




An Overview of Battery
Battery is something which we use in our daily life more oftenly. The sizes of a battery may vary. Batteries may be as small as which may fit in toys called button batteries because their size is similar to the size of button and batteries may be as large as what may be used to generate electricity to supply light for home appliances when powered. A battery is something which can store electricity. Some batteries can be used again and again because they are rechargeable while other batteries are only used once and can be discarded.
What is Battery?
A battery is a device which is used to convert chemical energy into electric energy. It is an electrochemical device. A battery may be charged with chemical reactions or may be charged by electric current. We are aware of a term called ‘cell’ which we used in clocks, remotes of t.v, remotes of air conditioners, remote control toys, etc. So, the battery is basically made up of multiple cells joined together either in series position or in a parallel position.

Battery
Parts of Battery
Battery consists of mainly three parts which are discussed below:
Anode: Anode is the negatively charged part of the battery.
Cathode: The cathode is the positively charged part of the battery.
Electrolyte: An electrolyte is a paste-like substance which is used to separate an anode from a cathode and helps in the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy.
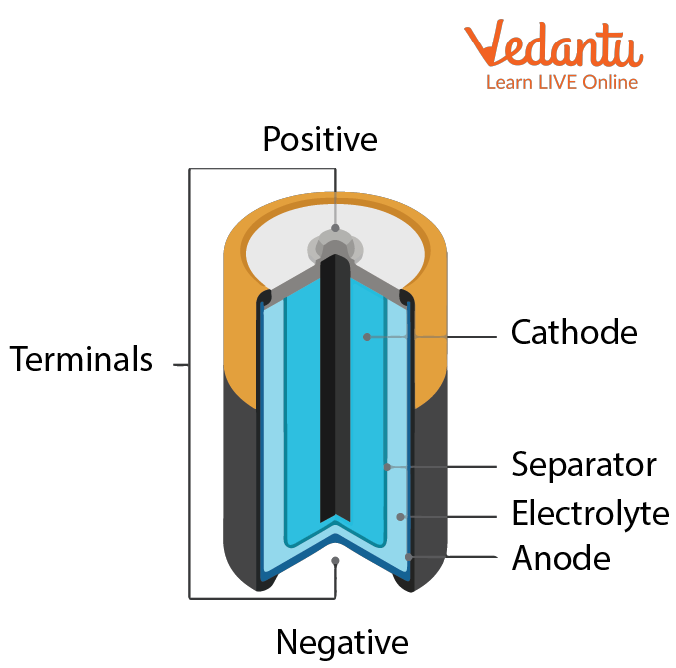
Parts of Battery
How a Battery Works
Battery is used to generate electricity. Electricity is produced by the movement of electrons through a conductive path. So the path followed by the electron is called a circuit. A battery consists of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. As an anode is negatively charged, it means it consists of extra electrons from the cathode. So, electrons from the anode flow towards the cathode as shown in the following picture. Due to the flow of electrons from one electrode to another electrode, an electric current is produced.

How a Battery Works
Types of Batteries
Batteries are basically of two types: primary battery and secondary battery.
Primary batteries are those batteries which are used only once, which means that they cannot be charged again. In batteries, certain types of electrochemical reactions occur. So, the electrochemical reaction that occurs in primary batteries is irreversible in nature which means the product cannot be converted into a reactant. So, due to the irreversible nature of the electrochemical reaction, primary batteries cannot charge or be used again. Example: zinc-carbon battery, dry cell.

Primary Batteries
Secondary batteries are those batteries which can be recharged again and again add reused. This is because of the reversible nature of the electrochemical reaction which is occurring inside the battery. For example, lithium-ion batteries, nickel-cadmium batteries, etc.
Secondary Battery
What is the Current out of a Battery?
Current is of two types: Direct current also called DC and alternating Current also called AC. The current which is generated through batteries is direct current. The difference between these two types of current is their direction of flow. Direct current will flow only in one direction while Alternating current will flow in two directions. In our daily life, the current which comes into our house from electricity mains is alternating current while the current which is generated through batteries is direct current.
Some Facts about Batteries
A day in a year is celebrated especially for batteries called National Battery Day which is celebrated on 18 February.
Power of batteries can be lost when the temperature is too high.
Every battery has the same components irrespective of its size.

National Battery Day
Sample Questions
1. What is a cell?
Ans: A cell is a device which is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy to generate electricity.
2. Name some different types of batteries?
Ans: There are three main types of batteries called alkaline batteries, nickel metal hydride, and lithium-ion batteries.
Summary
Battery is something which can produce current. Batteries vary in size; they can be as small as a button and can be as large as a huge box like inverter batteries. Every battery consists of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. A battery is used to convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
FAQs on Interesting Facts about Battery
1. What is a battery in simple terms?
A battery is a device that stores chemical energy and converts it into electrical energy. It acts like a portable power source, containing one or more electrochemical cells that produce an electric current when connected to a circuit. This allows us to power devices like remote controls, toys, and flashlights without plugging them into a wall socket.
2. Who is credited with inventing the first true battery?
The first true battery was invented by the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta in the year 1800. His invention, known as the 'voltaic pile', consisted of stacked pairs of copper and zinc discs separated by cloth or cardboard soaked in brine. This was the first device to produce a steady, continuous electric current.
3. How does a battery actually generate electricity?
A battery generates electricity through a chemical reaction. Inside every battery, there are three main parts: a negative electrode (anode), a positive electrode (cathode), and a chemical substance called an electrolyte. The electrolyte causes a chemical reaction between the anode and cathode, making electrons build up at the anode. When you connect the battery to a device, these electrons flow from the negative to the positive terminal through the circuit, creating an electric current.
4. What is the difference between a primary and a secondary battery?
The main difference is that primary batteries are single-use and cannot be recharged, while secondary batteries are rechargeable. The chemical reactions in a primary battery are irreversible. Once the chemicals are used up, the battery is dead. In a secondary battery, applying an external electrical current can reverse the chemical reaction, restoring the battery's charge so it can be used again.
5. What are some common examples of primary and secondary batteries?
Common examples of batteries we use in daily life include:
- Primary Batteries (non-rechargeable): These include AA or AAA alkaline batteries used in TV remotes and toys, and small coin-shaped lithium cells used in watches.
- Secondary Batteries (rechargeable): These include the lithium-ion batteries in our smartphones and laptops, and the lead-acid batteries used to start cars.
6. Is it true that the world's largest battery is in Australia?
Yes, one of the world's largest and most famous battery installations is the Hornsdale Power Reserve in South Australia, often called the 'Tesla Big Battery'. It is a massive lithium-ion battery system designed to store energy from wind farms and stabilize the power grid, providing electricity during peak demand or outages.
7. How did the invention of the battery change the world?
The invention of the battery was revolutionary because it provided the first source of portable and continuous electricity. This was crucial for early scientific experiments in electricity and magnetism. Over time, it led to the development of telegraphs, flashlights, and eventually all modern portable electronic devices like mobile phones, laptops, and electric vehicles, making technology accessible anywhere.
8. Why is it so important to recycle batteries properly?
Properly recycling batteries is crucial for environmental protection. Batteries contain heavy metals and toxic chemicals like lead, mercury, and cadmium. If thrown in regular trash, these substances can leak into the soil and groundwater, causing pollution. Recycling recovers valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel for reuse in new batteries, reducing the need for new mining and conserving natural resources.









