




An Introduction to the Phenomenon of Rainbow
One of the most magnificent natural phenomena we are aware of is the rainbow. We frequently stop and stand in awe when they appear in the sky. What, though, is a rainbow? You can learn interesting information about the rainbow, how a rainbow looks, and many other factors here. The rainbows you see in the sky are created by sunlight bouncing off of small water in the air.
The colours you see are produced when sunlight reflects off of these droplets, hitting your eyes at different angles, producing a different colour depending on how much light it received. Rainbows help scientists to understand the sun's role in the earth's climate and its impact on rainfall, temperature, and the oceans' role in climate change.
Rainbow
Now let’s see how does a rainbow actually look like:
Colours and Chrominance of a Rainbow
The spectrum of the rainbow is a mathematical representation of the light passing through a prism, which is split into seven bands, with each band representing a different colour. Most colours in this spectrum can be found in the visible light spectrum.
The colour spectrum of sunlight is in this order, from violet, through blue, green, yellow, orange, and red, to violet again and this is how rainbows work. Each colour has a different wavelength. Depending on the wavelength of light, different colours appear to our eyes.
The process that turns one colour into another is called chrominance. This happens because a wave of light can be split up into different colours. Each colour has its wavelength – a certain distance between each wave crest (or trough).
Spectrum and White Light
It is a prismatic sensation resembling the white light seen in rainbows that come from the sun. It appears as an arc or spectrum of colours (usually between red and violet) caused by sunlight refracted and reflected inside droplets of moisture suspended in the atmosphere.
All the different colours in the rainbow combine to make white light at some point. The part for each colour in a rainbow is called a "wavelength". Sunlight's longest waves are red and its shortest waves are violet. The colour purple does not exist because all the other wavelengths have more energy than violet and cancel it out when they mix to make white light. To get more rainbow information, what is the shape of a rainbow, what is its wavelengths and sunlight, read further!
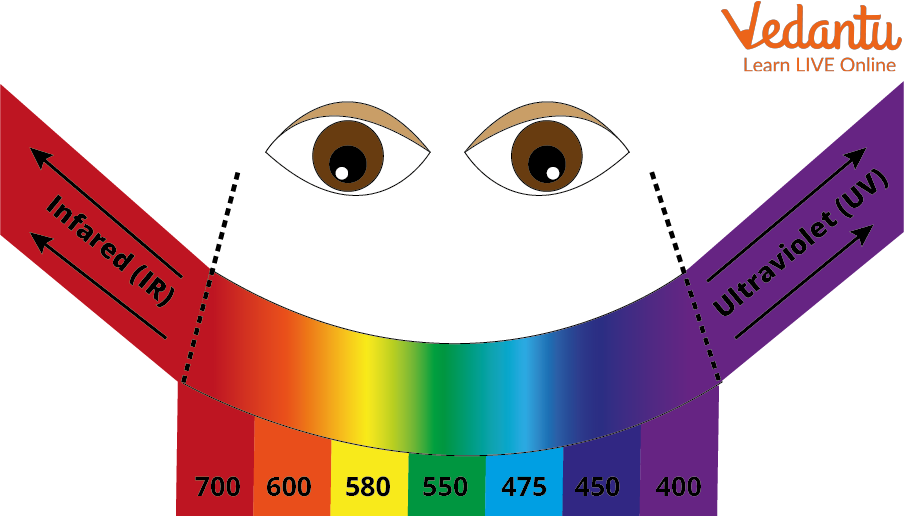
Visible Spectrum to Naked Eye
Sunlight and Wavelengths
Sunlight is composed of light and many parts of it are not visible to the naked eye because their wavelengths are larger than what humans can see. Sunlight has seven colours. Those colours are red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. When sunlight shines through the rain droplets it splits into these different colours. These longer, invisible wavelengths cause some light to be scattered in all directions, including inside the droplet where it will create fringes upon reflection on each surface of the liquid inside it.
Appearances and Shapes of a Rainbow
Rainbows are formed when it rains. A rainbow is most likely to appear in the sky after a clear and sunny day. It happens at the same time every day and it always appears in the same part of the sky. So if you are wondering what a rainbow's shape is, you might want to know that in a rainbow, all colours from red through violet appear at once, ending up as white light. This part of a rainbow is called "the bow". The part that looks like an upside-down bow is "the frame". The part that does not look like a bow but looks like a V is called "the limb".

Image Showing the Sequence of the Seven Colors of the Rainbow
Summary
Rainbows show us that the sun's light is a mixture of many, many different colours because the sun is made up of multiple particles. As you studied and gathered some information about rainbows, we hope now you can answer the question: how does a rainbow look and work? The universe consists of an amazing variety of elements; each one having certain characteristics that make it unique, one of which is the incredible Rainbow!
FAQs on What Does a Rainbow Look Like? Let’s Find out!
1. What is a rainbow?
A rainbow is a beautiful natural phenomenon that appears in the sky as a colourful arc. It is an optical illusion caused by sunlight interacting with water droplets in the atmosphere, most commonly seen after it rains while the sun is still shining.
2. What does a rainbow look like?
A rainbow looks like a large, curved band of light in the sky. It is made up of several distinct colours that are arranged in a specific order, creating a vibrant and colourful display against the clouds or blue sky. Its shape is most often a semi-circle or an arc.
3. What are the seven colours of a rainbow in order?
The seven colours of a rainbow always appear in the same order. A simple way to remember them is with the name ROY G. BIV. The colours are:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
4. How is a rainbow formed?
A rainbow is formed through a process called refraction and reflection. When sunlight enters a tiny, round raindrop, the light bends (refracts). It then reflects off the inside back of the raindrop and bends again as it leaves the drop. This process separates the white sunlight into its different colours, creating the spectrum we see as a rainbow.
5. Where can we usually see a rainbow?
You can usually see a rainbow when the sun is behind you and it is raining in front of you. They often appear during or immediately after a rain shower when the sun comes out. Rainbows are always located in the part of the sky opposite the sun.
6. Why does a rainbow have a curved or arc shape?
The curved shape of a rainbow is due to the way light reflects inside spherical raindrops. The light exits the raindrop at a specific angle (around 42 degrees). Since we see this effect from countless raindrops at once, the collection of light forms a circular arc in the sky. We only see the part of the circle above the horizon, which looks like a bow or arc.
7. Can we ever reach the end of a rainbow or touch it?
No, you can never reach the end of a rainbow or touch it. A rainbow is not a physical object; it is an optical effect that depends on your position relative to the sun and the raindrops. As you move towards it, the rainbow will appear to move away, because its location is always at a specific angle and distance from you.









