How to Transform Simple, Compound, and Complex Sentences with Examples
The transformation of sentences simple, compound, complex exercises with answers pdf is a crucial tool for enhancing English grammar skills. Mastering sentence transformation helps students improve writing clarity, construct varied sentences, and perform well in school assignments. This page provides definitions, clear rules, tables, examples, and practical exercises that support step-by-step learning and application.
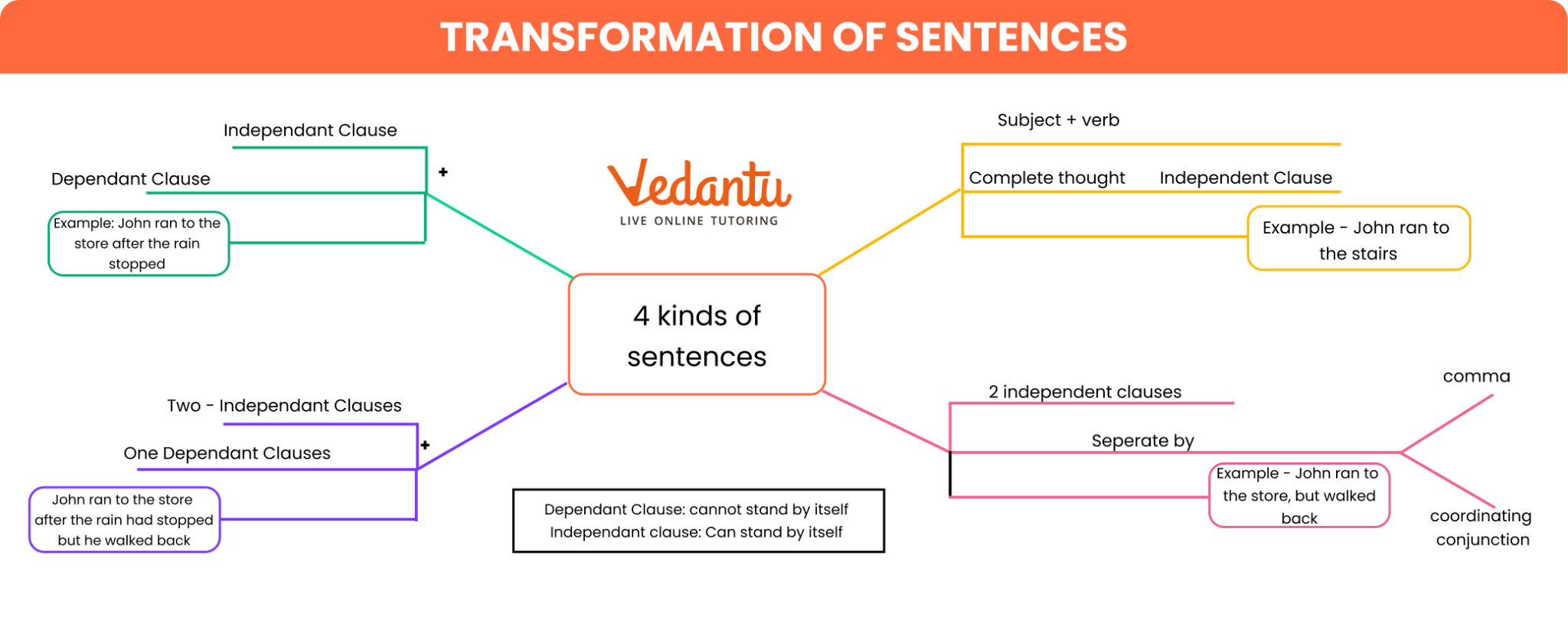
Types of Sentences and Their Transformation
| Sentence Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | One independent clause | She plays cricket. |
| Compound | Two independent clauses joined with a coordinator | She plays cricket, and he watches TV. |
| Complex | One independent and at least one dependent clause | She plays cricket because she enjoys it. |
**Understanding sentence transformation** is key for students as it provides flexibility in expression. Changing a simple sentence into compound or complex forms, or vice versa, teaches how context and meaning can shift with structure. This is especially useful for creative writing and formal communication.
Transformation of Sentences Simple, Compound, Complex Exercises with Answers PDF: Definition & Importance
**Sentence transformation** is converting a sentence from one form (simple, compound, complex) to another without altering its intended meaning. The transformation of sentences simple, compound, complex exercises with answers pdf strengthens accuracy, enhances vocabulary, and diversifies writing style for students of all grades.
This process helps in various grammar topics, such as Simple Sentences, Compound Sentences, and Complex Sentences. Practicing sentence transformation is vital for clarity in communication.
**Simple sentences** contain only one main clause and present a single idea.
**Compound sentences** join two independent clauses with conjunctions like 'and', 'but', or 'or'.
**Complex sentences** combine an independent clause with one or more dependent clauses, often using words like 'because', 'although', or 'when'.
Explore More Grammar Concepts
Rules and Tips for Simple, Compound and Complex Sentences Transformation Exercises
**Applying proper transformation rules** ensures accurate expression. The transformation of sentences simple, compound, complex pdf and worksheet sets help students systematically practice these changes while learning connectors and clause structures.
Consider checking related exercises such as Clauses Exercises or Types of Sentences Exercises to boost comprehension and flexibility in content creation.
**To change a simple sentence to compound,** split the complete idea into two main clauses joined by coordinators (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so).
**To convert a compound to simple,** compress the coordinated ideas into a single thought, often by using participles or prepositions.
**To transform complex to compound,** replace the subordinate clause with a main clause, using suitable conjunctions.
Practice with worksheets for each sentence type to reinforce skills. Download resources like a simple, compound complex sentences worksheet with answers for extra practice.
Sentence Correction Exercises
Practical Simple, Compound and Complex Sentences Transformation Exercises
Practicing transformation of sentences simple, compound, complex exercises with answers can significantly enhance your grammar understanding. Below are sample exercises, which you can see in the form of both practice and ready-to-use answer keys.
For more resources, see Simple, Compound and Complex Sentence Exercises or download the simple compound complex sentences transformation exercises pdf provided by Vedantu for classroom or personal revision.
Exercise Sample 1
Transform the following:
Simple: Having finished his work, he went home.
Compound: He finished his work and went home.
Complex: After he finished his work, he went home.
Exercise Sample 2
Transform the following:
Simple: Besides being rich, he is kind.
Compound: He is rich, and he is kind.
Complex: Though he is rich, he is kind.
These exercises, available in transformation of sentences simple, compound, complex exercises with answers pdf format, support learners moving from foundational knowledge to competent application. They are suitable for all levels, including class 7 and class 8, with pdf sets and answers for easy review.
Practice More Transformation Exercises
Common Errors and Solutions in Sentence Transformation
**Frequent errors occur** in sentence transformation when connectors are used incorrectly or clauses are wrongly structured. Use transformation of sentences simple compound complex exercises with answers pdf to identify and correct such mistakes. Regular practice helps avoid run-on sentences and mismatched clauses.
If you need more practice, try related quizzes like the Assertive to Interrogative Sentence Transformation Exercises for a broader understanding of sentence manipulation.
Advantages of Practicing Transformation of Sentences Simple, Compound, Complex Exercises
**Consistent practice** of sentence transformation ensures versatility in writing. Students gain confidence expressing the same idea in multiple ways. This skill is invaluable for paragraph writing, essay composition, and formal communication.
For more support on sentence construction, visit materials on Sentence Structure and Grammar Exercises for comprehensive learning paths.
Improves writing flexibility and clarity.
Reinforces understanding of grammar rules.
Boosts exam performance and daily communication.
Types of Sentences Explained
Mastering the transformation of sentences simple, compound, complex exercises with answers pdf builds a strong grammar foundation. By practicing varied sentence forms and applying key rules, learners improve expression, avoid common errors, and achieve better results in academic tasks. Vedantu provides detailed resources, worksheets, and solutions to ensure confident and effective sentence construction at every learning stage.
FAQs on Simple, Compound, and Complex Sentences: Definitions, Rules, and Practice
1. What are simple, compound, and complex sentences?
Simple, compound, and complex sentences are the three main types of sentence structures in English grammar, important for writing and exams.
Simple sentence: Has one main idea or clause.
Compound sentence: Combines two main clauses joined by a conjunction (and, but, or).
Complex sentence: Contains a main clause with one or more dependent (subordinate) clauses, linked by words like because, after, although.
These types help express ideas with clarity and are essential for mastering sentence structure and transformation exercises.
2. What is the rule for transforming a simple sentence into a compound sentence?
To change a simple sentence into a compound sentence, split the main idea into two clauses and join them using a coordinating conjunction.
Follow these steps:
- Identify the key idea in the simple sentence.
- Express it as two separate clauses, both able to stand alone.
- Join them with a coordinating conjunction such as and, but, or, so.
3. How do you identify a complex sentence?
A complex sentence is recognized by the presence of a main clause and at least one dependent (subordinate) clause.
Key features:
- It has one main idea (independent clause).
- Contains one or more subordinate clauses beginning with words like because, since, after, although.
- The dependent clause cannot stand alone.
4. What are the differences between simple, compound, and complex sentences?
The main differences are in the number and type of clauses in each sentence structure.
- Simple: One clause, one idea (e.g., "He reads every day.")
- Compound: Two main clauses joined with a conjunction (e.g., "He reads every day and writes in his journal.")
- Complex: Main clause plus one or more dependent clauses (e.g., "He reads every day because he loves books.")
5. Can you give 5 examples of compound sentences?
Here are 5 example compound sentences, using coordinating conjunctions:
- She finished her homework and went out to play.
- I wanted to buy the book, but it was too expensive.
- He was tired, so he went to bed early.
- We can go to the park, or we can stay home.
- The sun set, yet the children kept playing.
6. Where are these sentence transformations used in exams?
Sentence transformation exercises are commonly found in school, board, and entrance exams.
- English grammar sections often include them.
- Appearing in questions that ask you to change sentence types.
- Used in writing, editing, and sentence completion sections.
- Essential for classes 6 to 10 and higher-level exam preparation.
7. What is the rule for transforming a complex sentence into a simple sentence?
To transform a complex sentence into a simple sentence, express the meaning using a phrase or single clause without subordinate connectors.
- Remove the dependent clause.
- Replace it with a participle, infinitive, or phrase.
8. Why is sentence transformation important for higher-level writing?
Mastering sentence transformation is vital for advanced writing as it develops flexibility and clarity in expression.
- Enables you to write varied sentence structures for better style.
- Improves coherence and flow in essays and reports.
- Essential for persuasive, descriptive, and creative writing tasks.
9. What are the most common mistakes in sentence transformation?
Common mistakes when transforming sentences include:
- Changing the original meaning during transformation.
- Using incorrect conjunctions or subordinate clauses.
- Making fragments or run-on sentences instead of complete ones.
- Confusing simple, compound, and complex rules.
10. Are conjunctions the same for all sentence types?
No, different sentence types use different conjunctions:
- Compound sentences use coordinating conjunctions (and, but, or, so, yet).
- Complex sentences use subordinating conjunctions (because, although, since, after).
- Simple sentences generally do not use conjunctions, as they have one clause.