




Why Understanding Temperature Matters in EVS
In our everyday life, we have to find the severity of the fever. For example, our body temperature in general is 98 ⁰F. It increases when we suffer from a fever. We set our oven and electric stoves at a certain temperature so that we can cook yummy food.
Information about Temperature plays a very important role in almost every area of our lives as well as in scientific discoveries from physics to geology. Temperature can be referred to as the hotness or coldness of a body. It is the way of determining the Kinetic energy of particles within an object. The faster the movement of particles in a body, the more will increase the temperature of the body and vice versa. In this article let's see the definition of temperature, units of temperature, and some facts about temperature.
Temperature Measuring Instrument
Information About Temperature
Scientifically, temperature is a physical quantity that describes how quickly molecules move inside a material. In solids and liquids, the molecules are vibrating around a fixed point in the substance, but in gases, they are in the free state and bounce on each other as they travel. In gas, the temperature, pressure, and volume of the gas are closely related by the law of physics. The higher the temperature, the faster the movement of the particles composing the substance.
Temperature plays a significant role in medical care, food industries, beverages, and agriculture. Our overall health is often dependent upon temperature in many ways. Also maintaining proper temperature is crucial in medical cold storage.
What is Temperature?
Definition of Temperature
Temperature is how hot or cold something is. Our bodies can feel the difference between what is hot and what is cold. One reason for this is our developed senses but it is the temperature of the object which decides whether it is hot or cold. It also affects the amount as well as the properties of thermal radiation emitted from the surface of an object. Temperature also affects the rate and extent to which chemical reaction takes place. Temperature affects all the physical properties of materials whether it is solid, liquid, gaseous, or plasma: density; solubility; vapour pressure, and electrical conductivity.
Temperature
Scales and Units of Temperature
To measure temperature precisely a Thermometer is used. And what do thermometers do? A thermometer uses a temperature scale to record how hot or cold something is. The scale which thermometer is used in most of the world is in 'Degrees Celsius ' also called 'Centigrade'. Centigrade is the unit used to measure the temperature.
There are different scales and units used to measure temperature. Among them, the most common is Celsius or Centigrade (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K). 'Kelvin' is considered the basic temperature unit in the International System of Units (IS). The Celsius scale is used widely in which 0°C and 100°C correspond to the freezing and boiling points of water respectively. A thermometer measures temperature. On the Fahrenheit scale, 32°F and 212°F correspond to the freezing and boiling points of water.
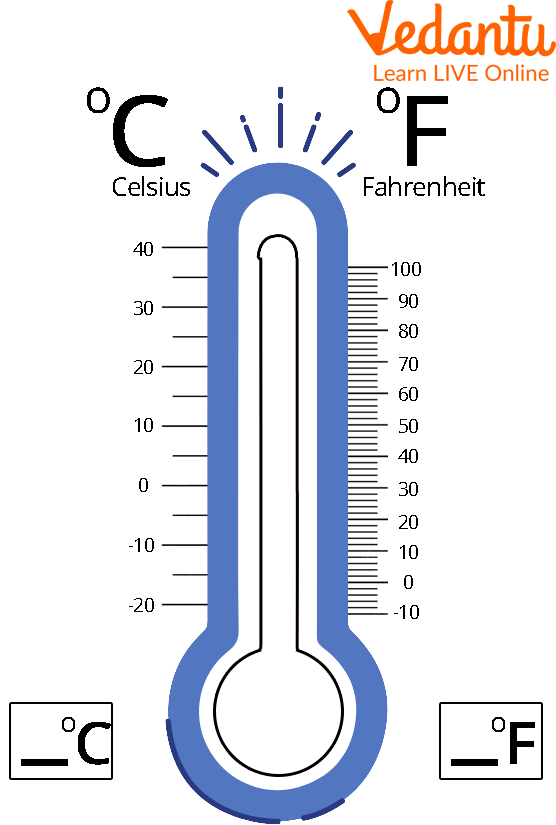
Temperature Scale in Celsius and Fahrenheit
In the USA and many other countries, 'Fahrenheit ' is more often used while scientists mostly use 'Kelvin' to measure the temperature. We hope you understood the temperature definition for kids.
Temperature Facts for Kids
We all have heard people asking, What is the temperature outside? Perhaps you have been often restricted not to play out when you had a fever. Maybe you have often complained that today's temperature was too hot. So let us explore some temperature facts for kids which will tempt you.
Water freezes at 0 °C and -32 °F.
Celsius is the world’s most common way of measuring temperature.
−89.2 °C (−128.6 °F) is the coldest temperature that has been ever recorded on Earth. It was recorded at Vostok Station located in Antarctica.
Absolute zero is the coldest theoretical temperature. When the substance reaches this temperature it does not possess any heat energy. It is defined as ‘Zero Kelvin’.
Summary
So, kids, we hope you are tempted with the temperature facts for kids. From interesting facts about temperature to the use of thermometers, we learned that knowledge of thermometers is important in our day-to-day lives. We also learned about temperature definition for kids, knowledge of scales and units of temperature, and some interesting facts about temperature. This knowledge will help us to scale the use of thermometers in our homes. Now, you will also be able to relate the temperature topic with other topics of Science and the Environment. We hope you enjoyed reading this article, in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Facts About Temperature: Essential Concepts & Examples
1. What is temperature in science?
In science, temperature is a measure of how hot or cold an object is. It is specifically a measure of the average kinetic energy of the atoms or molecules in a substance. The higher the temperature, the faster these particles are moving.
2. What is the main difference between heat and temperature?
Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance (intensity), while heat is the total thermal energy that flows from a hotter object to a colder one. For example, a small cup of boiling water has a high temperature, but a large bathtub of warm water contains more total heat energy.
3. What are the common scales used to measure temperature?
The three most common scales for measuring temperature are:
- Celsius (°C): Used by most of the world for daily temperature measurement. Water freezes at 0°C and boils at 100°C.
- Fahrenheit (°F): Primarily used in the United States. Water freezes at 32°F and boils at 212°F.
- Kelvin (K): The standard scale for scientific work. It is an absolute scale where 0 K represents absolute zero, the coldest possible temperature.
4. How does a liquid-in-glass thermometer actually work?
A liquid-in-glass thermometer works on the principle of thermal expansion. It contains a liquid (like alcohol or mercury) in a sealed glass tube. When the temperature rises, the liquid absorbs heat and expands, causing it to rise up the narrow tube. When it gets colder, the liquid contracts and falls. The tube is marked with a calibrated scale (like Celsius or Fahrenheit) to show the exact temperature.
5. Why does a metal chair feel colder than a wooden one, even if they are in the same room?
This happens because of differences in thermal conductivity, not temperature. Both chairs are at the same room temperature. However, metal is a good thermal conductor, meaning it quickly transfers heat away from your body when you touch it. This rapid loss of heat makes your brain interpret the sensation as 'cold'. Wood is a poor conductor (an insulator), so it transfers heat much more slowly, and therefore doesn't feel as cold.
6. What are some interesting facts about temperature?
Here are a few interesting facts about temperature:
- The first reliable thermometer was invented by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1714.
- The coldest possible temperature is absolute zero (0 Kelvin or -273.15°C), where all molecular motion ceases.
- The surface temperature of the Sun is approximately 5,500°C.
- The only temperature that is the same value in both Celsius and Fahrenheit is -40 degrees (-40°C = -40°F).
7. Can temperature be negative?
Yes, temperature can be negative on the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, as commonly experienced during winter in many parts of the world. However, temperature cannot be negative on the Kelvin scale. This is because the Kelvin scale is an absolute scale where 0 K (absolute zero) is the point of zero thermal energy. There is no state colder than absolute zero, so negative Kelvin values are not physically possible.









