




Why Is the Hubble Space Telescope So Important for Science?
Kids, did you know over the last century, scientists have discovered many new mysterious cosmic objects such as black holes, exoplanets, and new moons on planets? The recent discoveries may be impressive, but in just a few remarkable years in the 1920s, one man single-handedly changed our perception of our place in the universe. His name was Dr. Edwin Powell Hubble.

Dr. Edward Powell Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble was born in 1889 in Missouri, a state in the Western region of the United States. He developed an early passion for astronomy when he was 8 years old after receiving his first telescope. Let’s read more about scientist Edwin Hubble.
All About Scientist Edward Hubble
In 1917, scientist Edward Hubble received a life-changing job offer from George Ellery Hale, founder of the Mount Wilson Observatory in California, while working on his doctorate. But the opportunity came at a bad time. The United States entered World War 1st, and Hubble was enlisted in the military.
In 1919, Major Hubble returned from the war and immediately travelled to the Mount Wilson Observatory and announced that he was ready to start observing.
In 1923 Hubble made his first important discovery using the most advanced technology of that time. He discovered that some variables reside in galaxies outside our own. At the time, it was known that the universe consisted only of the Milky Way.
Hubble's discovery that our galaxy, the Milky way, is one of many that forever changed how we viewed our place in the universe.
Following this incredible discovery, Hubble began to sort and classify the galaxies he discovered. He arranged his discoveries according to their visual appearance. The first spiral, then elliptical, then lenticular, and then those which were irregular in appearance. This became known as the Hubble sequence and is still the most popular system for classifying galaxies.
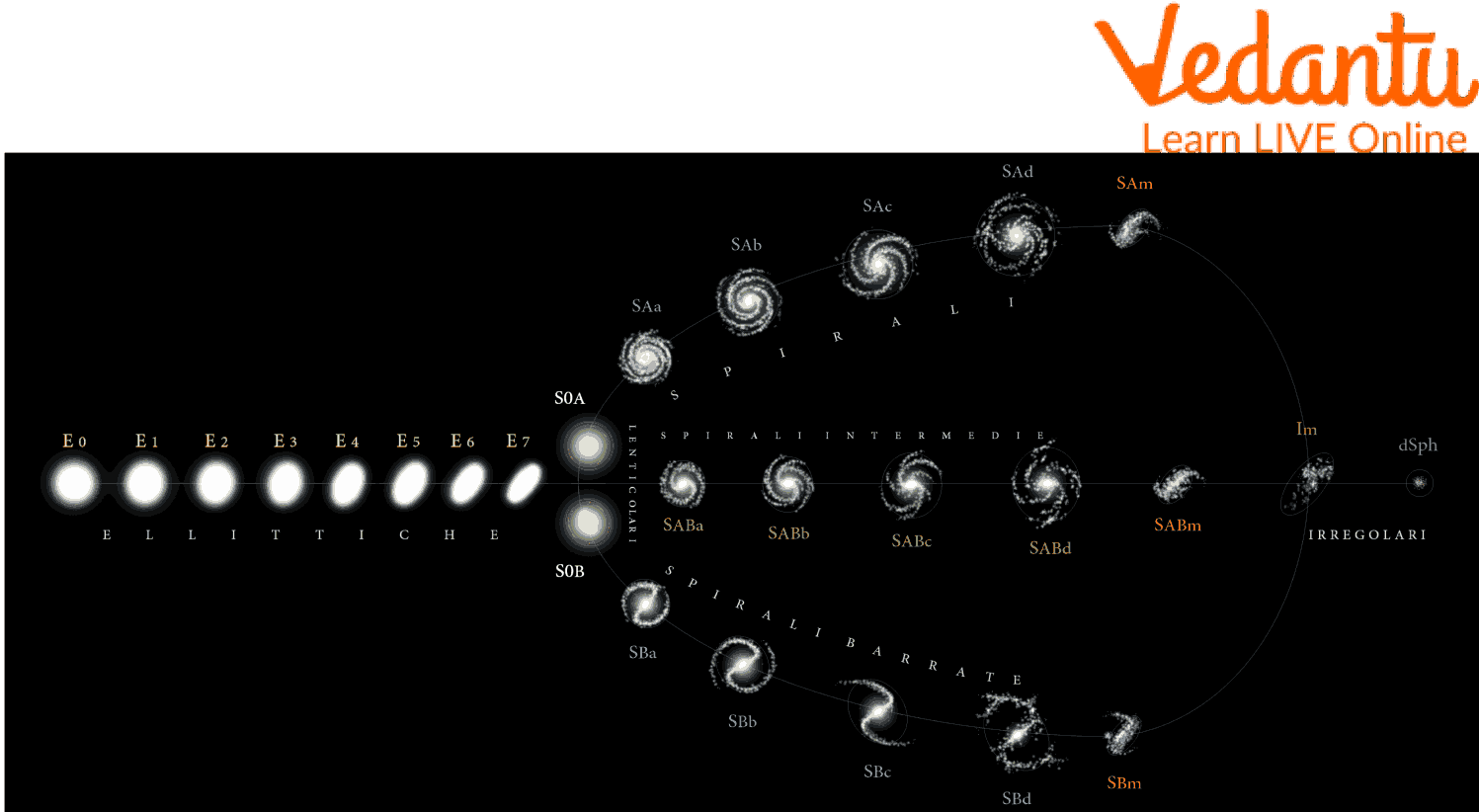
The Hubble Sequence
Edwin Hubble Discoveries
The Hubble space telescope was named after him by NASA and the European Space Agency. He was also the man behind the great Hubble's law, which proved that the universe is continuously expanding. Now let's learn about some more interesting discoveries made by the scientist Edward Hubble:
Hubble's greatest achievement came in 1929 when he determined that the light we receive from galaxies is redder the further away they are from us.
With this discovery of red light theory, Hubble was able to deduce that the farther away a galaxy is, the faster it recedes.
The redshift experiment was called Hubble's Law. The observational discovery of this relationship overturns the conventional view of a static universe.
Hubble's law also demonstrated that the universe was expanding. It also provided the first observational evidence for the big bang theory.
The discovery of Hubble's Law also led the great scientist of that time, Albert Einstein, to admit that ignoring the ideas of Hubble was some 'greatest blunders of life.'
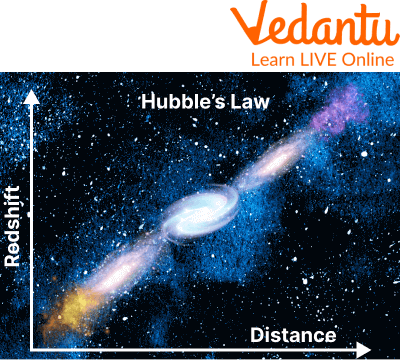
The Hubble's Law of Galaxies
Hubble Space Telescope Facts
Children, have you heard about the Hubble space telescope before? If not, let's learn some Hubble space telescope facts:
The European Space Agency and NASA, after 30 years of Hubble's death, named their new space telescope after Edward Hubble.
They chose Hubble for naming the telescope as he was the obvious choice when naming a new observatory that would add more to the field of astronomy.
Edward Powell Hubble changed our perception of the universe and our place within it. And his spirit of discovery lives on today through the Hubble Space Telescope.
The Hubble Space Telescope
Summary
Edward Powell Hubble was an American astronomer who became famous for demonstrating the existence of other galaxies in the universe. He died in 1953, but Hubble was a skilful athlete during his school days. Hubble focused on astronomy, philosophy, and mathematics at the University of Chicago. Hubble was an influential scientist, and his work led to many breakthroughs in astronomy. This article above helped us learn about Edwin Hubble, his discoveries and his life.
FAQs on Fascinating Facts About the Hubble Space Telescope
1. Who was Edwin Powell Hubble?
Edwin Powell Hubble (1889-1953) was a pioneering American astronomer whose work revolutionised our understanding of the cosmos. He is most famous for providing conclusive evidence that the universe is much larger than just our own Milky Way galaxy and that it is continuously expanding.
2. What is considered Edwin Hubble's most important discovery?
Edwin Hubble's most significant discovery, now known as Hubble's Law, is that the universe is expanding. He observed that galaxies are moving away from Earth, and the speed at which they are moving away is proportional to their distance from us. This was the first observational evidence to support the Big Bang theory.
3. How did Edwin Hubble prove that other galaxies exist outside the Milky Way?
Before Hubble, scientists believed the Milky Way was the entire universe. Hubble proved this wrong by using the powerful Hooker Telescope at Mount Wilson Observatory. He observed a type of star called a Cepheid variable in the Andromeda Nebula. By measuring its brightness, he calculated its distance and proved it was located far outside the boundaries of the Milky Way, confirming that Andromeda was a separate galaxy, not a nebula within our own.
4. How did Hubble's discoveries change our view of the universe?
Hubble's discoveries fundamentally changed our perspective on the universe in two major ways:
- Size and Scale: He showed that the universe was not just one galaxy (the Milky Way) but was filled with billions of other galaxies, making it vastly larger than ever imagined.
- Dynamic Nature: He replaced the old idea of a static, unchanging universe with a dynamic model of an expanding universe, which gave rise to the modern Big Bang model of its origin.
5. Why is the Hubble Space Telescope named after Edwin Hubble?
The Hubble Space Telescope, a large observatory launched into space in 1990, is named in honor of Edwin Hubble because his discoveries laid the foundation for modern cosmology. Naming the telescope after him was a tribute to the astronomer whose work on extragalactic astronomy and the expanding universe defined the very questions the telescope was designed to explore in greater detail.
6. Did Edwin Hubble ever win a Nobel Prize for his work?
No, Edwin Hubble did not receive a Nobel Prize. Despite his groundbreaking work that formed the basis of modern cosmology, astronomy was not considered a field of physics by the Nobel Committee at that time. The rules were changed shortly after his death, but Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously.
7. What is the difference between an astronomer's discovery and an invention?
This is an important distinction in science. An invention is the creation of a new device, process, or tool, like the invention of the telescope itself. A discovery, which is what astronomers like Hubble make, is the act of finding or identifying something that already exists in nature but was previously unknown to humans, such as a new galaxy or a fundamental law like the expansion of the universe.
8. Apart from the Hubble Space Telescope, what else is named after Edwin Hubble?
To honor his monumental contributions to science, several other objects have been named after Edwin Hubble. The most notable examples include the Asteroid 2069 Hubble and the Hubble Crater located on the Moon.









