ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 2 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Updated ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 2 - Structure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle and Cell Division Selina Solutions are provided by Vedantu in a step-by-step method. Selina is the most famous publisher of ICSE textbooks. Studying these solutions by Selina Concise Biology Class 10 Solutions which are explained and solved by our subject matter experts will help you in preparing for ICSE exams. Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions can be easily downloaded in the given PDF format. These solutions for Class 10 ICSE will help you to score good marks in ICSE Exams 2024-25.
The updated solutions for Selina textbooks are created in accordance with the latest syllabus. These are provided by Vedantu in a chapter-wise manner to help the students get a thorough knowledge of all the fundamentals.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 10 Biology Chapter No. 2 - Structure of Chromosomes, Cell cycle and Cell division
Progress check
Fill in the blanks
1. Chromatin fiber is made up of DNA & ______
Ans: Chromatin fiber is made up of DNA & Histones.
DNA contributes approximately 40% & Histones contributes approximately 60% in the formation of chromatin fiber.
2. The two sister chromatids of a chromosome are attached to each other at _____
Ans: The two sister chromatids of a chromosome are attached to each other at centromere.
The centromere appears as a small constricted region in the chromosome & serves as the point of attachment for the spindle fibers.
3. The structure of DNA was discovered by ______
Ans: The structure of DNA was discovered by Watson & Crick.
4. The three components of nucleotide are _____, _____ & _____
Ans: The three components of nucleotide are phosphate, sugar & nitrogenous Base. Each DNA strand consists of repeating units of nucleotides only.
5. DNA strands wound around a histone octamer forms a complex called a ______
Ans: DNA strands wound around a histone octamer forms a complex called a nucleosome.
A nucleosome is the fundamental unit of chromatin, which consists of a section of DNA wrapped around histone octamer proteins. One can imagine each nucleosome as a football around which a long rope with a one or two loop is wounded.
6. A specific sequence of nucleotides on a chromosome constitutes a ______
Ans: A specific sequence of nucleotides on a chromosome constitutes a gene. Genes act as the unit of heredity.
A. Multiple Choice Type
1. The chromatin material is formed of
(a) DNA only (b) DNA and Histones (c) Histones only (d) Nucleotides
Ans: Correct answer is (b) DNA and Histones.
DNA contributes approximately 40% & Histones contributes approximately 60% in the formation of chromatin fiber.
2. The term “chromosomes” Literally means
(a) Inherited bodies (b) Twisted thread (c) Coloured bodies (d) Shining threads
Ans: Correct answer is (c) Coloured bodies
The term “chromosomes” is made up of two words (chroma= coloured, soma=body).
3. The number of Chromosomes in a certain type of cell division is halved. This kind of cell division occurs in.
(a) Only testis (b) only ovary (c) both ovary and testis (d) all body cells
Ans: Correct answer is (C). Cell division in which no. of the chromosomes remain half occurs in both ovary and testis.
This kind of cell division is mainly named as meiosis that plays a very important role in the process of reproduction.
4. In which one of the following options the stage of mitosis have been given in the correct sequence?
(a) Prophase, metaphase, telophase, anaphase
(b) Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
(c) Anaphase, telophase, prophase, metaphase
(d) Telophase, anaphase, prophase, metaphase
Ans: Correct answer is (b). The correct sequence of mitosis is Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase.
Mitosis is the kind of cell division which mainly occurs in the vegetative or the somatic cells. The purpose of the mitosis is the growth, repair & the replacement of worn out cells.
5. Synthesis phase in the cell is called so for the synthesis of more of
(a) RNA (b) RNA and proteins (c) DNA (d) Glucose
Ans: Correct answer (c). Synthesis phase in the cell is called so for the synthesis of more DNA. It ensures the equal distribution of genetic material among the daughter cells.
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Name of the following-:
a) The repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise.
Ans: The repeating components of each DNA strand lengthwise is called a nucleotide.
The three components of nucleotide are phosphate, sugar & nitrogenous base.
b) The complex Structure consists of DNA Strand and a core of histones.
Ans: The complex Structure consists of DNA Strand and a core of histones is called nucleosomes.
One can imagine each nucleosome as a football around which a long rope with a one or two loop is wounded.
c) The type of bond which joins the Complementary nitrogenous bases
Ans: The type of bond which joins the Complementary nitrogenous bases is the hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for providing stability to the DNA.
d) The three components of a nucleotide
Ans: Nucleotides consist of phosphate, sugar & nitrogenous base. Each DNA strand consists of repeating units of nucleotides only.
2. Imagine one cell (A) has undergone one mitotic division and another cell (B) has completed its meiotic division. How many cells would the two produce?
Cell A: _________ Cell B: _________
Ans: Cell A - two cells
Cell B - four cells
This is because mitosis is the equational division that undergoes single nuclear division after the chromosomal duplication & ultimately leads to the production two daughter cells while meiosis is the reductional division that undergoes two nuclear division after the completion of chromosomal duplication & ultimately leads to the production of four daughter cells.
3. Match the events given in column A with the phase in mitotic cell division in column B.
Column A | Column B |
a) Chromosome get arrange in a horizontal plane at the equator | Anaphase |
b) Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite pole of spindle | Prophase |
c) Chromosomes become visible as fine long threads. | Telophase |
d) Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually transform into chromatin networks. | Metaphase |
Ans:
Column A | Column B |
a) Chromosome get arrange in a horizontal plane at the equator | Metaphase |
b) Daughter chromosomes move to the opposite pole of spindle | Anaphase |
c) Chromosomes become visible as fine long threads. | Prophase |
d) Chromosomes lose their distinctiveness and gradually transform into chromatin networks. | Telophase |
Concept:
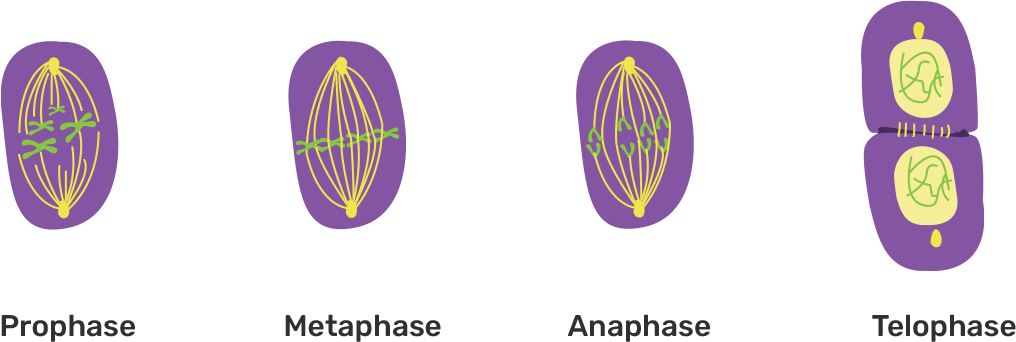
4. Fill in the blanks
a) DNA replicates in the _________ of the cell cycle.
Ans: DNA replicates in the S-phase of the cell cycle.
b) Mitosis occurs in our _________ cells.
Ans: Mitosis occurs in our somatic/vegetative cells.
It is mainly involved in growth, repair & the replacement of worn out cells.
c) Meiosis occurs only in _________ cells.
Ans: Meiosis occurs only in reproductive cells.
It plays a very important role in the gamete production.It is the reductional division that undergoes two nuclear divisions after the completion of chromosomal duplication. This ultimately produces four daughter cells or gametes.
d) Modern humans have 46 chromosomes. Their sperms and eggs will have _________ chromosomes each.
Ans: Modern humans have 46 chromosomes. Their sperms and eggs will have 23 chromosomes each.
This is because during gamete formation meiosis occurs. It is the reductional division that undergoes two nuclear divisions after the completion of chromosomal duplication & ultimately results in four daughter cells that are haploid(n) in nature.
e) During the pairing of chromosomes in meiosis, the _________ chromosomes come to lie side by side.
Ans: During the pairing of chromosomes in meiosis, the homologous chromosomes come to lie side by side.
f) The two non-sister chromatids of a paired chromosome are attached to each other at …………..during the process of crossing over
Ans: The two non-sister chromatids of a paired chromosome are attached to each other at chiasma during the process of crossing over.
Chiasma is the point of crossing over an X shaped structure formed due to crossing over between the non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes.
C. Short Answer Type
1. What is the difference between chromatin fibre and chromosome?
Ans:
Chromatin | Chromosome |
1. It is thin, long & the uncoiled structure. | 1. It is a thick, compact & ribbon like structure. |
2. It exists as an unpaired structure. | 2. It exists in paired form. |
3. It appears during the interphase of the cell cycle. | 3. It appears during the metaphase as well as the anaphase of the cell cycle. |
2. What are the rungs of the “DNA ladder” Made of?
Ans: The rungs of the “DNA ladder” are made up of nitrogenous bases. There are mainly four types of nitrogenous bases such as A (Adenine) ,T (Thymine) , C (Cytosine) & G (Guanine).
Adenine & Thymine join together by two hydrogen bonds while Guanine & Cytosine join together by three hydrogen bonds.
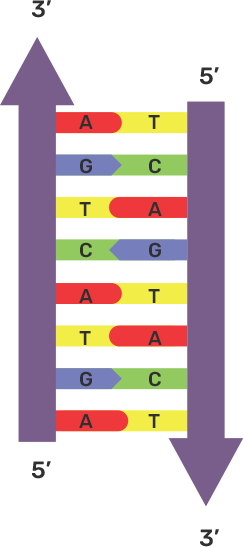
3. Correct the following statement if there is any mistake.
a) The four nitrogenous bases in the DNA are Guanine, Thiamine, Adrenaline and Cytosine.
Ans: The four nitrogenous bases in the DNA are Guanine, Thymine, Adenine and Cytosine.
Adrenaline is the hormone that is released from the adrenal gland. It is mainly released in emergency situations that is responsible for increasing the heart rate as well as the blood pressure etc.
Thiamine or Vitamin B1 is a water soluble vitamin found in many of the natural foods.
b) Genes are specific sequences of bases on a Chromosome.
Ans: Genes are specific sequences of nucleotides on a Chromosome. They act as the unit of heredity.
c) A nucleotide is composed of a sulphate, a sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base.
Ans: A nucleotide is composed of a phosphate, a sugar (pentose) and a nitrogenous base.
d) Nucleosomes are groups of cysteine molecules surrounded by DNA strands.
Ans: Nucleosomes are groups of histone molecules surrounded by DNA strands.
e) If there are 46 chromosomes in a cell there will be 23 chromatin fibre inside the nucleus during interphase
Ans: If there are 46 chromosomes in a cell there will be 46 chromatin fibre inside the nucleus during interphase. Chromosomes are condensed states of chromatin fibres found in the interphase.
D. Descriptive Type
1. Mention whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F). Give reason to support your answer.
(a) As you grow from childhood to adulthood, your skin cells divide only to replace such cells that are lost from the surface. T/F
Ans: This statement is true.
This is because the population of the cells remains constant due to mitotic division. The number of new cells will be equal to the number of dead cells.
(b) A nuclear membrane in a mitotically dividing cell remains intact up to metaphase and disappears only in the telophase. T/F
Ans: This statement is false.
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disappear in prophase, are absent in metaphase and then it is formed in telophase.
(c) Mitotic cell division can be a mode of reproduction. T/F
Ans: This statement is true.
Certain unicellular organisms such as Amoeba reproduce by mitotic division which results in two daughters Amoeba.
(d) Crossing-over between chromatids can occur only between homologous
chromosomes. T/F
Ans: This statement is true.
This is because the homologous pair of chromosomes are one received from the maternal and other from the paternal. They possess the same genes with the same or contrasting traits and are paired up during meiosis to undergo genetic exchange (or crossing over).
2. Define the following terms
a) Chromosome
Ans: It is defined as the thread-like structure of DNA that carries the gene (unit of heredity).
b) Gene
Ans: These are defined as the sequence of nucleotides that are present on the chromosome & responsible for the encoding of protein which are mainly expressed in the form of particular features of an individual
c) Cell division
Ans: It is defined as the process which involves the division of parent cells into two or more daughter cells.
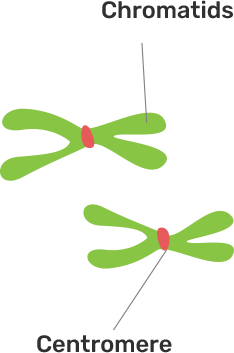
d) Chromatid
Ans: A chromatid is defined as one of the two identical halves of the replicated chromosome.
e) Aster
Ans: It is defined as the star-shaped cluster of microtubules that is radiated from the pericentriolar region found during cell division in animal cells.
3. Give reason
(a) Gametes must be produced by meiosis for sexual reproduction.
Ans: Meiosis is the reductional division that reduces chromosome no. into the half. The main purpose of meiosis is to form gametes, these are the sex cells that fuse together to form diploid individuals.
(b) Why is meiosis referred to as reductional division?
Ans: Meiosis is referred to as reductional division because it reduces the chromosome number into half of the parent cells in the daughter cells.
(c) The children of the same parents, however similar, are different from each other in certain aspects.
Ans: This is because of the generation of variations that occurs due to the crossing over. The process of crossing over occurs during the meiosis and gamete formation in the parents.
4. Distinguish between
Cytokinesis vs Karyokinesis
Ans:
Cytokinesis | Karyokinesis |
1. It is defined as the division of the cytoplasm. | 1. It is defined as the division of the nucleus. |
2. It occurs at the end of telophase as soon as nucleus division completes. | 2. It occurs during the M- phase and is completed by end of telophase |
DNA vs RNA
Ans:
DNA | RNA |
1. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. | 1. RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. |
2. It can replicate itself. | 2. It can’t replicate itself. |
3. Its quantity remains constant in each cell of a species. | 3. Its quantity varied in different cells. |
Nucleosome vs Nucleotide
Ans:
Nucleosome | Nucleotide |
1. DNA strands wound around a histone octamer & form a complex called a nucleosome. | 1. DNA is composed of repeating units of nucleotides that are composed of phosphate, sugar & nitrogenous bases. |
2. It is the fundamental unit of chromatin. | 2. It is the fundamental unit of the DNA strand. |
Centrosome vs Centromere
Ans:
Centrosome | Centromere |
1. It is defined as the region that is located outside the nucleus & major microtubule organising center. | 1. Small constricted region found in the chromosome that serve as a point of attachment of sister chromatids. |
2. Composed of condensed cytoplasm and centrioles that produce spindle fibres during cell division. | 2. They also serve as the point of attachment of spindle fibers during cell division. |
Haploid vs Diploid
Ans:
Haploid | Diploid |
1. It is denoted by (n). | 1. It is denoted by (2n). |
2. It contains only one complete set of the chromosomes. | 2. It contains two sets of the chromosomes. |
5. Enumerate the various changes that occur in the nucleus of the cell during (a) prophase (b) anaphase of mitotic division.
Ans:
Prophase-:
Centrioles move apart and reach the opposite poles.
Chromosomes become distinct.
Chromosomes are already duplicated (S-phase) as paired chromatids.
Sister chromatids are attached to each other at a small constricted region named centromere.
Spindle fibres appear between daughter centrioles & form the achromatic spindle.
The nucleolus & the nuclear membrane disappears during this stage.
Anaphase-:
Centromere attaching the two chromatids divides/splits.
The two sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move towards the opposite poles.
A furrow starts appearing in the cell membrane at the middle in the animal cell, which starts cytokinesis.
6. Name & explain the various stages of cell cycle?
Ans:
Cell cycle-: It is defined as the sequence of events that take place in the process of cell division. It is broadly divided into two stages-:
Interphase: It is the preparatory phase of cell division. No visible change in the chromosome, but active synthesis in the cells. The cell grows to its maximum size.
Prophase: Chromosomes become distinct, duplicated into sister chromatids. Centrioles move apart towards poles and spindle fibres appeared in between the centrioles. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate and disappear.
Metaphase: Each chromosome is attached to the spindle fibres at centromere and aligned at the equatorial region.
Anaphase: Spindle fibres pull apart the attached sister chromatids and split. The two sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move towards the opposite poles. A furrow starts appearing in the cell membrane, which starts cytokinesis.
Telophase: Daughter chromatids separate and reach poles to form two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes are less condensed and form chromatin fibres. Nucleus and nuclear membrane reappear, deepening of cleave furrow between the daughter nuclei.
Cytokinesis: It is the division of the cytoplasm. Cleave furrow deepens and separates the two daughter cells.
E. Structured / Application / Skilled type
1. Given below is a schematic diagram of a portion of DNA.
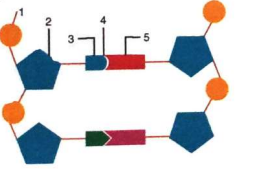
a) How many strands are shown in the diagram?
Ans: Two strands of the DNA are shown in the given diagram.
b) How many nucleotides have been shown in each strand?
Ans: In each strand there are two nucleotides.
c) Name the parts number 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 respectively.
Ans:
Part No. | Part Name |
1 | Phosphate group |
2 | Sugar (Deoxyribose) |
3 | Nitrogenous base ( Thymine and Cytosine) |
4 | Hydrogen bonds |
5 | Nitrogenous base (Adenine & Guanine) |
d) Name the DNA unit constituted by the part 1,2 and 3 collectively.
Ans: Part 1 , 2 & 3 constitute the nucleotides, the basic fundamental unit of DNA strand.
2. The three sketches given below (A, B and C) are intended to represent the replication of DNA. What should be their correct sequence starting with the first and ending with the last?
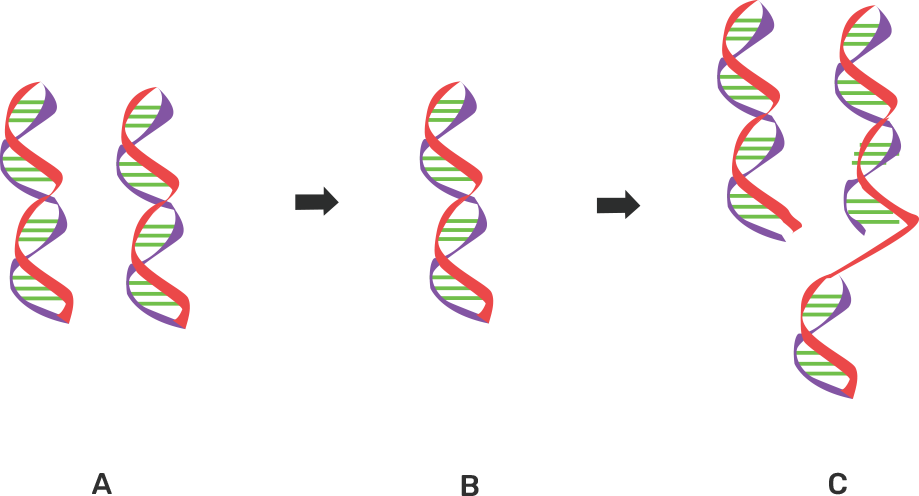
Ans:
DNA replication-: It is defined as the process by which a double stranded DNA gives rise to two identical copies of the DNA.The correct sequence is-:B → C → A
3. The diagram below represents a stage during cell division. Study the same and then answer the questions that follows:
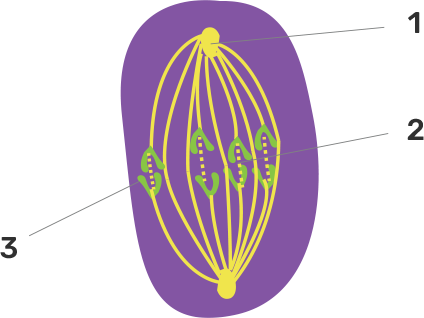
a) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
Ans:
Part No. | Part Name |
1 | Aster (It is defined as the star-shaped cluster of microtubules that is radiated from the pericentriolar region, found in animal cells. |
2 | Spindle fibers (These run in between the two centrioles) |
3 | Chromatid (It is defined as the one of the two identical halves of the replicated chromosome) |
b) Identify the above stage and give a reason to support your answer.
Ans: The stage that is described in the given diagram is of late anaphase of mitosis in an animal cell (no cell wall is there).
The stage can be identified by the following characteristics such as-:
1. Presence of separated chromatids which are found at the opposite poles of the cell.
2. The appearance of the furrow in the cell membrane classifies the given stage as the late anaphase.
c) Mention where in the body this type of cell division occurs.
Ans: This type of cell division occurs in somatic/vegetative cells of the body. The purpose of mitosis is the growth, repair & replacement of worn-out cells.
d) Name the stage prior to this stage and draw a diagram to represent the same.
Ans: The stage that is present prior to this stage is metaphase. Chromosomes are aligned at the equator, attached by the spindle fibres at the centromere in each chromosome. One can represent this stage by the given diagram-:
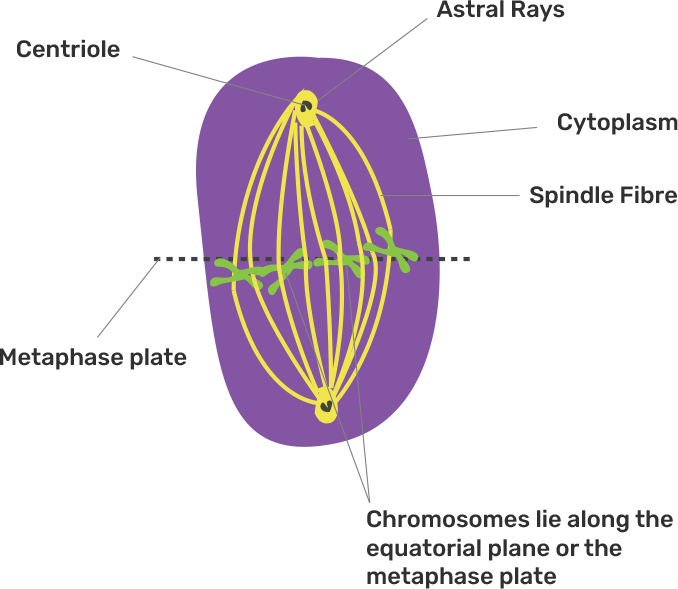
4. Draw a labelled diagram to show the metaphase stage of mitosis in an animal cell having a ‘6’ chromosome?
Ans: It is the stage during which chromosomes lie along the equatorial plane on the metaphase plate. Each chromosome is attached by spindle fibres at the centromere.
5. The diagram below represents a certain phenomenon which occurs during meiosis. Name and explain the phenomenon by using the terms – homologous chromosomes, chromatids, crossing-over.
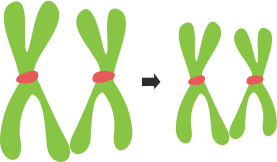
Ans:
In this stage the homologous chromosomes (one from maternal and other from paternal chromosomes) paired. During pairing some segments of chromatids of homologous chromosomes break and rejoin at the point of intersection which is called chiasmata. This causes crossing- over that is defined as the exchange of chromatid material between chromosomes from the parents. It is helpful to produce new combinations of genes & the production of variations.
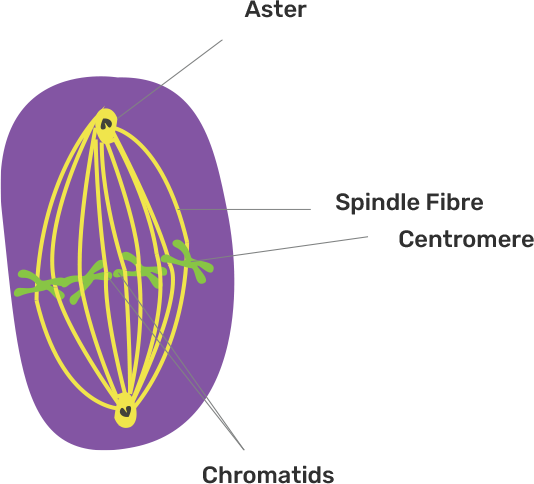
6. Gives below is a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division in an animal cell. Examine it carefully and answer the questions which follow-:
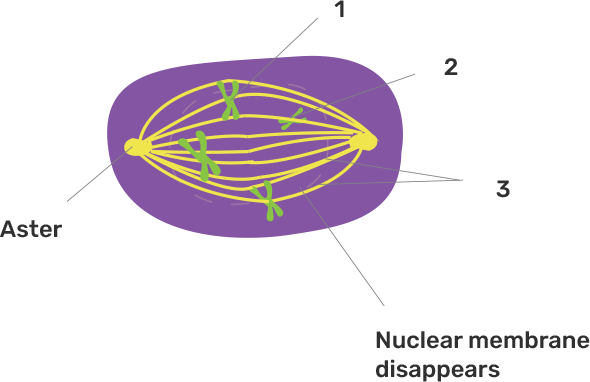
a) Identify the stage. Give one reason in support of your answer.
Ans: The given stage represents the metaphase because the chromosomes are condensed, aligned in the equatorial plate, attaching to the spindle fibres. The nuclear membrane disappears.
b) Name the cell organelle that forms the ‘aster’.
Ans: The cell organelle that forms the ‘aster’ is centrioles.
c) Name the part labelled 1, 2 and 3.
Ans:
Part no. | Part name |
1 | Centromere |
2 | Sister chromatids |
3 | Spindle fibres |
d) Name the stage that follows the one show here. How is that stage identified?
Ans: The given figure represents the metaphase.
It is the stage during which chromosomes lie along the equatorial plane on the metaphase plate.
The stage which follows is Anaphase in which the two sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move towards the opposite poles, pulled by the spindle fibres. A furrow starts appearing in the cell membrane, which starts cytokinesis.
e) Mention two difference between mitosis and meiosis with regard to:
(I) The number of daughter cells produced.
(II) The chromosome number in the daughter cells.
Ans:
Mitosis | Meiosis |
1. During mitosis two daughter cells are produced. | 1. During meiosis four daughter cells are produced. |
2. It is the equational division that the no. of the chromosome is the same as that of the parent cell (2n). | 2. It is the reductional division that is he no. of the chromosome reduced to half (n)at the end of this type of cell division. |
7. Given ahead are three diagrammatic sketches (A, B and C) of one and the same particular phase during mitotic type of cell division.
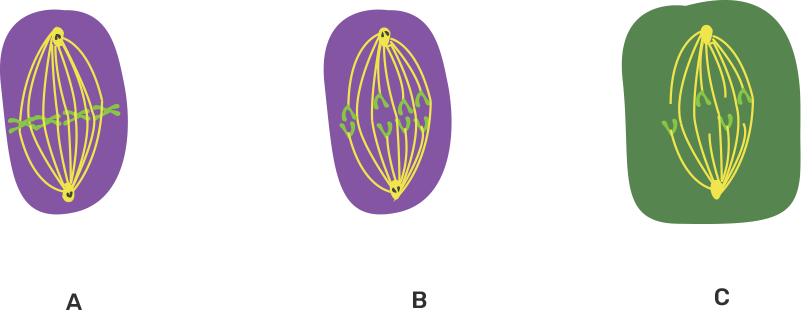
a) Identify the phase ________
Ans: Metaphase
b) What is the diploid number of chromosomes shown in them? ________
Ans: 2n=4
c) Identify whether these are animal cells or plant cells? Give a reason.
A ________, B ________, C ________,
Ans:
Figure A & B - Animal cell
This is because the centrosome has split into two centrioles and the centrioles formed asters. Another reason is that the cell wall is also absent.
Figure C - Plant cell
This is because the centrioles are absent. Another reason is that the cell wall is also present.
8. Shown below are four of the stages (A, B, C, D) (not in sequence) of a certain kind of cell division.
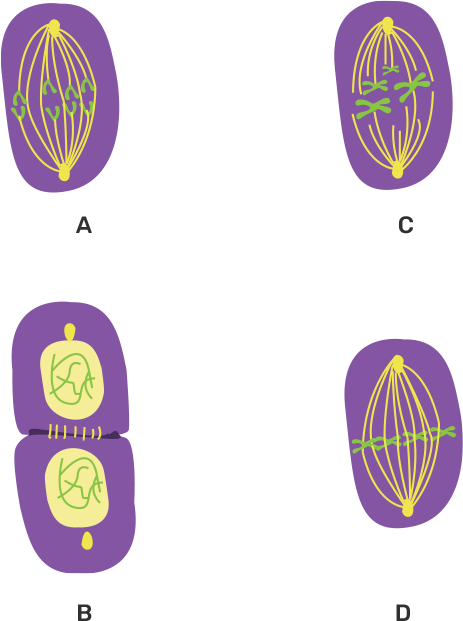
(a) Is it a plant cell or an animal cell? Give two reasons
Ans: The given diagram represents the animal cell because the asters are present here that are usually absent in plant cells.
(b) Is it undergoing mitosis or meiosis?
Ans: It undergoes mitosis (cell division that occurs in somatic /vegetative cells of the body. The purpose of the mitosis is the growth, repair & the replacement of worn out cells).
(c) What should be the correct sequence of these four stages among themselves?
Ans: The correct sequence of these four stages are-: B→C→D→A
(d) Name the stage that should precede the earliest of these stages.
Ans:
Interphase-: It is the preparatory phase of cell division. During this phase there is no division & the cell grows to its maximum size. It generally lasts for 18-20 hours. It further divides into three sub stages that are-:G1-Phase, S-Phase, G2-Phase.
(e) Draw the stages of the name above inside the blank space provided.
Ans: Interphase.
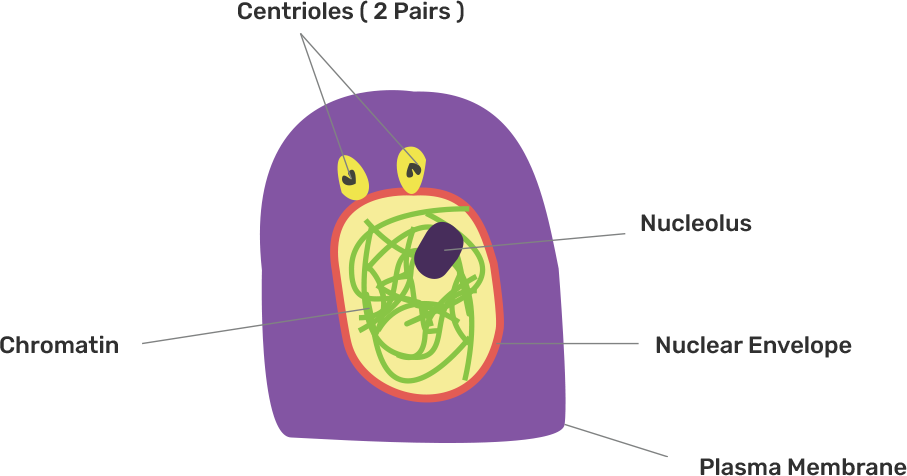
9. Given below is a diagram representing a stage during mitotic cell division. Study it carefully and answer the questions that following-:

(a) Is it a plant cell or an animal cell? Give a reason to support your answer.
Ans: The given figure represents the plant cell as the centrioles are not present.
(b) Identify the stage shown.
Ans: The given figure represents the Late Anaphase stage.
(c) Name the stage that follows the one shown here. How is that stage identified?
Ans: Telophase: Daughter chromatids separate and reach poles to form two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes are less condensed and form chromatin fibers. Nucleus and nuclear membrane reappear, deepening of cleave furrow between the daughter nuclei.
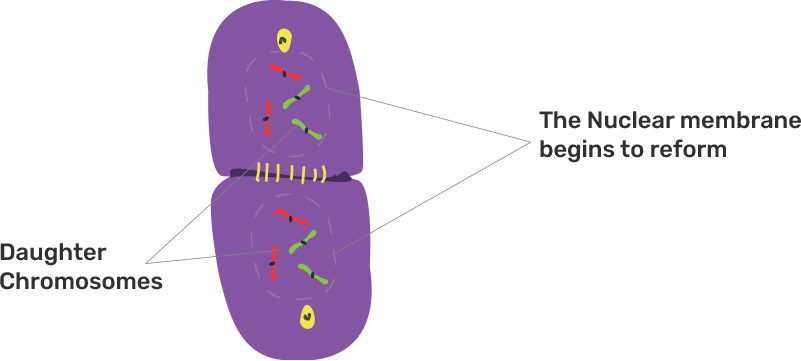
(d) How will you differentiate between mitosis and meiosis on the basis of the chromosome number in the daughter cells?
Ans:
Mitosis | Meiosis |
1. It is the equational division that the no. of the chromosome is the same as that of the parent cell (2n). | 1. It is the reductional division that the no. of the chromosome reduces to half (n) at the end of the cell division. |
(e) Draw a duplicate chromosome and label its parts
Ans: Duplicated chromosome-:
ICSE Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter - 2
The Class 10 Biology chapter 2 - Structure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle and Cell Division consists of a number of subtopics to help you learn more about the unit of life i.e. cell. In this chapter, you will get to know about the chromosomes, genes, DNA, meiosis, and a lot more.
While preparing this chapter, the ICSE Selina solutions will surely come in handy. In this reliable pdf, you will find all the answers you need to prepare for your board exams. Many professionals have worked on these questions and combined them into a single pdf for your convenience. You can download this pdf from the Vedantu website or application free of cost. This pdf makes it easier for you to attempt the exercise questions and enhance your knowledge of the concepts.
Since Biology is an important subject for future examinations, such as NEET, you will need all the available study material for preparations. The detailed answers in this pdf will be enough for you to apprehend a specific topic.
Types of Questions in Class 10 Biology Chapter 2
Here is a brief idea about the types of questions that the students can expect from the chapter:
Multiple Choice Type - 5 Questions
Very Short Answer Type - 4 Questions
Short Answer Type - 7 Questions
Long Answer Type - 5 Questions
Structure/ Application/ Skill Type - 9 Questions
With about 30 questions, solving this exercise would be enough for the revision of this chapter. The exercise asks the most important questions related to Chromosomes, DNA, Genes, etc. You will get to know the difference between chromosomes and chromatid, centrosome and centromere, Aster and spindle fiber, and much more.
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 2 - Structure of Chromosomes, Cell Cycle and Cell Division
1. Where can I get sample papers for ICSE Class 10 Biology?
The best place to look for sample papers of ICSE class 10 Biology is the Vedantu mobile application or site. Here, you will find sample papers as well as previous year question papers of Class 10 biology. As the leading education platform, Vedantu offers these sample papers for free. All you need to do is visit their website, register yourself, and download the study material you require for your exams. This way, you can have lifetime access to these notes, papers, and solutions that will assist you throughout the learning process.
2. Do I have to Attempt all the Exercise Questions?
Yes, it is very important to attempt all the exercise questions. These questions help you in self-assessment and focus on the critical points of the chapter. The exercises play a pivotal role in the preparation for your board exams. When you solve all the questions in the exercise accurately, you can move on to the next chapter. However, if you are having problems in solving a particular problem, you can refer to the Selina Solutions for Class 10 Biology pdf.
3. How do I score well in the ICSE Class 10 Biology Exam?
Since ICSE board exams consist of tough questions, it can be a little challenging to score good marks in a subject. However, whether you obtain a good score or a bad one depends entirely on your understanding of the concepts. The main part of the learning process is to comprehend the topics and have a firm grip on them. For this purpose, you can use all the study material that is easily available and accessible to you. Refer to these resources for answers and solutions, make notes, and make sure to assess yourself once in a while.
4. Are Selina’s Solutions Enough for a Higher Score in Board Exams?
5. How do I find Solutions to Exercise Questions?
Finding solutions to Selina’s textbook questions is much easier than you think. But you must try the questions yourself before taking any help from your teachers or the internet. It will not only help in learning but will also tell you how much you know about the essential concepts of a chapter. If you are having trouble with these questions, then you can refer to the Selina Solutions for ICSE Class 10 biology Chapter 2 pdf as it contains solutions to every exercise problem.







































