An Overview of Important Questions Class 8 Science Chapter 17
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 8 Science Chapter 17 Stars and The Solar System - 2025-26
1. From an exam perspective for the 2025-26 session, what is the fundamental difference between a star and a planet?
This is a frequently asked question in exams. The main differences are:
- Light Source: Stars, like our Sun, are celestial bodies that produce their own heat and light. Planets do not have their own light; they only reflect the light from a star they orbit.
- Motion: Planets revolve around a star in a fixed path called an orbit. Stars are not stationary but are so far away that their movement relative to each other is not easily noticeable. They appear to move across the sky due to the Earth's rotation.
- Nature: Stars are massive, hot balls of gas. Planets are much smaller bodies that can be rocky (like Earth) or gaseous (like Jupiter).
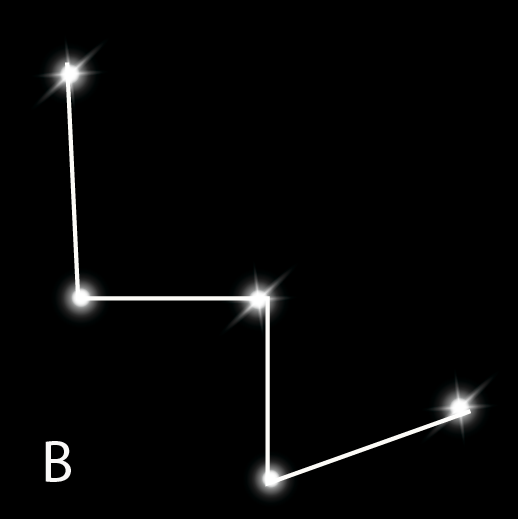
2. How can we locate the Pole Star in the night sky using a constellation?
The Pole Star (or Dhruva Tara) can be located using the Ursa Major constellation, also known as the Saptarishi or The Great Bear. To find it, first, identify the seven prominent stars forming a shape like a large ladle or question mark. Imagine a straight line connecting the two stars at the end of the ladle's bowl. If you extend this imaginary line northwards, it will point directly to a bright star that isn't moving. This is the Pole Star.
3. Why does the Pole Star appear to be stationary from any point on Earth?
The Pole Star appears to be fixed in the sky because it is situated very close to the Earth's axis of rotation, extended into space. As the Earth spins on its axis, all other stars seem to circle around this point. Since the Pole Star lies on this axis, it remains in the same position from our perspective, making it a reliable indicator of the north direction.
4. List the eight planets of our solar system in their correct order from the Sun.
For the CBSE Class 8 exam, it is crucial to know the correct order of the planets. Starting from the one closest to the Sun, they are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
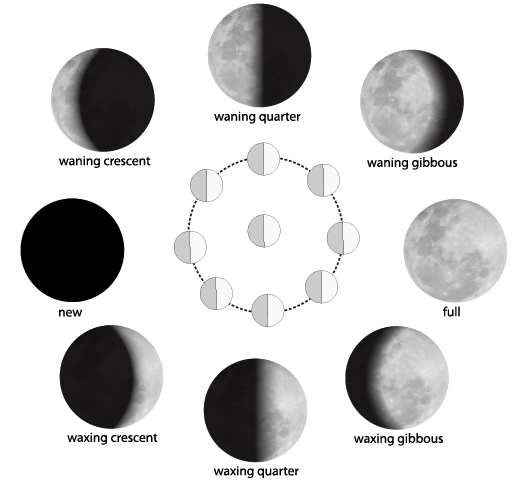
5. What are the phases of the moon and what causes them?
The different shapes of the bright part of the moon that we see over a month are called the phases of the moon. This phenomenon occurs for two reasons:
- The Moon does not produce its own light; it shines because it reflects sunlight.
- The Moon is constantly revolving around the Earth.
6. For a 3-mark question, how would you differentiate between an asteroid, a comet, and a meteor?
Here is a clear differentiation for scoring full marks:
- Asteroids: These are large, rocky celestial bodies that orbit the Sun. A large number of them are found in the asteroid belt, a region located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- Comets: These are lumps of ice, rock, and dust that orbit the Sun in highly elliptical paths. When a comet approaches the Sun, the ice turns into gas, forming a glowing head and a long tail that always points away from the Sun. Halley's Comet is a famous example.
- Meteors: Often called 'shooting stars', meteors are small pieces of rock or dust that burn up due to friction upon entering Earth's atmosphere, creating a bright streak of light. If a piece survives and lands on Earth, it is called a meteorite.
7. What makes Earth a unique planet capable of supporting life?
Earth's ability to support life is due to several critical factors, making it an important topic:
- Ideal Distance from the Sun: This allows for a moderate temperature range where water can exist as a liquid, which is essential for life.
- Presence of an Atmosphere: The atmosphere contains essential gases like oxygen for respiration and protects us by burning up most meteors.
- The Ozone Layer: A layer within our atmosphere that shields the surface from the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
- Abundance of Water: The presence of water in liquid form is crucial for all biological processes.
8. What are artificial satellites and what are their most important uses?
Artificial satellites are human-made objects that are launched into space to orbit the Earth or other celestial bodies. They are different from natural satellites like the Moon. Their important uses include:
- Communication: Transmitting television, internet, and telephone signals globally.
- Weather Forecasting: Observing cloud patterns and weather systems to predict weather.
- Remote Sensing: Monitoring Earth's geography, agriculture, and natural resources.
- Navigation: Providing precise location data for Global Positioning Systems (GPS).
9. Name the largest planet in our solar system and the planet known as the 'Red Planet'.
The largest planet in our solar system is Jupiter. The planet known as the 'Red Planet' is Mars, which gets its reddish colour from the iron oxide (rust) on its surface. These are common one-mark questions in exams.
10. What is a light-year and why is this unit necessary in astronomy?
A light-year is the distance that light travels in one full year. It is a unit of distance, not time. This unit is necessary because the distances between stars and galaxies are immense. Using kilometres or miles would result in incredibly large and impractical numbers. The light-year provides a more convenient and manageable scale for expressing these vast cosmic distances.
11. Why can't we see the stars during the daytime?
Stars are always in the sky, but we can't see them during the day. This is because our own star, the Sun, is much closer to us and its light is extremely bright. The Sun's light scatters throughout the Earth's atmosphere, making the sky so luminous that it overpowers the faint light coming from distant stars, rendering them invisible to our eyes.
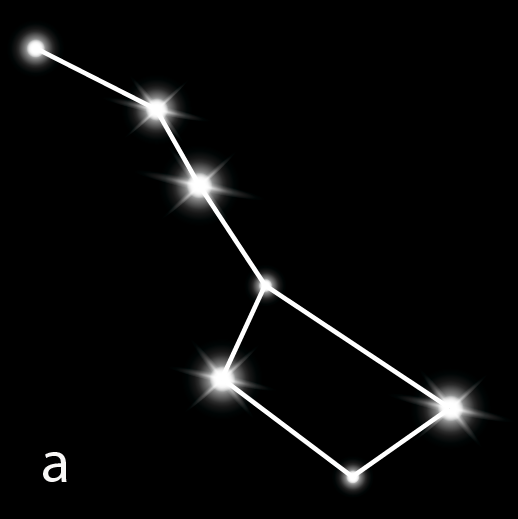
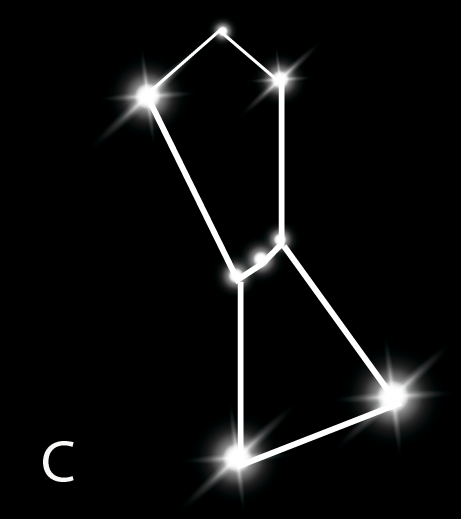
12. Describe the key features of the Orion constellation.
Orion, also known as 'The Hunter', is one of the most magnificent constellations in the night sky. Its key features are:
- It has seven or eight very bright stars.
- Three stars in the middle are aligned in a straight line, forming the 'belt' of the hunter.
- Four other bright stars appear to form a quadrilateral, outlining the hunter's body.
- The brightest star in the entire night sky, Sirius, can be located by extending the line of Orion's belt eastwards.
13. What was India's 'Mangalyaan' mission and why is it considered a significant achievement?
Mangalyaan, also known as the Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM), was India's first mission to another planet. Launched by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), it successfully entered Mars' orbit on September 24, 2014. It is a significant achievement because India became the first nation in the world to successfully reach Mars on its very first attempt, showcasing its advanced and cost-effective space technology.
14. Which planet is famous for its rings, and what are these rings made of?
Saturn is the planet renowned for its spectacular system of rings. These rings are not solid bands but are composed of billions of small particles of ice, rock, and dust, all orbiting the planet at different speeds. Although other gas giants like Jupiter also have rings, Saturn's are the largest and most easily visible from Earth.