




Functions and Importance of Muscular System for Kids
All of you have muscles in your body. You can touch and check. So, today we will learn about the muscular system. First, we will understand muscles. Muscles are soft tissues. Many stretchy fibres join and form muscles. Now, let's check the muscular system.
The muscular system is a system in the human body that includes - muscles, tendons, connective tissue, etc. The tissues that make up the human body can be broadly categorised into three groups: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and heart tendon tissues. It is also in charge of promoting fluid movement and upholding correct posture.
The muscular system is an organ system involved in the body's movement. The blood vessels, skeletal muscles, nerves, and muscles that make up every muscle are considered to be independent organs.
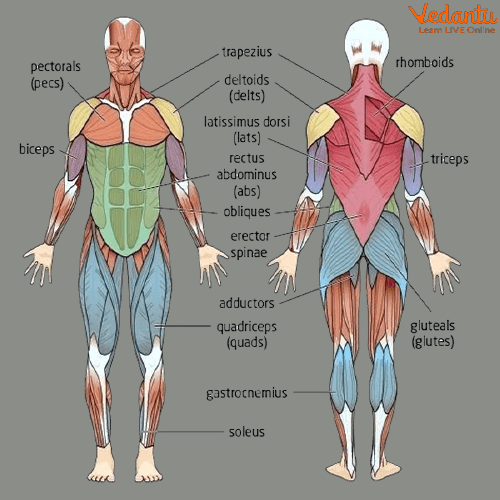
Muscular System
The Muscular System
The muscles provide the tug on the bones needed to bend, straighten, and support joints. The muscles can pull on bones, but they can't push them back to their original position, so the muscles work in pairs of flexors and extensors.
The extensor muscle helps to relax and stretch as the flexor muscle contracts to bend the joint.
Total Muscles in the Human Body
There are 600 total muscles in the human body. Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle are the three basic forms of muscle.
The brain, nerves, and skeletal muscles work together to result in movement – this is all collectively known as the neuromuscular system.
Functions of Muscles
The primary function of the muscular system is movement. Only muscle tissue in the body can contract and move other bodily parts.
The second function of the muscular system is maintaining posture and body position. The muscles often contract to hold the body still or in a particular position rather than that result in movement.
The muscles are responsible for the correct posture of the body. Also, they hold up the body throughout the day without becoming tired.
The main functions of the muscular system are movement, support, protection, heat generation, and blood circulation.
The functions of muscle are as follows:
Movement
Maintenance of posture
Body temperature
Communication
Construction of organs and vessels
Contraction of the heart
The muscular system consists of different types of muscles that each play a very important role in the body's function. The muscles help a person to make a move, speak, and chew.
The major properties of the muscular system are as follows:
Excitable or Irritable
Contractible
Extensible
Elasticity
Adaptability
The Strongest Muscle in the Human Body
The strongest muscle, according to its weight, is the masseter. With all the jaw muscles working together, it can close the teeth with force as great as 25 kilograms on the incisors or 90.7 kilograms on the molars.
Facts about the Muscular System
The muscles are divided into smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and skeletal muscle.
The muscles are made up of special cells known as muscle fibers.
The largest muscle present in the human body is called the gluteus maximus.
The smallest muscles found in the body are present in the inner ear.
In total body weight, 40% percent of weight is muscle.
The heart is the largest hard-working muscle of the body.
The muscles that control eye movement work the most.
The muscle contraction produces most of the heat in the body.
The muscles can only pull, they can't push.
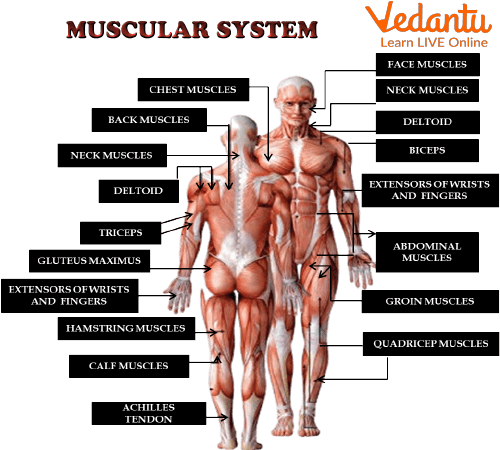
Muscular System Diagram
Summary
The muscular system is a system in the human body that includes - muscles, tendons, connective tissue, etc. In a broad sense, the human body's tissues can be divided into three parts: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and tendons of the heart. The muscles are responsible for the correct posture of the body. Also, they hold up the body throughout the day without becoming tired. Mostly, the muscles work in pairs. We have discussed different types of muscles in this article. We have added a muscular system diagram for your better clearance. Still, if you have any doubts please ask in the comments.
FAQs on What Is the Muscular System?
1. What muscles explain to kids?
The muscles move the body parts by contraction and then relaxation. The muscles can pull the bones, but they can't push them back to their original position. The muscular system is an organ system involved in the body's movement. Every muscle is a separate organ composed of blood vessels, skeletal muscles, nerves, and muscles. The muscle tissue is found in the heart, blood vessels, and digestive system.
The muscles provide the tug on the bones needed to bend, straighten, and support joints. The muscles act in pairs of flexors and extensors because they may pull on bones but not push them back into place. The extensor muscle helps in the relaxation and stretches as the flexor muscle contracts to bend the joint.
2. How do you explain the Visceral, Cardiac, and Skeletal muscles to kids?
All these muscles are explained below:
Visceral muscle is also known as smooth muscle. It is present inside the organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels.
Cardiac muscle: The cardiac muscle pumps blood throughout the body. This muscle is present only in the heart.
Skeletal muscle: The skeletal muscle is the only voluntary muscle tissue in the human body. The function of the skeletal muscle is to contract to move parts of the body closer to the bone to which the muscle is attached.
3. Why do we need muscles?
The muscles help the person to move, lift different things, pump blood all over the body, and even help the person to breathe. When the term muscles come to mind, we probably think most about the ones we can control. The muscles that can be controlled by the person are called voluntary muscles.









