10 Common Omnivores Animals Names and What They Eat
Are you curious about how some animals eat both plants and meat? This page explores **omnivores animals names** with clear examples, images, and their diets. Discover the unique features of omnivorous animals and learn why they are important for students’ vocabulary, understanding, and school projects. Let’s explore the diverse world of omnivorous animals in English together!
Omnivorous Animals Names: Chart with Diets and Examples
| Animal Name | Diet Example | Real-life Use |
|---|---|---|
| Bear | Fish, berries, honey | Found in forests and nature documentaries |
| Crow | Insects, fruits, grains | Common near towns and cities |
| Pig | Roots, nuts, small animals | Commonly seen on farms |
| Human | Vegetables, fruits, meat | Our own varied diet |
| Dog | Meat, bread, vegetables | Popular pets and street animals |
| Raccoon | Frogs, berries, eggs | Known as urban scavengers |
| Chicken | Seeds, worms, insects | Common farmyard bird |
| Rat | Seeds, meat, cheese | Found in homes, fields, cities |
| Ant | Fruits, dead insects, grains | Observed almost everywhere |
| Fox | Rabbits, fruits, insects | Woodlands and rural areas |
| Turtle | Fish, plants, insects | Common in biology classes |
| Squirrel | Nuts, fruits, bird eggs | Frequent in parks and gardens |
| Duck | Seeds, insects, small fish | Seen in ponds or on farms |
| Ostrich | Plants, insects, small animals | Largest living bird |
| Chimpanzee | Fruits, leaves, insects | Popular zoo animals |
| Seagull | Fish, eggs, grains | Often by the sea |
| Mouse | Grains, fruits, insects | Found in homes, fields |
| Sparrow | Seeds, insects, bread | Common urban bird |
| Catfish | Small fish, plants, insects | Freshwater habitats |
| Baboon | Fruits, seeds, insects | African monkey species |
These omnivores animals images with names and descriptions help you master animal vocabulary. Having both text and pictures makes it simple to identify and remember these species.
What Are Omnivorous Animals? Meaning and Explanation
Omnivorous animals are species that eat both plants and animals. Their flexible diet includes seeds, fruits, insects, and meat. This adaptability sets them apart from herbivores (plant-eaters) and carnivores (meat-eaters). The word 'omnivore' comes from Latin: 'omni' meaning "all", and 'vorare' meaning "to eat".
Many common animals, such as humans and pigs, are omnivores because they thrive on a mixed diet. Understanding omnivores animals names and their characteristics can enhance your English vocabulary and nature knowledge. Learn more about herbivores animals and animal names to see the difference.
Key Features of Omnivorous Animals for Students
Most **omnivorous animals** have a combination of teeth—sharp ones for tearing meat and flat ones for grinding plants. Their digestive system can handle both animal and plant food. They often live in various environments, from forests to cities, and can survive on whatever food is available. **Bears, dogs, chickens**, and even **humans** are all examples of true omnivores.
Recognising these **features makes identifying omnivores easier**, especially when describing animals for schoolwork or projects. This knowledge also helps when creating an **omnivores animals chart with names** or choosing the right images for presentations.
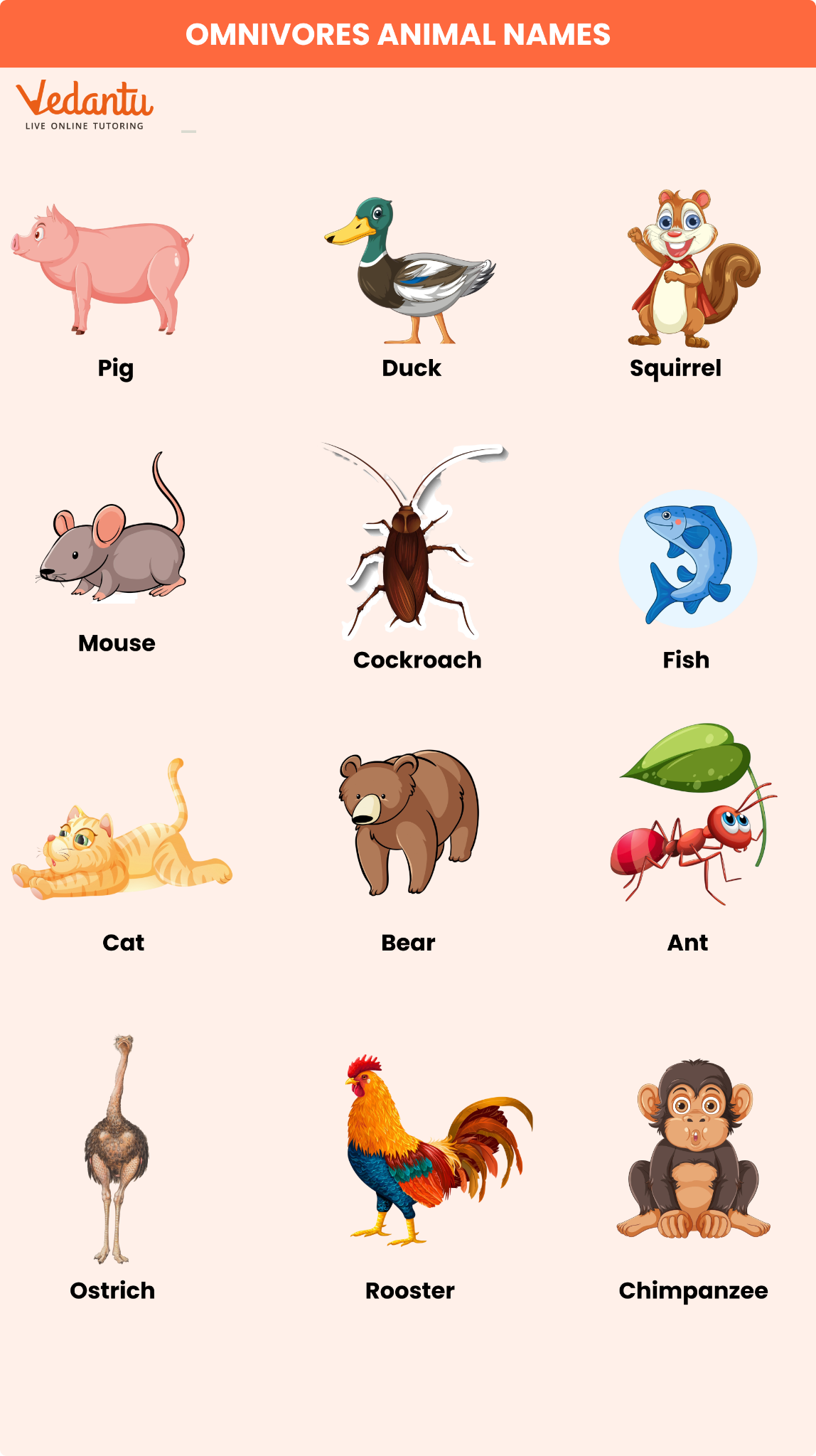
List of 20 Omnivores Animals Names (with Images and Examples)
Here’s a handy **omnivores animals names list** to expand your vocabulary and visual memory. You may even find images of omnivores animals with names in English to help with memorisation. These are found across different habitats:
Bear
Crow
Pig
Human
Dog
Raccoon
Chicken
Rat
Ant
Fox
Turtle
Squirrel
Duck
Ostrich
Chimpanzee
Seagull
Mouse
Sparrow
Catfish
Baboon
If you need an **omnivores animals chart with names** or pictures of omnivores animals with their names, use this list for assignments and projects. Also, check resources like names of things for kids to expand your word bank.
Importance of Omnivorous Animals in Ecosystems
Omnivorous animals keep food chains balanced. By eating both plants and animals, they control populations on both sides. This prevents certain plants or animals from overpopulating. Their adaptability also means omnivores can survive changes better than other creatures, often helping them thrive in new or urban habitats.
Studying the roles of omnivores helps students understand biodiversity. If you want to see more about animal roles, visit the wild animals name page.
How Knowing Omnivorous Animals Names Helps You
Learning the **omnivores names of animals** boosts your animal vocabulary, helping in science, English, and social studies. It aids in reading animal stories or understanding news articles better. School presentations often require an **omnivores animals list with names, pictures, and examples** for clarity and creativity.
Next time you answer “write the names of two herbivores, two carnivores and two omnivores’ animals,” you’ll have plenty of examples. For hints, explore animal pictures with name for kids as well as other educational activities in Vedantu’s kids topics section.
Use Cases and Examples of Omnivorous Animals
Let’s look at how to use **omnivores animals names** in real-life sentences and situations. This ensures strong communication and correct animal classification in projects, essays, and casual conversation:
The bear is an omnivorous animal, often seen eating fish and berries in forests.
A crow picks seeds, insects, or leftover bread around houses.
Many humans enjoy vegetables and chicken, showing their omnivorous diet.
A fox may hunt rabbits but also eat fruits when hungry.
A pig roots for fruit and small animals, being a classic farm omnivore.
For more example sentences and creative uses, try exploring exercises under grammar exercises and learn how to create animal charts in English class.
Want to Learn More About Animal Diet Types? Herbivores, Carnivores, and Omnivores
Understanding animal diets is key for many school lessons. **Herbivores animals** eat only plants and are different from omnivores, who eat both plants and meat. **Carnivorous animals** rely solely on animal foods. If you want to master all types, check out these related topics for a complete understanding:
Herbivores animals name – animals who eat only plants
Animal names – a great list for children
These pages help you answer questions like "write the names of two herbivores, two carnivores and two omnivores’ animals" and increase your English fluency. For students, this supports reading, project work, and essay writing.
Page Summary
This topic covered the definition, key features, and a list of **omnivores animals names** with practical examples and images for student learning. By distinguishing between omnivores, herbivores, and carnivores, you build strong animal science vocabulary. Use Vedantu’s resources to further grow your English skills and knowledge about animals.
FAQs on Omnivores Animals Names in English with Examples and Hindi Meaning
1. What are omnivores animals?
Omnivores animals are those that eat both plants and animals as their food sources. This mixed diet distinguishes them from herbivores and carnivores.
- Eat both plant and animal matter
- Examples: Bear, Pig, Crow, Human, Dog
- Part of animal classification in Science and English vocabulary
2. Name 10 omnivores animals.
Ten examples of omnivores animals names commonly found in English vocabulary are:
- Bear
- Pig
- Crow
- Human
- Dog
- Rat
- Fox
- Chimpanzee
- Chicken
- Ant
3. What do omnivore animals eat?
Omnivore animals eat a variety of foods including both plants and animals.
- Plants: fruits, grains, seeds, vegetables
- Animals: insects, fish, small animals, eggs, meat
- This varied diet helps them survive in different environments
4. Give 5 omnivores animals names with examples.
Here are five omnivores animals names with typical foods they eat:
- Bear: fruits, fish, insects
- Pig: plants, worms, small animals
- Human: vegetables, fruits, meat
- Dog: meat, grains, milk
- Crow: seeds, insects, small animals
5. What is the difference between omnivores, carnivores, and herbivores?
Omnivores eat both plants and animals, carnivores eat only animals, and herbivores eat only plants.
- Omnivores: Bear, Human, Pig
- Carnivores: Lion, Tiger, Eagle
- Herbivores: Cow, Deer, Rabbit
6. Are dogs omnivores animals?
Yes, dogs are omnivores animals because they eat both plant and animal products.
- Dog food often includes meat, grains, vegetables
- They can digest and benefit from a mixed diet
- This is a common question in science and English exams
7. Can you give omnivores animals names in Hindi?
Here are omnivores animals names in Hindi:
- Bear: भालू
- Pig: सूअर
- Crow: कौआ
- Human: इंसान
- Dog: कुत्ता
8. Why is it important to learn omnivores animals names in English?
Learning omnivores animals names in English improves vocabulary, aids in Science and English exams, and helps in describing animals accurately.
- Useful for school assignments and projects
- Helps in story writing and daily conversation
- Essential for understanding the food chain and animal classification
9. Are humans classified as omnivores?
Yes, humans are considered omnivores because they eat both plant foods (like fruits and vegetables) and animal products (like meat, eggs, and dairy). This shows dietary variety, which is a key feature of omnivores.
10. Give example sentences using omnivores animals names in English.
Here are some simple sentences using omnivores animals names:
- Bears eat both fish and berries in the wild.
- Crows eat grains as well as insects.
- Humans eat vegetables, fruits, and meat.
- Chickens eat seeds and small bugs.
- Foxes hunt rabbits and also eat berries.