus, if we donate our one kidney, our other kidney is sufficient to remove waste from our body.
We urinate fewer times in summer than in winter and the urine passed is generally thicker.
Ans: During Summer, we lose water from perspiration (Sweating) to maintain our body temperature whereas perspiration is negligible during winters. Thus, the kidneys reabsorb more water from the filtrate and urine is thicker during summer as compared to winter.
4. What is a uriniferous tubule? How does it function?
Ans: Uriniferous tubules are tiny and minute, they are so many in number or The kidney is composed of an enormous number of minute tubules called uriniferous tubules of nephrons. These are structural as well as functional units of kidneys.
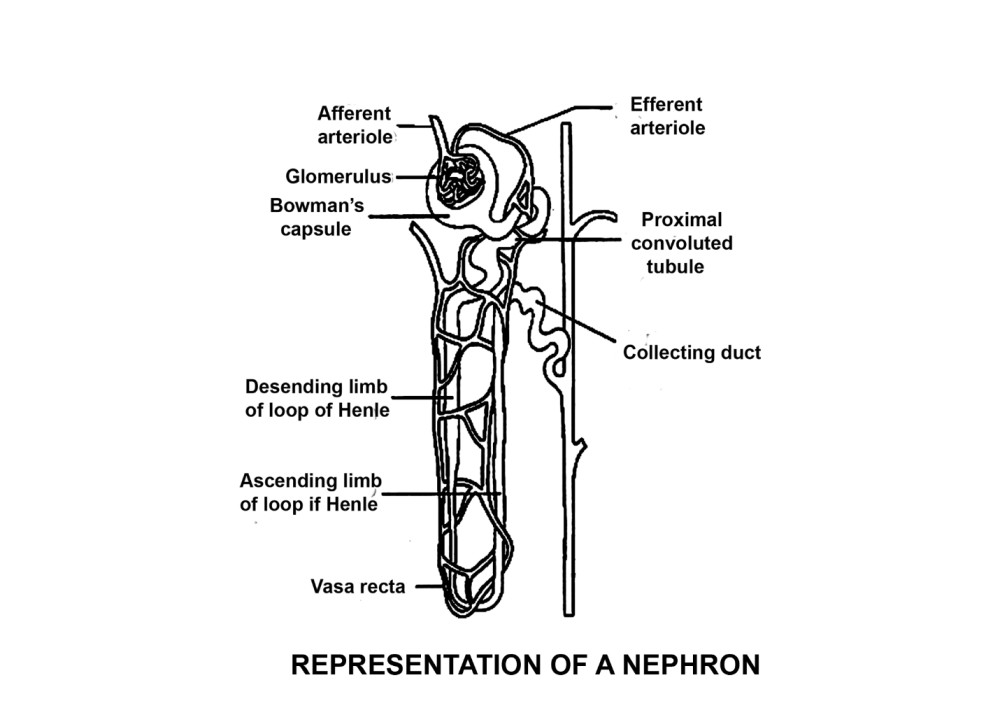
The main components of the nephron - glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tubule.
The glomerulus is the tuft of blood capillaries, containing blood plasma, arises from an afferent arteriole empties into an efferent arteriole. Glomerulus enters Bowman’s capsule, then it extends into highly coiled tubules called PCT.
In Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), the reabsorption of essential substances like glucose, proteins, amino acids, electrolytes and water takes place. PCT selectively secretes ions such as \[H^{+}, K^{+}, and NH_{3}\] into the filtrate and absorbs \[HCO^{3-}\] from it.
Henle’s Loop has a descending and an ascending limb. The descending limb reabsorbs water but does not reabsorbs electrolytes, while the ascending limb reabsorbs electrolytes but not water.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) also secretes ions such as \[H^{+}, K^{+}, and NH_{3}\] into the filtrate and reabsorbs the \[HCO^{3-}\] from the filtrate.
Collecting Duct is a straight tubular region where \[H^{+} and K^{+}\] ions are secreted to maintain osmolarity of the blood. Then, the urine is formed and passed into the collecting duct.
5. Why is it necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration of the blood?
Ans: It is necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration in the body for regulating the percentage of water and salts in blood. If this regulation mechanism fails, we either end up losing vital salts and water or may accumulate unwanted salts and excess water in our body.
6. Explain the terms ultrafiltration and selective absorption.
Ans: Ultrafiltration is the process of filtration of the liquid part of blood flowing through afferent arteriole into glomerulus due to high hydrostatic pressure because of narrower width of efferent arterioles as compared to afferent arterioles.
During ultrafiltration, blood plasma (including glucose, amino acids, minerals and water) comes out of Bowman’s capsule and enters in renal tubules. This is called glomerular filtrate.
Selective absorption - The glomerular filtrate is an extremely dilute solution, containing a lot of useful minerals such as glucose and ions such as sodium. The filtrates pass down to renal tubule and reabsorption of all useful substances occur along with water. This continues till the normal concentration of blood is not distrubed and this is called selective absorption.
7. What is dialysis? Under what conditions is it carried out?
Ans: Artificial kidney is a dialysis machine and removal of unwanted nitrogenous wastes, salts and extra water from specific organs is called dialysis.
In case of failure of both the kidneys dialysis should be carried out in a person.
E. Structured / Application / Skill Type
1. Look at the figure given below. It is a section of the human kidney as seen from the front.
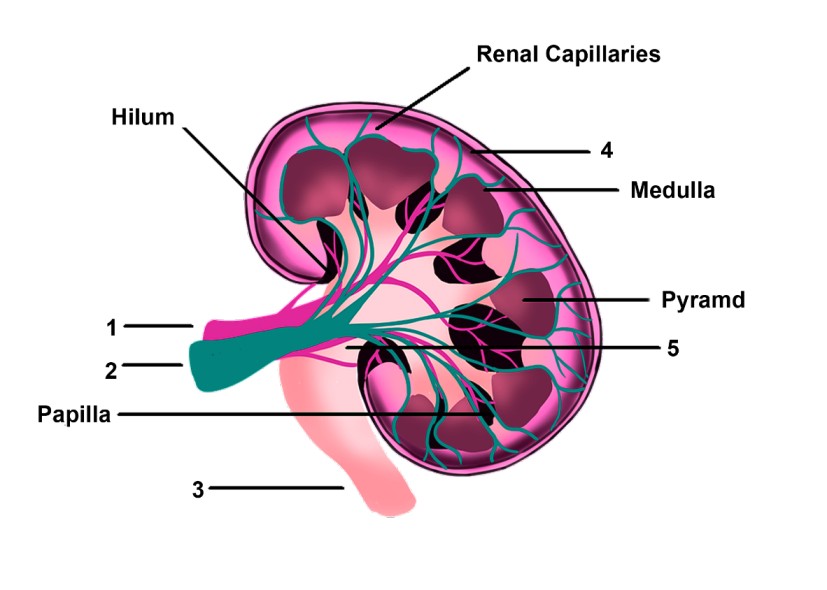
Is it a longitudinal section or a cross-section?
Ans: Longitudinal Section
Name the parts numbered 1-5.
Ans: 1- Renal artery,
2 - Renal vein,
3 - Ureter,
4 - Cortex,
5 - Pelvis
Which area/part (give its name and number given on the diagram) which contains the following.
Malpighian capsule
Ans: No 4- Cortex,
It contains a malpighian capsule which comprises glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule together.
"The pyramids" to The blood vessel with least/no nitrogenous waste
Ans: Medulla
Freshly collected urine
Ans: No 5- Pelvis,
The renal pelvis extends into the ureter on the outside of the kidney. The renal pelvis opens into ureters, and empty into the urinary bladder.
2. Given below is the figure of certain organs and associated parts in the human body. Study the same and answer the questions that follow.
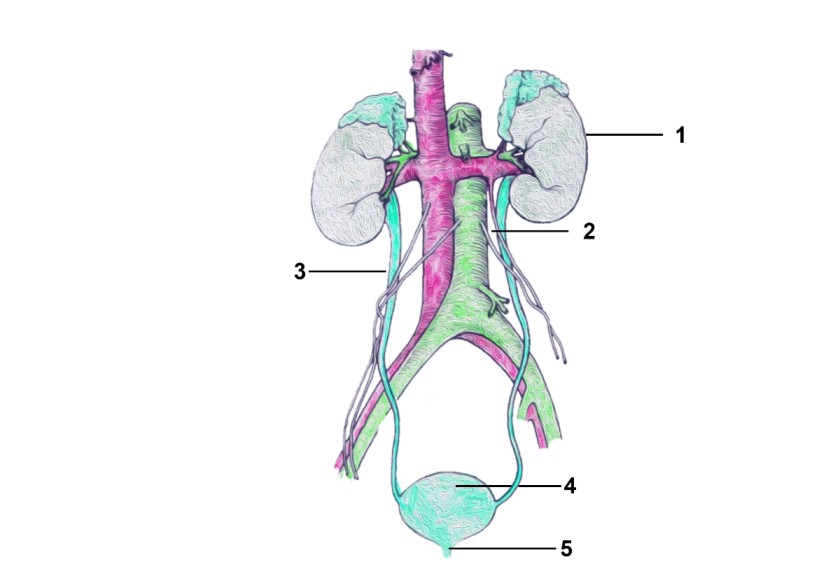
Name all the organ-systems shown completely or even partially.
Ans: Excretory system - completely
circulatory system - partially
endocrine system - Partially
Name the parts numbered 1 to 5.
Ans: 1 - Left Kidney
2 - Aorta
3- Ureter
4- Urinary bladder
5- Urethra
Name the structural and functional unit of the part marked '1'.
Ans: The structural and functional unit of kidney is nephrons which are approx 4.5million in number.
Name the two main organic constituents of the fluid that flows down the part labeled '3'.
Ans: Urea and Creatinine
Name the two major steps involved in the formation of the fluid that passes down the part labeled '3'.
Ans: 1. Ultrafiltration
2. Reabsorption
3. The following diagram represents a mammalian kidney tubule (nephron) and its blood supply.
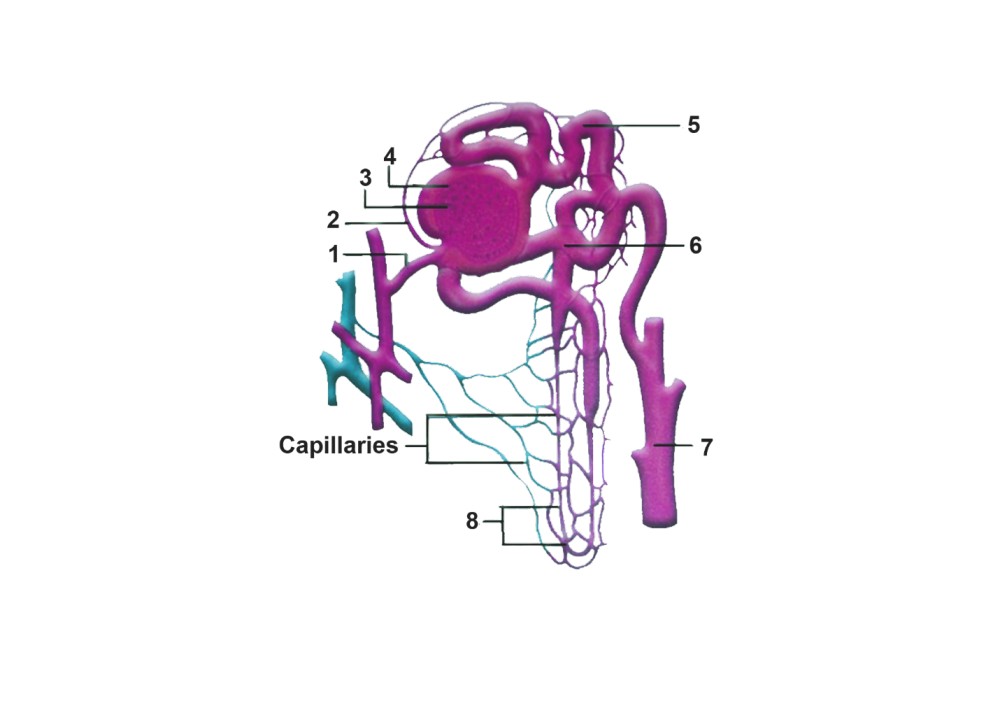
Parts indicated by the guidelines 1 to 8 are as follows.
Afferent arteriole from renal artery
Efferent arteriole
Bowman's capsule
Glomerulus
Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
Distal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
Collecting tubule
U-shaped loop of Henle
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
Where does ultrafiltration take place?
Ans: 4, Glomerulus
Which structure contains the lowest concentration of urea?
Ans: 2, Efferent Arteriole
Which structure contains the highest concentration of urea?
Ans: 1, Afferent arteriole from renal artery
Which structure (normally) contains the lowest concentration of glucose?
Ans: 7, Collecting tube
Where is most water reabsorbed?
Ans: 5, Proximal convoluted tubule with blood capillaries
State the reason for the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
Ans: The high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus is due to the narrower width of efferent arterioles as compared to afferent arterioles.
Name the part of the nephron which lies in the renal medulla.
Ans: Loop of Henle
4. Given alongside is a simplified diagram of the human kidney cut open longitudinally. Answer the questions that follow.
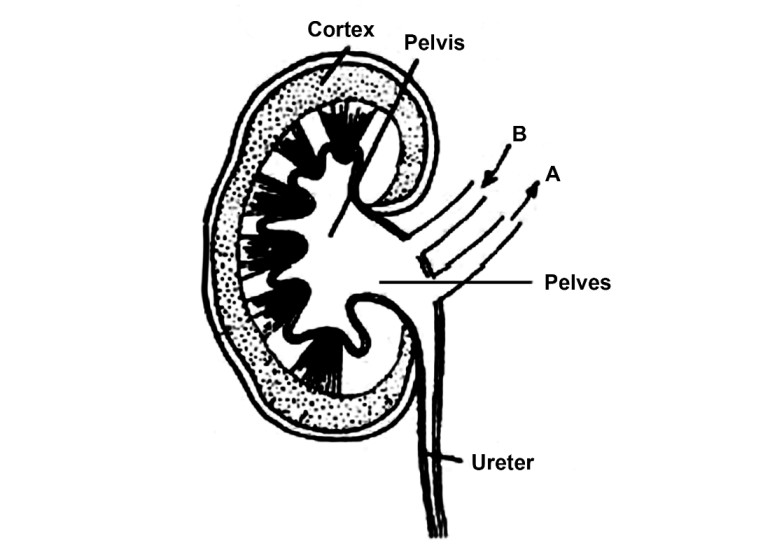
Define Excretion.
Ans: Excretion is defined as the removal of unwanted and harmful substances from the body to maintain homeostasis. Some unwanted substances are the byproducts of cellular respiration and metabolic reactions such as nitrogenous wastes - Urea, Ammonia and uric acid
Why does the cortex of the kidney show a dotted appearance?
Ans: The cortical region of the kidney contains nephrons which are approximately 4.5 million. These nephrons are responsible for the dotted appearance of the cortex of the kidney.
Why does the medulla of the kidney show a striped appearance?
Ans: The medullary of the kidney contains conical pyramids due to which it shows striped appearance.
Write two differences in the composition of the blood flowing through the blood vessels, 'A' and 'B'.
Ans: The blood vessel ‘A’ is a renal vein, containing deoxygenated blood with low concentration of nitrogenous waste such as urea and minerals such as glucose. Whereas the blood vessel ‘B’ is the renal artery. It contains oxygenated blood with high concentration of urea and glucose.
5. Study the diagram given alongside and then answer the questions that follow.

Name the region in the kidney where the above structure is present?
Ans: Bowman’s Capsule
Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, and 4.
Ans: 1 - Afferent arteriole
2 - Glomerulus
3 - Bowman's capsule
4 - Efferent arteriole
Name the stages involved in the formation of urine.
Ans: The two stages are involved in the formation of urine -
1. Ultrafiltration
2. Reabsorption
What is the technical term given to the process occurring in 2 and 3? Briefly describe the process.
Ans: The process occurring in 2 and 3 is known as ultrafiltration.
Ultrafiltration is the process of filtration of the liquid part of blood flowing through afferent arteriole into glomerulus due to high hydrostatic pressure because of narrower width of efferent arterioles as compared to afferent arterioles.
During ultrafiltration, blood plasma (including glucose, amino acids, minerals and water) comes out of Bowman’s capsule and enters in renal tubules. This fluid is called glomerular filtrate.
About Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system is available now at Vedantu. With a thorough understanding of the subject, experts at Vedantu provide a detailed guide for the study of ICSE Class 10 Selina Solutions that allows the students to prepare for their upcoming Class 10 board exams and ace the exam with the best marks. Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system is our choice of best study solution which is recommended to all the students without fail as it helps them understand concepts without any doubts remaining.
Key points to Be Noted of Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory System:
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system tends to have some features that make it studying a bit easier than other references books and these points can be provided as follows:
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system provides a change in the traditional problem-solving skills.
Gives a distinct difference between the relevant and irrelevant questions which means you can filter out those that are not as necessary.
Tables to compare difficult terms and their meanings are provided in a structured manner.
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system
1. According to Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system what does dialysis mean and under what conditions is it done?
According to Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system via Vedantu, dialysis is a process where the artificial kidney functions are performed by a machine. The patient's blood is led from the radial artery to his arm through the machine in which the Urea and the excess salts are removed and the purified blood is then sent back to the body with the help of a vein in the same arm. Here only the waste is removed and the useful nutrients are left behind. Such a process is performed only when there is permanent damage observed in the kidneys. This process is conducted for about twelve hours a week.
2. Why does the diagram or images in Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system help in studying effectively?
The diagram or the images included in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system are in line with the content provided and the explanation given in the solution. This allows the students to both reads and perceives how it actually seems like in reality. This makes the studying process a bit more interesting than the usual way of studying. The usage of colors in between the completely black and white text also helps the students bring about a change in the view. It also helps increase the concentration span of the students.
3. What are the main subtopics included in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system?
The main subtopics that are included in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system can be provided as follows:
Excretion in the human system and other organisms
A detail about the substance that is eliminated and what remains behind
The excretory organs that help with the process
Kidneys
Constituents of urine and what is harmful
Regulation of urine output
Osmoregulation
Artificial kidney and the concept of dialysis in humans due to kidney damage
All of these topics clustered in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system via Vedantu provides a detailed explanation of how excretory systems work in the human body.
4. How many questions are there for each type of question in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system?
Depending on the type of question there are a various number of questions involved and a detailed list of the same can be provided as follows:
Multiple choice question: 4
Very short answer type questions: 3
Short answer type questions: 10
Long answer questions: 3
Application-based or structure questions: 6
Practicing all these questions based on their types and numbers given students can achieve a high level of practice that provides them with immense knowledge regarding the topics that are involved. These also help the students prepare for their Class 10 exams along with other competitive exams that involve biology as one of the main subjects.
5. Why is it easier for students to score with the help of Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system rather than just reading the NCERT textbook?
Just reading the NCERT textbooks will provide a lot of information on a single page which does not help the students understand everything. Instead of using the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 9 - The Excretory system via Vedantu, students get segregated and properly segmented details on the subtopics that are included. The way the questions and the answers are structured takes the level from an easy one to a difficult one which will gradually help students improve their level of skills.







































