




What Are Thermal Conductors? Core Concepts for Students
Temperature is measured as a measure of thermal conductivity in a material. A low thermal conductivity material will transfer heat at a slower rate than a high thermal conductivity material. A metal, for instance, is normally very thermally conductive and efficient at conducting heat, while insulating materials like Styrofoam have the opposite property. The Greek letter "kappa" is often used to represent thermal conductivity. Temperature is measured in watts per meter-kelvin. Meters, watts, and kelvins are all measures of power. Aerogel, Polyurethane, and Vacuum are some effective thermal insulators. Silver, copper, and diamond are effective thermal conductors. In this article, we are going to learn about difference between conductor and insulator and their examples.
What is Conductor?
Electrical conductors are substances or materials that allow electricity to flow. An electrical conductor allows charge carriers, such as electrons or ions, to travel effortlessly between atoms when voltage is applied. The majority of metals, including copper, are regarded as good conductors, whereas nonmetals, or insulators, are regarded as poor conductors. Typically, good conductor of electricity include metals, metal alloys, electrolytes, and even some nonmetals like graphite and liquids like water.
Thermal Conductors
It is called thermal conductors when the material allows heat to pass through very easily. Ideally, metals such as aluminium, copper, steel, and iron conduct thermal energy well. Cooling items or warming them quickly can be accomplished using thermal conductors.
According to thermal conduction theory, molten motion moves across a temperature gradient to transport energy. Energy is transported by convection without involving macroscopic flows or internal stresses producing work, whereas molecular work does.”
What is Insulator?
Insulators are materials that prevent electrons from freely flowing from one particle of an element to another. If we apply some charge to such an element at any point, the charge remains at the original place and does not spread throughout the surface.
Thermal Insulator
A thermal insulator stops heat from flowing from one place to another. The term "thermal insulator" typically refers to a substance that prevents conduction. Conduction occurs when something hot physically contacts something cold. Heat travels from the hot to the cold surface, warming it. To prevent this from happening, you employ a material that heat cannot easily pass through (a thermal insulator).

Thermal Energy Experiment
Cold objects will remain cold for a long time when they're insulated, while hot objects will remain hot for longer when they're insulated.
Wool, plastic, and many fabrics, including wood and plastic, provide good thermal insulation. Materials that keep people warm are thermal insulators. Thermo-insulation materials in everyday life include clothing, carpets, and curtains.
Examples of Conductors and Insulators
Graphite, the human body, and the earth are all excellent electrical conductors. Metals such as copper, gold, and iron are examples of common conductors.
The following are some of the examples of insulators: Plastic, wood, and glass are some of them.
Difference Between Conductor and Insulator
Following are some of the difference between conductor and insulator:
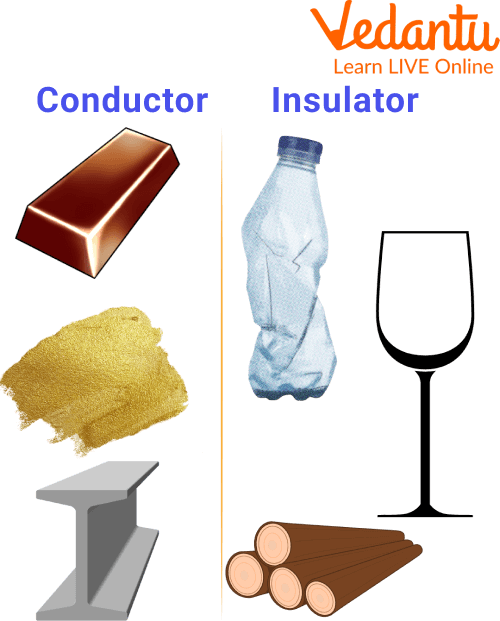
Example of Conductor and Insulator
Summary
In this article, we have seen that conduction is the flow of heat energy between matter particles that are in contact. Thermal conductors are materials that are good thermal energy conductors. Materials that allow electricity to flow easily through them are referred to as conductors, whereas materials that do not allow electricity to flow through them are referred to as insulators. In the end we have seen the differences between them. The major difference between them is- in conductor there is the presence of an electric field but in insulator it doesn’t happened.
FAQs on Thermal Conductors: Meaning, Examples & Applications
1. What is a thermal conductor?
A thermal conductor is a material that allows heat energy to pass through it easily and quickly. This transfer of heat, known as conduction, occurs from a hotter part of the material to a colder part without any visible movement of the material itself. Metals are the most common examples of good thermal conductors.
2. What are some common examples of good thermal conductors?
Many materials are effective at conducting heat. Some of the best examples include:
- Metals: Silver, copper, gold, aluminium, and iron are all excellent thermal conductors, which is why they are widely used in industrial and household applications.
- Diamond: A non-metal that is an exceptional thermal conductor, even better than most metals.
- Graphite: Another form of carbon (a non-metal) that also conducts heat very well.
- Water: While not as efficient as metals, water is a better thermal conductor than air or wood.
3. What is the main difference between a thermal conductor and a thermal insulator?
The primary difference is their ability to transfer heat. Thermal conductors, like copper and steel, allow heat to travel through them with very little resistance. In contrast, thermal insulators, such as wood, plastic, wool, and air, significantly slow down or resist the flow of heat, making them poor conductors.
4. Why are cooking pots made of metal but have handles made of plastic or wood?
This design cleverly uses both conductors and insulators. The body of the pot is made from metal, a good thermal conductor, to ensure that heat from the stove is transferred efficiently to the food inside. The handles are made from plastic or wood, which are good thermal insulators, to prevent the heat from travelling to your hand, allowing you to hold the pot safely.
5. How do metals conduct heat so effectively?
Metals possess a unique atomic structure containing a 'sea' of free electrons that are not bound to any single atom. When a metal is heated, these free electrons gain kinetic energy and move rapidly throughout the material, colliding with other electrons and atoms and transferring energy. This rapid, widespread energy transfer by free electrons makes metals exceptionally good thermal conductors.
6. Are all non-metals poor thermal conductors?
No, this is a common misconception. While most non-metals like glass, rubber, and wood are indeed poor conductors (insulators), there are important exceptions. Diamond and graphite, both forms of the non-metal carbon, are excellent thermal conductors. The strong, rigid lattice structure of diamond allows heat vibrations to travel through it with extreme efficiency, making it a better thermal conductor than any metal.
7. Can you give some examples of thermal conductors used in everyday life?
Thermal conductors are essential in many daily items. Some common applications include:
- Cooking Utensils: Metal pots, pans, and kettles are designed to heat food and water quickly.
- Car Radiators: These use metal fins to transfer excess heat away from the engine.
- Computer Heat Sinks: Small aluminium or copper components that draw heat away from the processor to prevent overheating.
- Soldering Irons: The metal tip is designed to get very hot to melt solder.
8. What is meant by the term 'thermal conductivity'?
Thermal conductivity is a specific property that measures how well a material can conduct heat. It is usually represented by the symbol 'k'. Materials with a high thermal conductivity value, like silver and copper, are excellent conductors. Materials with a low 'k' value, like styrofoam or air, are excellent insulators. The standard unit for measuring this property is watts per metre-Kelvin (W/m·K).









