




What are the Main Functions of the Human Skeletal System?
How can humans stand upright? How can we even move? How do we hold any rigidity in our body and are not puddles? That is because of the Skeletal system.
The human body is made up of 206 bones. The total collection of all the bones in a human's body is known as the Skeletal system. Have you ever seen a jellyfish or a worm? Both these animals lack any rigidity in their body, that is due to the absence of a hard skeletal system. The human skeletal system provides rigidity to our bodies alongside strength. It also plays an integral part in movement alongside our muscles.
Human Skeleton
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system supports the entire body. For example, the spine made up of vertebrae is responsible for holding up and supporting the entire upper body
It is also responsible for movement. Bones are often attached to two or more muscles and they work together to allow the body to move.
Lastly, the skeleton is essential in protecting soft and important organs. The skull protects the brain, the lungs as well as the heart are protected by the ribcage, and the spinal cord is enclosed in the vertebral column of the spine.
What Are Bones Made of?
Our bones are made up of a combination of hard minerals, such as calcium that make up about 70 per cent of the body. It's hard, smooth, and solid. Inside the cortical bone is a previous, spongy bone material called the trabecular or cancellous bone. This way our bones will not break so fluently. At the centre of bones is a softer substance called gist.
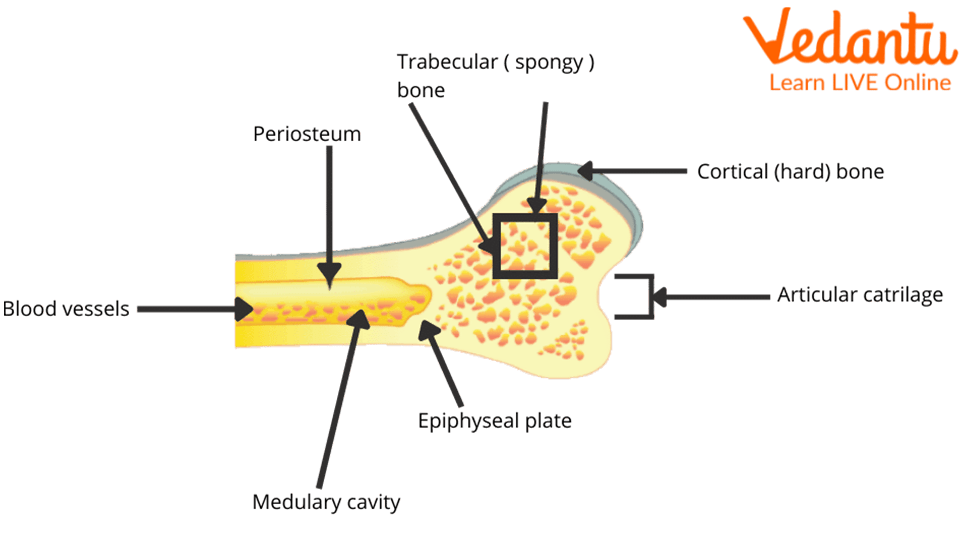
The Bone Process
Bone Attribute
Bones are calcified connective tissue present in our body. It forms the maximum portion of the skeleton. Bones are dense, semirigid and porus. It consists of an organic matrix and various mineral components inside them. Bones are tough structures.
Parts of the Skeletal System
Aside from bones, it also consists of cartilage, tendons, ligaments, and joints. Let us discuss these components -
Bones: They are the most basic part of the skeletal system. Bones are made up of a special kind of tissue known as connective tissue which is made stronger with the help of a mineral called calcium. Inside the hard covering of the bone there is a soft sponge part. This part of the bone is lighter and allows for blood vessels to pass through. At the center of the bone lies the Bone Marrow.
Bone marrow is a soft spongy substance mainly responsible for the production of blood cells.
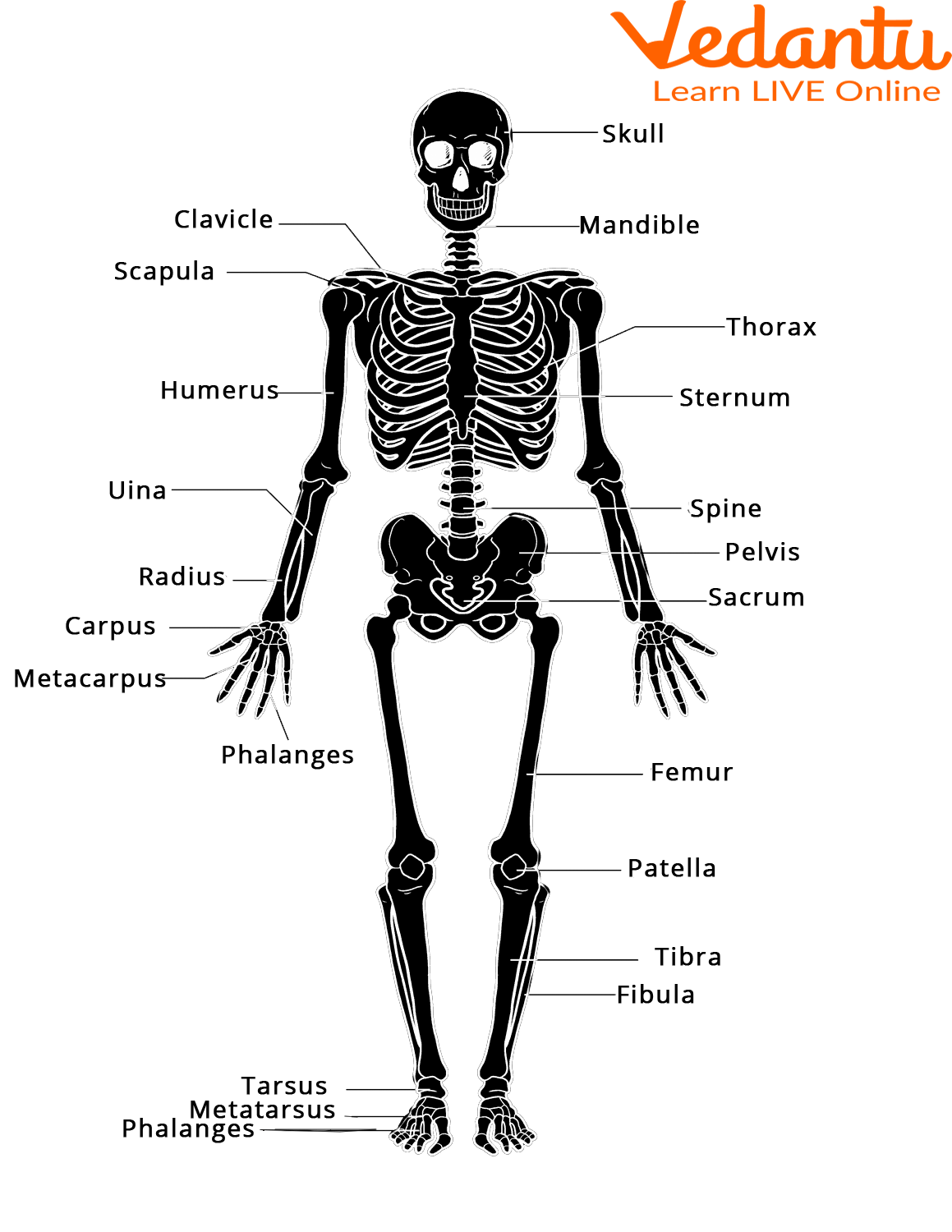
Bones in the Human Body
Ligaments: These are tough elastic bands of tissues that are responsible for attaching one bone to another and keeping them stable
Cartilage: Cartilage refers to a smooth protective covering found over joints. It and synovial fluid allows movement in the joints while protecting the bones from rubbing against one another and wearing down. It is also found between the ribs.
Tendons: Tendons are rope-like structures that join bone to muscle. They also facilitate movement while holding the skeletal system together. They also prevent injury to the muscles by absorbing impact when performing strenuous activities such as jumping.
Joints
Joints refer to the areas within the body where two bones meet or connect. They are essential for movement. Some joints allow for a wide range of motion while others allow more restricted or no movement at all.
Based on the kind of movement they allow, there are three types of joints-
Fibrous Joints- These allow no movement and are also called immovable joints. For example the ones present in the skull.
Cartilaginous Joints- These allow for some movement, and thus are called Partially moveable joints. For example the spine
Synovial Joints- these joints have a wide range of motion and can be subdivided into subcategories based on the kind of movement they allow. These are also called movable joints. For example the shoulder (Ball and socket joints), the knee (Hinge joint), the neck (pivot joint), etc. They are also filled with a liquid known as the synovial fluid which lubricates the joints and makes movement easier and smoother.
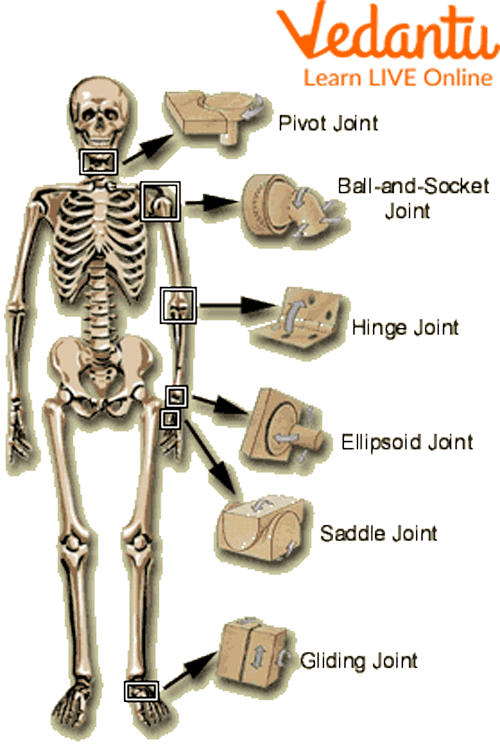
Different Types of Movable Joints
How Do Broken Bones Heal?
Bones can heal themselves on their own if they become broken. A broken bone will heal in stages. When it first breaks there will be blood around it and it'll form a kind of scab over the broken portions.
Bringing collagen and cartilage together will allow the gap between the two sides of the break to be bridged. This ground will continue to transfigure and harden until the bone is healed. It can frequently take months for bones to heal back to normal. While the bone is repaired, it cannot take the stress of a normal bone, it cannot bear a heavy weight or more stress.
Functions of Bones
Bones support our bodies and help us to move.
Bones protect our internal organs like the heart, lungs, etc.
Some bones produce our red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Certain bones store fats present in our body and provide us when we need them.
Bones can also store important minerals for our bodies.
Fun Data about Bones for Kids
Stapes bone which is present in the middle ear is the smallest bone present in our body.
Femur, the thigh bone, is the longest bone in the human body.
Tooth enamel is the hardest substance present in the human body.
Although your bones stop growing when you're around 20, they do constantly rebuild new bone cells.
The chine is made up of 33 bones.
Redbone gist can produce around 5 billion red blood cells each day.
Your bones can become weaker if your body does not have enough calcium. A good reason to drink your milk!
Summary
We have a shape and the power to move because of the skeletal system. As a storehouse of minerals like calcium, it protects and supports the internal organs. The skeletal system of males and females differs slightly. Women, on the other hand, have a wider pelvis and more space in the womb for babies to grow. Males have larger legs and arms, while females have bigger legs and arms.
No matter your age or gender, everyone should exercise and eat healthy to maintain a healthy skeletal system. Always take care of your bones by being kind to them. In this article, we have discussed what are bones made of and what bone attributes are in detail.
FAQs on Human Skeletal System: Complete Guide for Students
1. What is the human skeletal system?
The human skeletal system is the internal framework of the body, composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons. In an adult, it consists of 206 bones that provide shape, support, and protection to the body, allow for movement, and are responsible for producing blood cells and storing minerals.
2. What are the main functions of the human skeletal system?
The skeletal system performs several vital functions for the body. The five main functions are:
- Support: It provides a rigid framework that supports the body and gives it shape.
- Protection: It shields vital internal organs from injury. For example, the skull protects the brain, and the rib cage protects the heart and lungs.
- Movement: Bones act as levers that muscles pull on to produce movement. This is made possible by joints.
- Blood Cell Production: The soft tissue inside some bones, called bone marrow, produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Mineral Storage: Bones serve as a reservoir for minerals, particularly calcium and phosphorus, releasing them into the bloodstream when needed.
3. How are the 206 bones of the adult skeleton organised?
The human skeleton is organised into two main parts: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton forms the central axis of the body and includes the skull, vertebral column (spine), and rib cage. The appendicular skeleton consists of the bones of the limbs (arms and legs) as well as the shoulder and pelvic girdles that attach the limbs to the axial skeleton.
4. What is the difference between cartilage, ligaments, and tendons?
While all are crucial connective tissues in the skeletal system, they have distinct functions. Cartilage is a smooth, flexible substance that covers the ends of bones at joints, acting as a shock absorber and preventing them from rubbing together. Ligaments are strong, fibrous bands that connect bone to bone, providing stability to joints. Tendons are tough, flexible cords that connect muscles to bones, enabling the transfer of force from muscles to move the skeleton.
5. What is bone marrow and why is it important?
Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found in the centre of most large bones, such as the hip and thigh bones. It is incredibly important because it functions as a factory for the body's blood cells. Red bone marrow is responsible for producing red blood cells (which carry oxygen), white blood cells (which fight infection), and platelets (which help with clotting).
6. Are bones considered living tissues? Explain why.
Yes, bones are very much alive. They are complex, living tissues made up of active cells, nerves, and blood vessels. Bones continuously remodel themselves by breaking down old tissue and replacing it with new tissue. They require a steady supply of blood to deliver oxygen and nutrients and to remove waste. This living nature allows bones to grow, heal after a fracture, and adapt to stress.
7. Why do babies have more bones than adults?
A baby is born with about 300 bones, many of which are made of soft cartilage. As the baby grows, many of these smaller bones and cartilage pieces fuse together. For example, the bones in the skull fuse to form a solid cranium, and parts of the pelvis join to form a single hip bone. This process of fusion reduces the total bone count to the 206 bones found in an adult skeleton.
8. Which are the smallest and largest bones in the human body?
The largest and strongest bone in the human body is the femur, or the thigh bone. The smallest bones are the three ossicles found in the middle ear: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup). The stapes is the smallest of all, measuring only about 3 x 2.5 mm.
9. What are joints and what role do they play in movement?
A joint is the location where two or more bones meet. Joints are essential for movement and flexibility. They can be classified by the amount of movement they allow. For example, the shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint that allows a wide range of motion, while the knee is a hinge joint that primarily allows for bending and straightening in one direction. Without joints, our skeleton would be rigid and unable to move.
10. How does the skeletal system protect our vital organs? Give some examples.
The skeletal system provides a protective casing for the body's most delicate organs. Key examples of this protective function include:
- The skull, which acts as a hard helmet to protect the soft tissue of the brain from impact.
- The vertebral column (or spine), which encases and protects the spinal cord, the main pathway for nerve signals.
- The rib cage, which forms a protective shield around the heart and lungs in the chest cavity.









