




How Do Human Organs Work Together in the Body?
Kids, do you know how many organs we all have? Our human bodies contain lots of different organs all working together. Firstly, an organ is a part of the body that performs a specific job. Each organ has its particular job to do. Inside our head, protected by our skull, is our brain. On our chest are our heart and lungs, both so close to one another. The nose, ears, eyes, and skin are a few other organs we have outside our body. Some of the body's vital organs are the lungs, kidneys, heart, intestine, and brain. Let’s learn about these organs in detail.
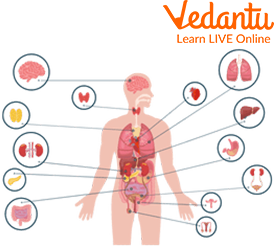
The Organs of the Body
Major Organs of the Body
All organs of the body are crucial in their way. But some vital organs are discussed here. We have the lungs, the heart, the kidneys, the intestine, the stomach, the brain, and many more. These organs work together for the proper functioning of a body. So, let's learn about some of the major organs of the body.
Heart
The heart is a vital part of the body. It is known as the symbol of love and is a nature's wonder. The heart is located on the middle-left side of our chest. The heart pumps blood through the circulatory system and provides oxygen-rich blood to the other body parts.
Brain
It is due to an essential organ in our body called the brain. Our brain is the 'boss' of our body as it controls everything we do. The brain controls things like feeling, learning, talking, dancing, and even breathing.
Kidneys
There is a pair of kidneys inside the human body. Kidneys are located in the upper abdominal area against the back muscles on both the left and right sides of the body that act like filter devices. Kidneys clean the blood and separate waste compounds from the blood when it passes through the kidneys.
Lungs
Breathing air is necessary for keeping us alive, and the lungs are the vital organ for helping us with breathing. They are one of the largest organs of our body. They work with our respiratory system to allow us to take in fresh air and get rid of stale air.
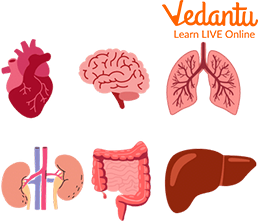
Major Organs of the Body
The System of Organs
In the above paragraph, we read about the vital organs of our body. But children, our organs work in a complex system associating with other organs. So now, let's learn about the system of organs.
Circulatory System
The heart works in the circulatory system and pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body's organs. The circulatory system contains blood vessels in which the blood travels.
Nervous System
Our nervous system is the in-charge of every work our body does. A nervous system is a network of organs and nerves that send signals throughout the body. Nerves are associated with the brain, and they are the main components for providing signals to work.
Respiratory System
We breathe oxygen through our nose and store a portion of it in our lungs. Lungs play a significant role in filtering the air we inhale and are a vital organ of the respiratory system. Lungs have small balloon-like structures called alveoli which fill them with oxygen and let go of carbon dioxide, the bad air.
Excretory System
The excretory system is made up of the urinary organs, which produce and expel urine from the body. The major role of the excretory system is to get the body rid of waste substances. A Urinary bladder, the ureters, the urethra, and the kidneys constitute the excretory system that helps to clean our blood.
Digestive System
The digestive system is a tube of organs beginning with the mouth, and extending as far as the anus. The digestive system is made up of many different parts all connected.
Reproductive System
The reproductive system is a general term that describes the organs and their functions in human beings and the lower animals, which are involved in reproduction. The function of the reproductive system can be summarized as producing, maintaining, and eventually transporting spermatozoa (in males) for fertilization of ova (in females) as part of sexual reproduction.
Musculoskeletal System
A musculoskeletal system is the body's support and connective tissue. It consists of bone, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and many other connective tissues that help to support and protect the various body organs. The function of a musculoskeletal system is passive (not requiring conscious thought).
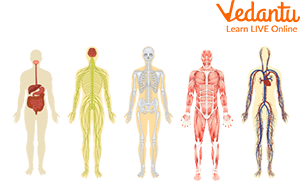
Different Organ Systems of the Body
Fun Facts About Organs
Let's learn some fun facts about organs.
A human heart pumps around two thousand gallons of blood every day. Heart beats about one hundred thousand times in one day and approximately thirty-five million times a year. The human heart will beat more than three billion times during an average lifetime.
A human brain generates about 12-25 watts of electricity. This electricity is enough to power a low-wattage LED light.
If you habitually hold your pee for a long time, you're subjecting yourself to severe long-term effects, including a higher risk of infection. Holding pee weakens the bladder muscles.
The left lung is slightly smaller than the right lung in humans. This is because the right lung consists of three lobes whereas the left lung has two lobes. And also, the left lung gives space for our heart to fit in.
Summary
In this article, we learned some interesting facts about the human body. We learned that the human body is an amazing creation of nature. Some human organs are internal body parts such as the heart, kidneys, lungs, stomach, brain, and liver while others are outside the body, such as the nose, eyes, ears, and skin. Organs within the organ system perform a specific task. If any of our body's organs face proper functioning issues, the whole human body suffers. All the organs are interconnected with one another for the proper functioning and maintenance of the body. An individual needs to take appropriate care of the body to safeguard these organs. We hope you enjoyed reading this article, in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Human Organs: Key Functions and Surprising Facts
1. What are the major internal organs in the human body and their functions?
The human body has several vital internal organs, each with a specific job. The main ones are:
- Brain: The control centre of the body, responsible for thoughts, memory, and controlling body movements.
- Heart: Pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to all cells.
- Lungs: Allow us to breathe by taking in oxygen from the air and removing carbon dioxide.
- Stomach: Helps in the digestion of food by breaking it down with special acids.
- Liver: Cleans the blood, produces an important digestive liquid called bile, and stores energy.
- Kidneys: A pair of organs that filter waste from the blood to produce urine.
2. What are the five sense organs and what is their importance?
The five sense organs help us perceive and interact with the world around us. They are the eyes (for sight), ears (for hearing), nose (for smell), tongue (for taste), and skin (for touch). Each organ contains special receptors that send information to our brain, allowing us to understand our surroundings, enjoy things like food and music, and stay safe from danger.
3. Why is the brain often called the 'control centre' of the body?
The brain is called the 'control centre' because it manages nearly every function of the body. It processes information from our sense organs, allowing us to see, hear, and feel. It also controls our thoughts, emotions, memory, and voluntary actions like walking and talking. Furthermore, it regulates involuntary functions essential for life, such as our heartbeat, breathing, and digestion, making it the master organ in charge of the entire system.
4. How do the heart and lungs work together as a team?
The heart and lungs work in a closely coordinated partnership to supply the body with oxygenated blood. The process is a continuous cycle:
- The lungs inhale air, extracting oxygen.
- The heart pumps deoxygenated (oxygen-poor) blood to the lungs.
- In the lungs, this blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide.
- The now oxygen-rich blood returns to the heart, which then pumps it to the rest of the body to fuel our cells.
5. Which organ in the human body is known to perform the most functions?
The liver is an incredibly complex organ and is considered the body's powerhouse, responsible for over 500 different functions. Its key roles include filtering toxins from the blood, helping to regulate blood sugar levels, producing cholesterol and proteins, and creating bile, which is essential for digesting fats.
6. How do human bodies differ based on their reproductive organs?
The primary difference is the reproductive system, which is designed for creating new life. Males have organs like the testes, which produce sperm, while females have organs like the ovaries, which produce eggs. These distinct sets of organs determine a person's biological sex and the role they play in reproduction. All other major organ systems, like the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems, are the same in both males and females.
7. Can a person live without all of their organs? Explain why some are vital.
No, a person cannot live without all their organs. Certain organs are considered vital, meaning the body cannot function without them. These include the brain, heart, liver, at least one lung, and at least one kidney. Life is impossible without the functions these organs perform. However, a person can live without some other organs, such as the appendix, gallbladder, or one of the two kidneys, as the body can adapt or be supported by medical intervention.
8. What are some amazing facts about human organs?
The human body is full of incredible organs with surprising abilities. Here are a few interesting facts:
- Your heart beats over 100,000 times a day, pumping blood through thousands of miles of blood vessels.
- The brain itself cannot feel pain because it lacks pain receptors.
- The liver has a remarkable ability to regenerate. It can regrow to its full size even if a significant portion is removed.
- Your stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve some metals.
- The skin is the body's largest organ and constantly renews itself to protect you from the environment.









