




Protein is a Superdiet
You might have heard the word protein so many times, but do you really know what the word really means? Let’s find out! In this article we will briefly discuss protein, what it is and what is its importance in our diet and also state some facts about it.
Proteins are complex molecules which play an important role in body building. They are abundantly present in things like eggs, pulses, cheese, fish, etc. Protein contains elements like hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur etc. which are very beneficial for our body.
Protein
General Structure and Properties of Proteins are Discussed Below
The common property of all proteins is that they consist of long chains of α-amino acid.
The primary structure of a protein and its amino acid sequence drives the folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain, which ultimately determines the protein's unique three-dimensional shape.
The secondary structure of protein refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone.
The tertiary structure of protein arises from further folding of the secondary structure of the protein.
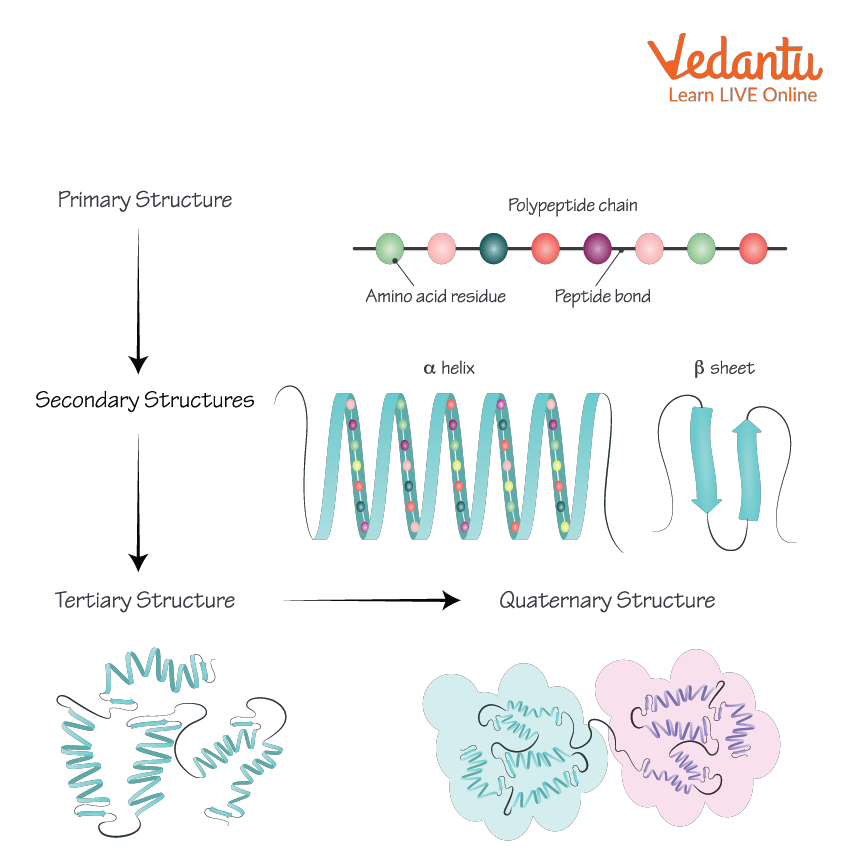
Protein Structure
Protein Facts
The word protein is derived from the Greek word “Proteios” which means “Primary”.
Proteins are classified into four categories primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary based upon their structural variations.
Proteins help in normal body growth.
Enzymes are the quaternary proteins.
After water, they are present in abundant quantities in the human body.
Eggs contain the highest quality of proteins.
Albumin is a protein in blood which maintains fluid balances in the body.
Some proteins are called complete proteins because they contain all the required amino acids. This category includes eggs, dairy products, soya, etc.
Men require more protein as compared to women.

Nuts and Beans Contain Proteins
Protein for Kids
Protein is the second most abundant compound in the human body, so it is required in large amounts in the human body. Therefore, sufficient amounts of protein must be there in the diet to meet the requirement for normal growth and development of the body.
The requirement of the proteins varies with age and as one’s age increases, the requirement of protein also increases, especially during adolescence. The age-wise daily protein requirement is shown below.
1-3 years: 14g
4-8 years: 20g
9-13 years (boys): 40g
9-13 years (girls): 35g

Protein for kids
Protein as a Superfood
Protein contains a lot of essential amino acids which helps in increasing muscle mass. So, athletics all over the world are trying to shift towards a protein based diet. These days, more and more people are consuming protein supplements for increasing muscle mass. Studies show that weight-trainers who do not eat extra protein (either in food or protein powders) still gain muscle at the same rate as weight-trainers who supplement their diet with artificial protein sources.

Protein as a Superfood
Biological Importance of Proteins
Our body shows a considerable variation in the amount of protein contained in various parts; generally organs contain more protein than plasma. The most important proteins, such as enzymes and hormones, occur in extremely small amounts. All enzymes identified thus far are proteins. Higher organisms such as vertebrates require a carrier molecule for the transport of oxygen so in all vertebrates haemoglobin serves this purpose which is also a protein.
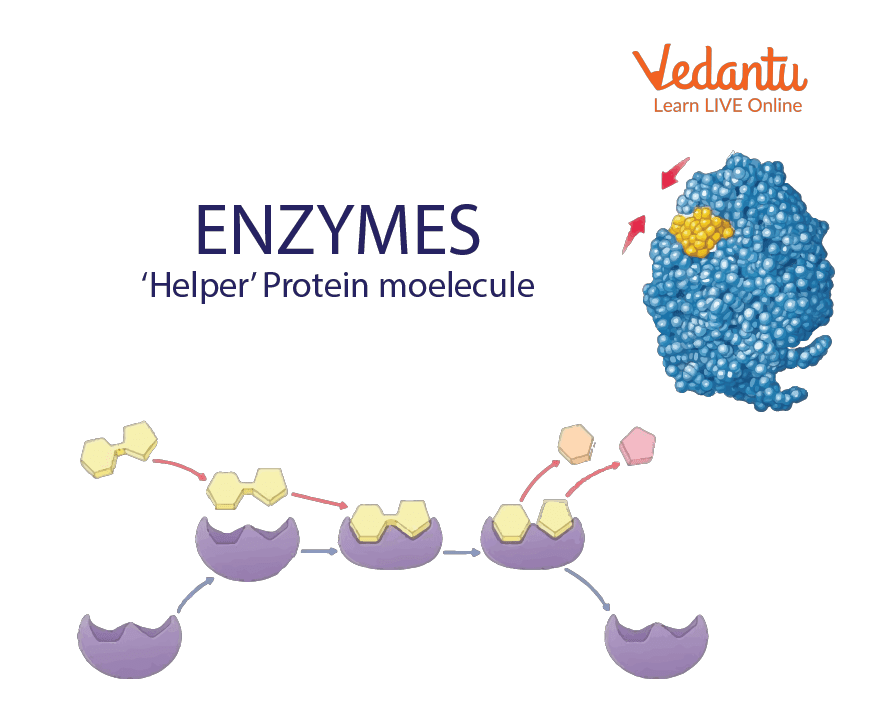
Enzymes
Solved Questions
1. How many types of amino acids are there in a protein?
Ans: Amino acids are mainly categorised as essential and non-essential amino acids. So in proteins, we can find either essential or non-essential amino acids or even both kinds of amino acids.
2. What makes secondary protein different from the primary protein?
Ans: Secondary proteins are more complex as compared to primary proteins because the structure of secondary proteins have interlink between the polypeptide chain.
3. What are the major biological functions of protein?
Ans: Proteins can perform many functions; they can form the structure of most of the cells. They regulate the osmotic balance in the body as well as most of the catalyst and enzymes or protein.
Summary
A protein molecule is very large compared to molecules of sugar or salt. There are about 20 different amino acids that occur naturally in proteins. Proteins are generally obtained from plants or animals. Plants can synthesise all proteins but animals cannot. So there are some proteins which are essential to be taken from outside.
FAQs on Must-know and Interesting Facts about Proteins
1. What are some of the best food sources of protein for both vegetarians and non-vegetarians?
Proteins are available from a wide variety of food sources. The best sources can be categorised as follows:
- Animal-Based Sources: These are often called complete proteins as they contain all essential amino acids. Examples include eggs, dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt), meat, poultry (chicken, turkey), and fish.
- Plant-Based Sources: These are excellent sources, especially when varied. Top examples include lentils, chickpeas, beans, tofu, edamame, nuts, seeds, and quinoa.
2. What are the main functions of proteins in the human body?
Proteins are essential macromolecules with a wide range of critical functions in the body. Their primary roles include:
- Building and Repair: They are the primary building blocks for tissues like muscles, bones, skin, and hair.
- Enzymatic Action: Most enzymes, which speed up biochemical reactions, are proteins.
- Transport and Storage: Proteins like haemoglobin transport oxygen in the blood.
- Immune Defence: Antibodies that fight off infections are made of protein.
- Hormonal Regulation: Some hormones, like insulin, are proteins that regulate bodily functions.
3. How are proteins different from carbohydrates in their structure and function?
Proteins and carbohydrates are both essential nutrients but differ significantly. Structurally, proteins are complex polymers made of building blocks called amino acids, while carbohydrates are polymers made of simpler units called monosaccharides (sugars). Functionally, the primary role of proteins is structural and functional (building tissues, acting as enzymes), whereas the primary role of carbohydrates is to provide a quick source of energy for the body.
4. Why are some amino acids called 'essential' while others are 'non-essential'?
The distinction between essential and non-essential amino acids is based on the body's ability to produce them. The nine essential amino acids cannot be synthesised by the human body in sufficient amounts, so they must be obtained from our diet. In contrast, the body can produce non-essential amino acids on its own, so it is not critical to get them directly from food.
5. What is the most abundant protein found in the animal kingdom and on Earth?
While there are countless proteins, two stand out for their abundance. The most abundant protein in the animal kingdom is collagen, which is a key structural component of skin, bones, and connective tissues. On a global scale, the most abundant protein on planet Earth is RuBisCO, an enzyme crucial for photosynthesis in plants and other organisms.
6. Is it true that protein requirements are based on gender?
This is a common misconception. Protein requirements are not directly based on gender but are primarily determined by individual factors such as body weight, muscle mass, age, and physical activity level. While men, on average, may require more protein due to typically larger body size and higher muscle mass, an active woman will have higher protein needs than a sedentary man of the same weight.
7. Can you share some interesting facts about proteins?
Certainly. Here are a few interesting facts about these vital molecules:
- Your hair and fingernails are made almost entirely of a tough, fibrous protein called keratin.
- Proteins are responsible for muscle contraction. Two key proteins, actin and myosin, slide past each other to make your muscles work.
- The word 'protein' comes from the Greek word 'proteios', which means 'primary' or 'of first importance', highlighting their crucial role in life.
- The shape of a protein is critical to its function. Even a small change in its 3D structure can make it ineffective.
8. What happens to a protein when it is cooked, and why can't it be reversed?
When a protein is cooked, it undergoes a process called denaturation. The heat breaks the weak bonds that hold the protein in its specific three-dimensional shape, causing it to unfold and change its properties. A common example is an egg white turning from clear and liquid to white and solid. This process is generally irreversible because the original, complex folded structure is lost, and the protein cannot easily refold into its functional form.









