




Key Discoveries and Scientific Impact of Isaac Newton
Why are the objects around held down to the ground and not floating around the universe? Why do earth and other planets have a specified path they follow and don’t go about any random path? Probably there is a strong force holding us down to the ground. Maybe another strong force dictating the paths of another planet. Perhaps a similar force keeping the Moon in its orbit.
What if I tell you the ‘strong force’ mentioned in all the above cases is the same kind of force? Well, it’s easier for us to state so given the scientific and technological advancements, this man thought about it back in the 1600s with just an apple! We’re talking about Sir Isaac Newton. This article is all about looking back into his contributions across various subjects.

Sir Isaac Newton
Early Life
Isaac Newton was born on 4th January 1643 in England. His father passed away 3 months before he was born. His mother thought he could barely survive as he was a premature baby and was super weak.
When Newton was 3 years old, his mother fell in love again and got married to a minister. Newton and his step-father had a strained relationship due to which he was sent back to his maternal grandmother to be taken care of.
He pursued schooling in The King’s School, Grantham where he learned ancient Greek, Latin, and Mathematics.
Following his high grades in school, he went on to Trinity College, Cambridge, to pursue graduation.
In 1665, his university closed as a precautionary measure for the Great Plague due to which he was sent home.
His private study during the following years gave birth to his inventions on gravitation, calculus, laws of motion, optics, etc.,
Isaac Newton's Early Life
Contributions to Science and Mathematics
Isaac Newton is one of the greatest scientists of all time. His contributions to Physics and Mathematics in particular have re-written the fate of these subjects for the centuries to come. Some of his important contributions and discoveries are discussed below.
Gravity
The force that keeps us bound to the ground, the force that is responsible for the rotation and revolution of planets in an orbit, and the force that keeps the Moon in its orbit are all the same force, the gravitational force.
The phenomenon of gravity was first thought about by Newton. The famous ‘apple fell on Newton’s head’ story is often associated with the discovery of gravity and gave the law “Universal Law of Gravitation”
Isaac Newton’s Contribution to Discovering Gravity
Optics
White light can be split into the colours of the rainbow! You’ll learn about this property in higher classes, known as the ‘splitting of white light’. Putting this into easier understanding, when white light passes through a glass prism, the prism refracts (bends) the rays of light at various angles producing the colours of the rainbow. Though the result of this experiment would have been fascinating, it came as a surprise that white light was made up of several colours. This observation and inference were first given by Newton. It was a breakthrough in the field of optics.
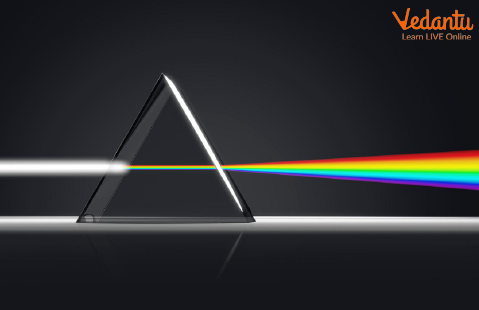
Splitting of White Light Performed by Newton
Laws of Motion
Isaac Newton proposed the three laws of motion, famously known as Newton’s Law of Motion. These laws revolutionised the motion of objects. Though these are considered simple observations in the present day, these were complex ideas to be put in the form of laws back in the days. These laws help us understand the motion of big objects in a bigger picture..
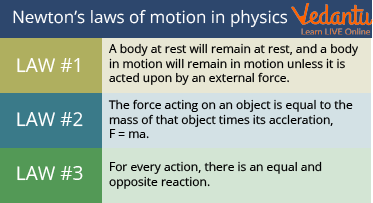
Laws of Motion
Reflective Telescope
From his earlier understanding of refraction (bending) of light and splitting of white light, Newton understood that the refractive telescope found by Galileo (another famous scientist around that time) had a few limitations. He applied his knowledge of optics to invent the reflective telescope which had better scope than its earlier counterpart. It is now famously known as the Newtonian telescope.

First Reflective Telescope was Invented by Newton
Calculus
The concept of calculus is pretty complex to understand. In simple words, calculus is a branch of Mathematics that deals with dynamic quantities. In other words, any fast-changing quantity can be determined using calculus. Calculus has important applications in Physics, Chemistry, astronomy, etc. The basics of calculus were brought together by Isaac Newton in the late 1600s
Summary
Let’s summarise what we’ve learned up until now.
Sir Isaac Newton is the greatest Scientist of all time from England. He did his schooling in the King’s School, Grantham, and graduated from Trinity College, Cambridge. During the Great Plague of the 1600s, he was doing a lot of self-study due to which he invented gravity, laws of motion, splitting phenomenon of white light, reflective telescope, and calculus. His contributions to science and Mathematics are enormous and have revolutionised these subjects for the better ever since.
FAQs on Isaac Newton: His Groundbreaking Contributions and Laws
1. What were Isaac Newton's biggest contributions to science?
Sir Isaac Newton made monumental contributions that formed the bedrock of classical physics. His most significant works include:
- The Three Laws of Motion: These laws describe the relationship between an object and the forces acting upon it, explaining concepts like inertia, acceleration (F=ma), and action-reaction.
- The Law of Universal Gravitation: This groundbreaking law explains that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres.
- Calculus: He developed a new branch of mathematics, calculus, which is essential for modelling and understanding change, motion, and rates.
- Optics: He demonstrated that white light is composed of a spectrum of colours, which he showed using a prism. This led to his invention of the reflecting telescope.
2. What are the three laws of motion formulated by Isaac Newton?
Newton's three laws of motion are fundamental principles of physics. They are:
- First Law (Law of Inertia): An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
- Second Law (Law of Acceleration): The acceleration of an object is dependent upon two variables - the net force acting upon the object and the mass of the object. It is most commonly expressed as Force = mass × acceleration (F=ma).
- Third Law (Law of Action-Reaction): For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that in every interaction, there is a pair of forces acting on the two interacting objects.
3. Why was Newton’s invention of the reflecting telescope so important?
Newton invented the reflecting telescope to solve a major problem in the existing refracting telescopes of his time. Refracting telescopes used lenses, which bent light of different colours at slightly different angles, causing a blurry fringe of colours around images known as chromatic aberration. Newton's brilliant solution was to use mirrors instead of lenses. Mirrors reflect light instead of refracting it, which meant all colours were reflected at the same angle, eliminating chromatic aberration and producing a much sharper, clearer image.
4. How did Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation change our understanding of the universe?
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation was revolutionary because it unified the heavens and the Earth under a single, predictable mathematical law. Before Newton, it was believed that the rules governing celestial bodies (like planets) were different from those on Earth (like a falling apple). Newton showed that the same force of gravity that pulls an apple to the ground is also what keeps the Moon in orbit around the Earth and the planets in orbit around the Sun. This transformed our understanding from a mysterious cosmos to a rational, clockwork universe governed by universal laws.
5. What was Newton's most important contribution to mathematics?
Isaac Newton's most significant contribution to mathematics was the invention of infinitesimal calculus. He developed this powerful tool to accurately describe and calculate rates of change, such as the velocity and acceleration of moving objects. Calculus provided the mathematical language needed to express his laws of motion and gravitation, making it the essential foundation for modern physics, engineering, and many other scientific fields.
6. Beyond physics and mathematics, did Isaac Newton contribute to any other fields?
Yes, while he is most famous for physics and math, Newton spent a significant amount of time on other intellectual pursuits. He was deeply involved in alchemy, the precursor to modern chemistry. His alchemical experiments, though not always successful, contributed to his understanding of the properties of matter. He also wrote extensively on biblical interpretation and theology, demonstrating the vast and diverse scope of his interests.
7. What major honours did Sir Isaac Newton receive for his scientific achievements?
In recognition of his immense contributions, Sir Isaac Newton received several prestigious honours. He was elected President of the Royal Society in 1703, a position he held until his death. In 1705, Queen Anne knighted him, making him Sir Isaac Newton. This was a rare honour for a scientist at the time, signifying the profound impact of his work on the nation and the world.









