
Our Environment Class 10 important questions with answers PDF download
Class 10 is a very important year for students as it is the first time students are attempting to write their board examinations. Their 10th board examination marks play a very important role in determining their future grades as well. In this article, we will take a detailed look into class 10 science chapter 13 important questions so that students can prepare better for their examinations. It is very important that students must utilize this time to study hard and these important questions will help students to revise better and go over the main points in the chapter. It is of importance that students be conscious of the important questions which have a high potential of coming within the exams. Students who don’t understand the topic alright must study these questions of sophistication for class 10 so that students can have a better understanding of the chapter and also know what are the important topics to specialize in.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. You can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Important Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Our Environment - 2025-26



Study Important Questions for Class 10 Chapter 13- Our Environment
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. A food chain always starts with
respiration
photosynthesis
decay
nitrogen fixation
Ans: Photosynthesis
2. Ozone layer is damaged by-
methane
carbon-dioxide
Sulphur-dioxide
CFCs
Ans: CFCs.
3. Which of the following limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain?
water
polluted air
deficient food supply
decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
Ans: Decrease in energy at higher energy levels.
4. Name the main source of energy in self-sustaining ecosystem?
Ans: Sun.
5. Write an aquatic food chain.
Ans: An aquatic food chain is as follows:
Phytoplankton $\to $ Zooplankton $\to $ Small fish$\to $ large fish.
6. Which of the following is non-biodegradable-?
paper
wood
cloth
plastic
Ans: plastic
7. Which of the following is not a terrestrial ecosystem-?
forest
desert
aquarium
grassland
Ans: Aquarium
8. What will happen if deer is missing in the given food chain?
Grass $\to $ Deer $\to $ Tiger
The population of tiger decreases and the population of grass increases
The population of grass decreases
Tiger will start eating grass
The population of tiger increases
Ans: Population of tiger decreases and population of grass increases.
9. What is trophic level?
Ans: The position that an organism occupied in a food chain is called trophic level.
10. Write a fresh water food chain?
Ans: Phytoplankton $\to $ zooplankton $\to $ small fish $\to $ large fish.
11. The decomposers in an ecosystem-
convert organic material to inorganic forms
convert inorganic material to simpler forms
convert inorganic material into organic compound
do not break down organic compound
Ans: Convert organic material to inorganic forms.
12. The second trophic level is always of-
herbivores
autotrophs
carnivores
producers
Ans: Herbivores
13. The percentage of solar radiation absorbed by all the green plants for the process of photosynthesis is about-
1%
8%
5%
10%
Ans: 1%
14. Which of the following belong to the same trophic level: grasshopper, spider, grass, hawk, and lizard?
Ans: Grasshoppers and spider
15. What is acid rain?
Ans: Any form of precipitation that contains high levels of nitric and sulfuric acids is called acid rain. It can also occur in the form of snow, fog, and tiny bits of dry material that settle to Earth.
16. The ecosystem of earth is known as-
biome
community
biosphere
association
Ans: Biosphere
17. Which of the following constitute a food chain?
Grass, goat and human
Goat, cow and elephant
Grass fish and goat
Grass, wheat and mango
Ans: Grass, goat, human.
18. Flow of energy in an ecosystem is always-
Unidirectional
bidirectional
multidirectional
no specific direction.
Ans: Unidirectional
19. Name the main source of energy in any self-sustaining system.
Ans: Sun
20. Which of the following in not a part of biotic component of an ecosystem: water, algae, fish, bacteria?
Ans: Water
21. Which of the following limits the of trophic levels in a food chain-
Water
polluted
deficient food supply
decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
Ans: Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels.
22. In natural ecosystems, decomposers include-
only bacteria and fungi
only microscopic animals
herbivores and carnivores
both (b) and (c)
Ans: Only bacteria and fungi
23. All living organisms of the earth constitute a-
biosphere
biotic community
biome
ecosystem
Ans: Biosphere
24. What are the various steps of food chains called?
Ans: Trophic levels
25. Which one is not biodegradable: paper, plastic, sewage?
Ans: Plastic
26. Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable items?
Grass, flowers and leather
Grass, wood and plastic
Fruit peels, cake and lime-juice
Cake, wood and grass
Ans: Groups (a), (c) and (d).
27. Which of the following constitute a food chain?
Grass, wheat and mango
Grass, goat and human
Goat, cow and elephant
Grass, fish and goat.
Ans: Grass, goat, human
28. Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
Carrying cloth-bag to put purchases in while shopping.
Switching off unnecessary lights and fans.
Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter.
All of the above.
Ans: All of the above.
29. Construct a food chain composing the following Snake, Hawk, Rats, Plants.
Ans: Plants $\to $ Rats $\to $ Snake $\to $ Hawks
30. Name the process that is a direct outcome of excessive burning of fossil fuels?
Ans: Global warming is a direct outcome of excessive burning of fossil fuels.
31. Using Kulhads as disposable cups to serve tea in trains, proved to be a bad idea. Why?
Ans: Yes, because making Kulhads on large scales leads to the loss of top soil.
32. Why is plastic not degraded by bacteria?
Ans: Plastic is not degraded by bacteria because they do not have enzymes which is used to degrade plastic.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. Give scientific terms for the following-
(a) The process of eating and being eaten
Ans: Food chain
(b) The relationship between abiotic and biotic component
Ans: Ecosystem
2. What is meant by environment? Name its components.
Ans: All the surroundings which have an impact on human lives is called an environment. It has two components-
(a) Abiotic component (non-living)
(b) Biotic component (living)
3. What is 10% law? Give an example
Ans: Only 10% of energy is available at the next trophic level in 10% law. For example-Suppose 1000 Joules of light energy emitted by the sun falls on the plants. Then the plants or first trophic level has 10 joules of energy in it. Now according to 10 percent law, only 10% of 10 joules of energy (which is 1 joule) will be available for transfer to the next trophic level, so that the herbivore will have only 1 joule of energy stored as food at the second trophic level. 10% of the remaining 1 joule will be transferred to third trophic level of carnivore. So, the energy available in the lion as food will be only 0.1 joule.
4. What is artificial ecosystem? Give two examples.
Ans: Ecosystem which are made by humans are known as artificial ecosystem. For example- Dams, parks.
5. Energy transfer is said to be unidirectional whereas biochemical transfer is said to be cyclic. Why?
Ans: Energy transfer is unidirectional because when the energy is absorbed by autotrophs from the sun, it is never reabsorbed by it. And when consumers eat up the producers directly or indirectly the energy transferred in this process can never be reversed in the food chain. In biogeochemical transfer is cyclic because chemical elements move from environment to organism and back to the environment.
6. Why is there a need to ban the use of polythene bags?
Ans: Polythene bags need to be banned because-
They are non-biodegradable.
Cannot be able to decompose them.
One of the cause of land pollution.
7. What is the significance of food chain?
Ans: Significance of food chain is-
It is used to transmit energy from one organism to the next.
It is the method by which a particular organism collects its food.
It is a way of depicting the flow of energy.
8. How would you dispose the following wastes?
(a) domestic wastes like vegetables peels
Ans: Domestic wastes should be disposed off in a pit.
(b) industrial wastes
Ans: Industrial wastes should be treated first to remove poisonous chemicals and then disposed off in water resources.
9. Why vegetarian food habit helps us in getting more energy?
Ans: Vegetarians obtain food directly from plants so due to 10 percent rule only 10% of energy is available at the successive level than previous level thus, vegetarian food habit helps us in getting more energy.
10. Write a food chain having two trophic levels.
Ans: Grass $\to $ deer
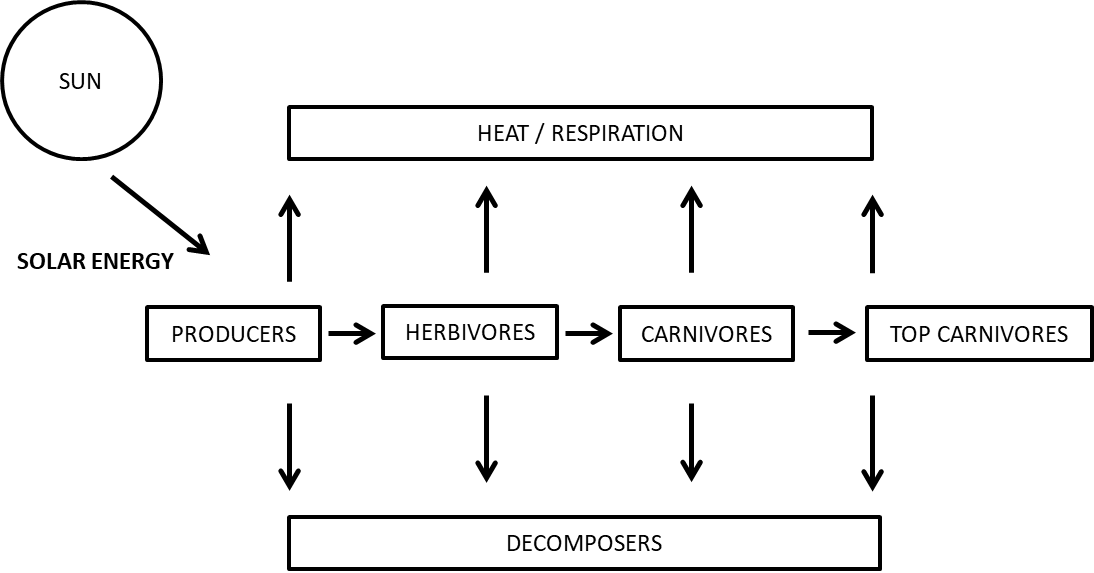
11. Diagrammatically represent the transfer of energy in a food chain.
Ans:
12. Consider the following food chains-
Plants $\to $ mice $\to $ hawks
If energy available at the producer level in both the food chains is 100J. In which case will hawks get more energy and how much?
Ans: Hawk get more energy in food chain having three trophic levels.
Plants $(100J)$ $\to $ mice $(10J)$ $\to $ hawks $(1J)$
Thus, Energy available to hawk is $\text{1J}$.
13. Why is there a need to ban the use of polythene bags?
Ans: Polythene bags need to be banned because-
They are non-biodegradable.
Cannot be able to decompose them.
One of the cause of land pollution.
14. What are the two functions of ecosystem?
Ans: The two functions of ecosystem are-
Ecosystem regulates essential ecological processes and life support systems and renders stability.
It regulates and maintains itself and resists any stresses or disturbances upto a certain limit. This is known as cybernetic system.
15. What percentage of solar energy is trapped and utilized by plants?
Ans: 1% of solar energy is trapped and utilized by plants.
16. What are the harmful effects of acid rain?
Ans: The harmful effects of acid rain are-
It effects human nervous system, respiratory system and digestive system.
It can also leach aluminium from the soil.
It affects soil fauna and lead to reduced forest productivity.
It may cause extensive damage to materials and terrestrial ecosystems such as water, fish, vegetation, soils, building etc.
17. Differentiate between abiotic and biotic components of ecosystem.
Ans: The difference between abiotic and biotic components of ecosystem is as follows:
Abiotic components | Biotic components |
Abiotic factors are the non-living things of an ecosystem. | Biotic factors are the living things of an ecosystem. |
It cannot adapt as per the environmental conditions | It can adapt to the changes in the environment |
Sunlight, temperature, water are the examples of abiotic components. | Plants, trees, and animals are examples of biotic components. |
18. Give any two methods reducing the problem of waste disposal.
Ans: The two methods reducing the problem of waste disposal are-
Practicing the 3 R's: Reduce, Reuse and Recycle.
By throwing biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste into separate dustbins so that recycling can be done easily.
19. Give reason: “Life on earth depends on the sun.”
Ans: All living beings needs energy to be alive and they get energy in the form of food. And the food directly or indirectly comes from green plants. Sun plays an important role to produce food in the process of photosynthesis.
20. What are trophic levels? Give an example of a food chain and state the different trophic level in it.
Ans: The position that an organism occupied in a food chain is called trophic level. An example of a food chain and state the different trophic level in it is as follows:
Plants (Producer) $\to $ Deer (Primary consumer) $\to $ Lion (Secondary consumer)
21. What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
Ans: Decomposers play a critical role in the flow of energy through an ecosystem. They break apart dead organisms into simpler inorganic materials, making nutrients available to primary producers.
22. What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Ans: Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen. Its molecular formula is ${{O}_{3}}$ . It forms a layer in the upper atmosphere. It is very essential for the life on this planet. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet radiation (UV) coming from sun as these radiations are very harmful causing skin cancer and cataract in humans. It also does harm to the crops.
23. How can you help in reducing the problems of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Ans: The two methods reducing the problem of waste disposal are-
Practicing the 3 R's: Reduce, Reuse and Recycle.
By throwing biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste into separate dustbins so that recycling can be done easily.
24. What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Ans: If all the organisms of one trophic level are killed, the food chain will become completely imbalanced. The organisms in the immediate higher trophic level will die out due to unavailability of food. Thus, the whole food chain will collapse.
25. Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Ans: Yes, the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level will be different for different trophic levels. It will not be possible to remove any organism in any trophic level without causing damage to the ecosystem.
26. If all the wastes we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Ans: If all the wastes we generate is biodegradable, it will have impact on the environment-
The production of harmful gases causes pollution.
Microbes will not be able to decompose all the biodegradable waste.
27. What are the problems caused by non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Ans: The problems caused by non-biodegradable wastes that we generate are-
Since, waste cannot be broken down into simpler forms hence they keep on accumulating which leads to pollution.
They cause diseases.
It also causes biological magnification.
28. What limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain.
Ans: The loss of energy from one trophic level to the next limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain.
29. What is the harm of clay cups?
Ans: The clay cups contain a chemical known as styrene that causes side effects such as fatigue, irritation and many more health problems. It causes depletion of top fertile soil.
30. State one reason to justify the position of man at the apex of most food chains?
Ans: As humans are an intelligent organism so they can take advantage of position by manipulation. This is the main reason the position of man at the apex of most food chains.
31. Which food chains are advantageous in terms of energy?
Ans: Short food chains i.e two step chains are more efficient in terms of energy.
32. If all the wastes we generate is bio-degradable what impact may this have on the environment?
Ans: If all the wastes we generate is biodegradable, it will have impact on the environment-
The production of harmful gases causes pollution.
Microbes will not be able to decompose all the biodegradable waste.
33. Write the harmful effect of ozone depletion.
Ans: The harmful effects of ozone depletion are-
Causes skin cancers
Causes eye cataracts
Leads to immune deficiency disorders.
Affect plant growth
Reduces agricultural productivity.
34. Which of the following will have the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in its body? Peacock, frog, Grass, Snake, Grasshopper
Ans: Peacock will have maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in its body among Peacock, frog, Grass, Snake, Grasshopper.
35. Why energy of herbivores never come back to the autographs?
Ans: Energy of herbivorous never comes back to autographs because flow of energy is always unidirectional in food chain.
36. Give the correct sequence of various & trophic levels in a food chain.
Ans: The correct sequence of various & trophic levels in a food chain is as follows:
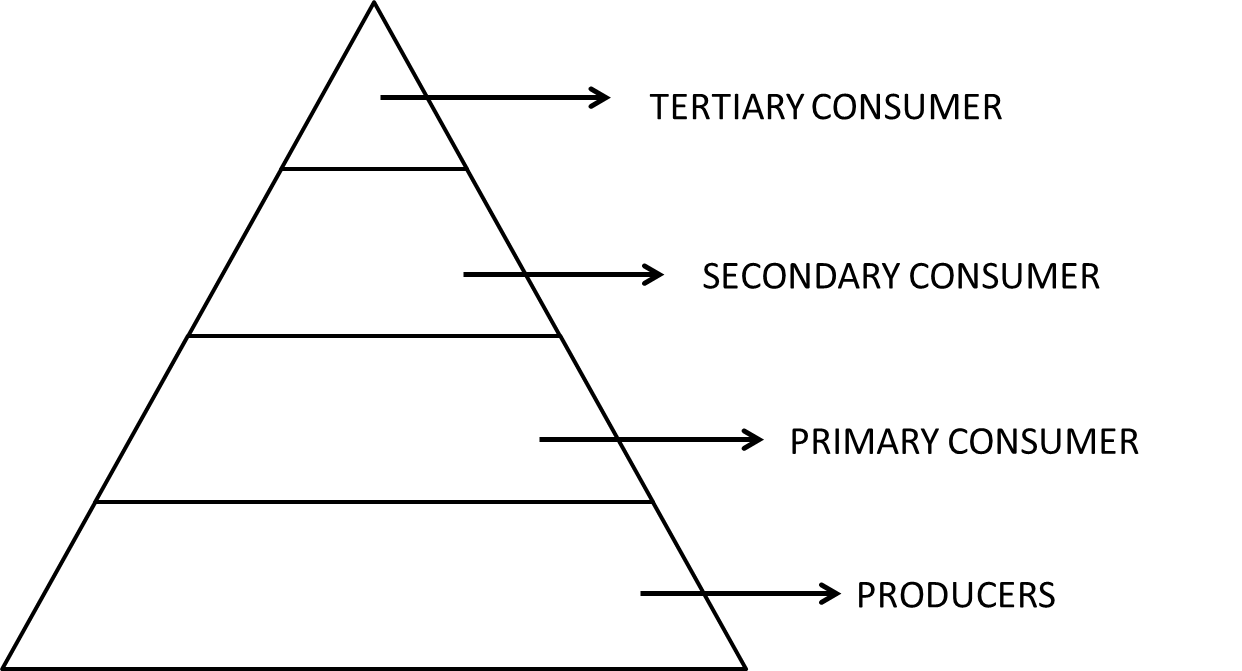
37. What is biological magnification and give its causes?
Ans: Gathering of various unimportant and harmful substances by organisms at different levels of a food chain is known as biological magnification. Its causes are the excessive use of pesticides which enter our food chain. As The bottom feeders of a food chain consume these and gradually it is carried to the top of that particular food chain.
38. DDT has entered food chain. Which food habit is safer- vegetarian or non-vegetarian?
Ans: Vegetarian habit is safer. Because less DDT will accumulate in our body. And due to Bio magnification higher level of DDT in higher trophic levels is found.
39. Aquarium requires regular cleaning whereas lakes normally do not. Why?
Ans: Lake has more diverse forms of life due to that they have larger number of food chains which leads to natural cleaning. Thus, the ecosystem is more stable. The aquarium has a very limited number of food chains and unable to sustain itself. That’s why Aquarium requires regular cleaning whereas lakes normally do not.
40. How will accumulation of bio degradable waste effect our environment?
Ans: The accumulation of bio degradable waste effect our environment because-
The production of harmful gases causes pollution.
Microbes will not be able to decompose all the biodegradable waste.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. DDT that was sprayed in minute amount on food plants was detected in high concentration in man? How did it happen? Explain.
Ans: The phenomenon behind this is biological magnification because when DDT are used to protect crops from diseases and pests. They enter the soil. From soil these are absorbed by plants. And then consumed by organisms. They get accumulated at different trophic levels. As the human beings occupy the top position in any food chain, maximum concentration of such harmful chemicals get accumulated in the bodies of man.
2. Describe how ozone layer is formed?
Ans: Formation of the ozone layer is as follows-
During the origin of life Earth, some of underwater micro-organisms were to photosynthesize due to molecular oxygen was released in atmosphere.
This oxygen is released to stratosphere where it began to react with ultraviolet radiations from sun to form free oxygen (O).
Free oxygen combines with molecular oxygen to form ozone the reaction is given as-
${{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{+u}\text{.v light O+O}$
$\text{2O+2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\text{2}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{(ozone)}$
3. What are the major components of environment?
Ans: The major components of environment are as follows-
Lithosphere - It is the solid outer section of Earth which includes Earth's crust. It extends from the surface of Earth to a depth of about $70-100km$ .The main component of lithosphere is earth’s tectonic plates.
Hydrosphere- It comprises of all forms of water bodies on earth including marine (oceans, seas) freshwater (rivers, lakes, ponds, streams) and groundwater resources etc. It covers $71\%$ of earth’s surface. $97\%$ of water found on Earth is in the oceans in the form of salt water. Only $3\%$ of water on Earth is freshwater. Out of this, $30.8\%$ is available as groundwater and $68.9\%$ is in frozen forms as in glaciers. Amount of $0.3\%$ is available in rivers, reservoirs and lakes and is easily accessible to man.
Atmosphere – It is gaseous layer enveloping the Earth. The atmosphere with oxygen in abundance is unique to Earth and sustains life. . It mainly comprises $78.08\%$ nitrogen, $20.95\%$ oxygen, $0.93\%$ argon, $0.039\%$ carbon dioxide, and traces of hydrogen, helium, and noble gases. The amount of water vapor present is variable $\left( 0-3 \right)\%$ Earth's atmosphere has a series of layers, each with its own specific traits.
Biosphere- It refers to all the regions on Earth where life exists. The ecosystems that support life could be in soil, air, water or land.
4. Why are some substances biodegradables and some non-biodegradable?
Ans: Some substances are biodegradable and some non-biodegradable because some substances can be decomposed by microorganisms and some cannot as he micro-organisms like bacteria and other decomposers organisms (called saprophytes) present in our environment specific in their action. They break down the materials or products made from natural materials (paper) as they have some peculiar enzymes for this process. But as enzymes are specific in their action, these cannot break down many man-made materials likes plastic. These can be acted upon by physical processes but not by biological processes. Therefore, these types of substances persist for long time and cannot be decomposed into simpler substances.
5. Explain why a food chain consists of few steps only? Write a food chain having five steps.
Ans: This is because of 10% law as only 10% of energy is available at the next trophic level. As If a food chain has six or more than six steps, energy is not sufficient for the survival of organism at that trophic level. A food chain having five steps is as follows:
Grass $\to $ insects $\to $ frog $\to $ snake $\to $ eagle
6. What is the difference between food chain and food web?
Ans: Food chain- The food chain describes which organism in the environment eats another organism. In ecology, the food chain is the series of transfer of matter and energy from organisms to organisms in the form of food. It is the sequence of events in an environment or ecosystem in which one living organism eats another living organism and another larger organism eats that organism later. It is a part of food web.
Food web- Food web means, mutually, many food chains via which energy flows into the ecosystem. The Food web is an interconnection of the various food web. A food web is just like the food chain except that the food web is larger than the food chain. Rarely, one organism is eaten by multiple predators, or it consumes many other organisms. The food webs are more complex.
7. What is biological magnification? Illustrate with the help of example.
Ans: Biological magnification refers to the process where toxic substances move up the food chain and become more concentrated at each level. For example-
Water $\to $ Phytoplankton $\to $ Fish $\to $ Bird
$ \text{(0}\text{.02 ppm}\text{of harmful chemical)}$ $\left( 5.0ppm \right)$ $\left( \text{240ppm} \right)$ $\left( \text{1600ppm} \right)$
8. What are the ill effects of ozone layer depletion?
Ans: The ill effects of ozone layer depletion are-
Human health: -
Causes skin cancers
Causes eye cataracts
Leads to immune deficiency disorders.
Agriculture and plant life: -
Affect plant growth
Reduces agricultural productivity.
Marine environment
Photosynthesizing phytoplankton presents in the sea which also help in reducing the
global warming.
The lives of many plastics have been found to be shortened due to exposure to UV radiations.
9. What is the significance of food chains?
Ans: The significance of food chains is-
It is a means of transfer of food from one trophic level to another.
It provides information about the living component of an ecosystem.
It helps us in understanding the interactions and interdependence amongst different organism in an ecosystem.
It is a pathway for the flow of energy in any ecosystem.
10. How Garbage pollution can be controlled?
Ans: Garbage pollution can be controlled as-
By practicing 3 R’s .
By recycling of certain wastes products like plastic and paper.
By making use of biodegradable products as much as we can.
By producing biogas from the organic wastes.
Proper separation of biodegradable and non-bio-degradable waste during disposal.
By making the compost of biodegradable wastes by burying them under soil.
11. What are the components of an ecosystem? Explain with examples
Ans: An ecosystem has two major components-
Biotic Components- It includes producers (plants), consumers (animals) and decomposers (bacteria and fungi).
Producers- Organisms which are able to photosynthesis are called producers. It includes all green plants.
Consumers- Organisms which depends upon other are called consumers. It is of few types-
Herbivores- Animals which directly depends upon plants.
Carnivores- These animals eat herbivores.
Secondary carnivores- Animals which depends upon carnivores.
Tertiary carnivores- Largest animals which depends upon secondary carnivores.
Decomposers- These organisms depend upon dead plants and animals. They change complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances.
Abiotic components- Non-living components. It include physical and chemical factors such as light, water, soil, air temperature, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen and other nutrients.
12. Write any three activities which are eco-friendly.
Ans: The three activities which are eco-friendly.
Separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances.
By practicing 3 R’s .
Rainwater harvesting.
13. Energy transfer is said to be unidirectional whereas biochemical transfer is said be cyclic. Why?
Ans: Energy transfer is unidirectional because when the energy is absorbed by autotrophs from the sun, it is never reabsorbed by it. And when consumers eat up the producers directly or indirectly the energy transferred in this process can never be reversed in the food chain. In biogeochemical transfer is cyclic because chemical elements move from environment to organism and back to the environment.
14. Give difference between producers and consumers. Mention one example of each.
Ans: The difference between producers and consumers is as follows:
Producers | Consumers |
They are autotrophs. | They are heterotrophs |
They occupy first trophic level. | They occupy second to third trophic level. |
They synthesises their own food. | They cannot synthesises their own food. |
15. There are no predators for tiger or lion. Why?
Ans: Lions and tigers are at the highest trophic level. They are largest animals which feed upon the secondary carnivores like wolves etc. they are not killed and eaten by other animals.
16. What are the measures to protect ozone depletion?
Ans: The measures to protect ozone depletion are-
Avoid the consumption of gases dangerous to the ozone layer, due to their content or manufacturing process. Some of the most dangerous gases are CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons), halogenated hydrocarbon, methyl bromide and nitrous oxide.
Minimize the use of cars. The best transport option is urban, bicycle, or walking. If you use a car to a destination, try to carpool with others to decrease the use of cars in order to pollute less and save.
Do not use cleaning products that are harmful to the environment and to us. Many cleaning products contain solvents and substances corrosive, but you can replace these dangerous substances with non-toxic products such as vinegar or bicarbonate.
Buy local products. In this way, you not only get fresh products but you avoid consuming food that has travelled long distances. As the more distance travelled, the more nitrous oxide is produced due to the medium used to transport that product.
Maintain air conditioners, as their malfunctions cause CFC to escape into the atmosphere.
17. Describe three biotic components of ecosystem. Also give examples.
Ans: The three biotic components of ecosystem are-
Producers- All the green plants have a unique capability to synthesis organic substance such as sugar and starch by the process of photosynthesis. Therefore, they are called producers.
Consumers- These are the living organisms which depend directly or indirectly on plants for their food. Consumers may be herbivore, carnivores, and omnivores. Example- Lion, tiger.
Decomposers- Decomposers are the organisms which depend upon the dead and decaying organisms their waste material. They form important link between living and non-living components. Example-algae.
18. What is the role of decomposers in an ecosystem?
Ans: Decomposers play a critical role in the flow of energy through an ecosystem. They break apart dead organisms into simpler inorganic materials, making nutrients available to primary producers. they are the important link between living and non-living components of environments.
19. What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Ans: If all the organisms of one trophic level are killed, the food chain will become completely imbalanced. The organisms in the immediate higher trophic level will die out due to unavailability of food.
If the herbivores are killed, then the carnivores would not able be to get food and would die.
If carnivores are killed, then the population of herbivores would increase to unsustainable level.
If producers are killed, then the nutrient cycle in the area would not be completed.
Thus, the whole food chain will collapse.
20. What is Ozone? How does it affect any ecosystem?
Ans: Ozone is a gas composed of three atoms of oxygen. Its molecular formula is ${{O}_{3}}$ . It forms a layer in the upper atmosphere. It is very essential for the life on this planet. It shields the surface of the earth from ultra-violet radiation (UV) coming from sun as these radiations are very harmful causing skin cancer and cataract in humans. It also does harm to the crops.
21. Why are some substances biodegradable and some non-biodegradable?
Ans: Some substances are biodegradable and some non-biodegradable because some substances can be decomposed by microorganisms and some cannot as he micro-organisms like bacteria and other decomposers organisms (called saprophytes) present in our environment specific in their action. They break down the materials or products made from natural materials (paper) as they have some peculiar enzymes for this process. But as enzymes are specific in their action, these cannot break down many man-made materials likes plastic. These can be acted upon by physical processes but not by biological processes. Therefore, these types of substances persist for long time and cannot be decomposed into simpler substances.
22. Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
(a) They will serve as breeding ground for flies and mosquitoes which are carriers of 3disease like cholera, malaria etc. Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Ans: Excess use of non-biodegradable pesticide and fertilizers run off with rain water to water bodies cause water pollution.
(b) They produce foul smell, thus causing air pollution.
Ans: They may choke the sever system of city or town that may overflow over roads.
23. What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Ans: Biological magnification refers to the process where toxic substances move up the food chain and become more concentrated at each level. The concentration of harmful chemicals will be different at different trophic levels. It will be lowest in the first trophic level and highest in the last trophic level of the food chain.
24. Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Ans: Ozone layer stops ultraviolet radiations from the Sun from reaching the earth. Ultraviolet rays cause cancer, cataract and damage to the immune system of human beings.
To limit this damage following steps should be taken-
We should minimize the use of vehicles.
We should not encourage the burning of fossil fuels.
It is now mandatory for all the manufacturing companies to make CFC- free refrigerators throughout the world.
In $1987$, United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) succeeded I forging an agreement between nations to freeze chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) production to $1986$ levels. CFCs are the main cause of ozone layer depletion.
25. Why some substances are degraded and others not?
Ans: Some substances are degraded and others not because different components of food are changed to simpler substances by digestive enzymes and these enzymes are very much specific in nature and action. Similarly, substances are broken down by bacteria and saprophytes. They are also very specific in action and breakdown of the particular substance. Therefore, some substances are biodegradable and other are non-biodegradable.
25. What will happen if all the carnivores are removed from the earth?
Ans: If all the carnivores are removed from the earth, the population of herbivores will increase. Large population of herbivores will overgraze. And all plants will disappear from the earth surface and ultimately the earth may become a desert. The biosphere will get disturbed which will lead to end of life on earth.
26. What will happen to grasslands if all the grazers are removed from there?
Ans: If all the grazers are removed from grassland, then because carnivores keep the populations of other carnivores and herbivores in check. If there were no carnivores, the herbivore populations would explode and they will rapidly consume large amounts of plants and fungi, growing until there is not enough food to sustain them. Eventually, the herbivores would starve, leaving only those plants that were distasteful or poisonous to them. Species diversity would, therefore, drop dramatically.
27. The number of malarial patients in a village increase tremendously, when a large number of frogs were exported from the village. What could be the cause for it? Explain the help of food chain.
Ans: Phytoplankton $\to $Zooplankton $\to $ Mosquito larva $\to $ Frog
In the absence of frog, more mosquito larva survives, giving rise to large number of mosquitoes which cause increase incidence of malaria.
28. What are decomposers and what is the importance of them in the ecosystem?
Ans: Decomposers are the organisms which depend upon the dead and decaying organisms their waste material. They form important link between living and non-living components. They are important because Decomposers decompose the complex substances into simple ones so that plants can use it again.
29. Why food chains consist of three or four steps only?
Ans: Food chains consist of three or four steps only is because of 10% law as only 10% of energy is available at the next trophic level. As If a food chain has six or more than six steps, energy is not sufficient for the survival of organism at that trophic level.
30. What will happen if decomposers are not there in the environment?
Ans: If decomposers are not there in the environment, then dead leaves, dead insects, and dead animals would pile up everywhere. So, presence of decomposers is essential for the replenishment of soil and biogeochemical cycle of elements or substances.
31. Are plants actually producers of energy?
Ans: No, plants are not actually producers of energy, they can trap the energy of sun and can convert solar energy into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates and other food materials so they are called transducers.
32. Look at the following figures. Choose the correct one and give reason for your Choice.
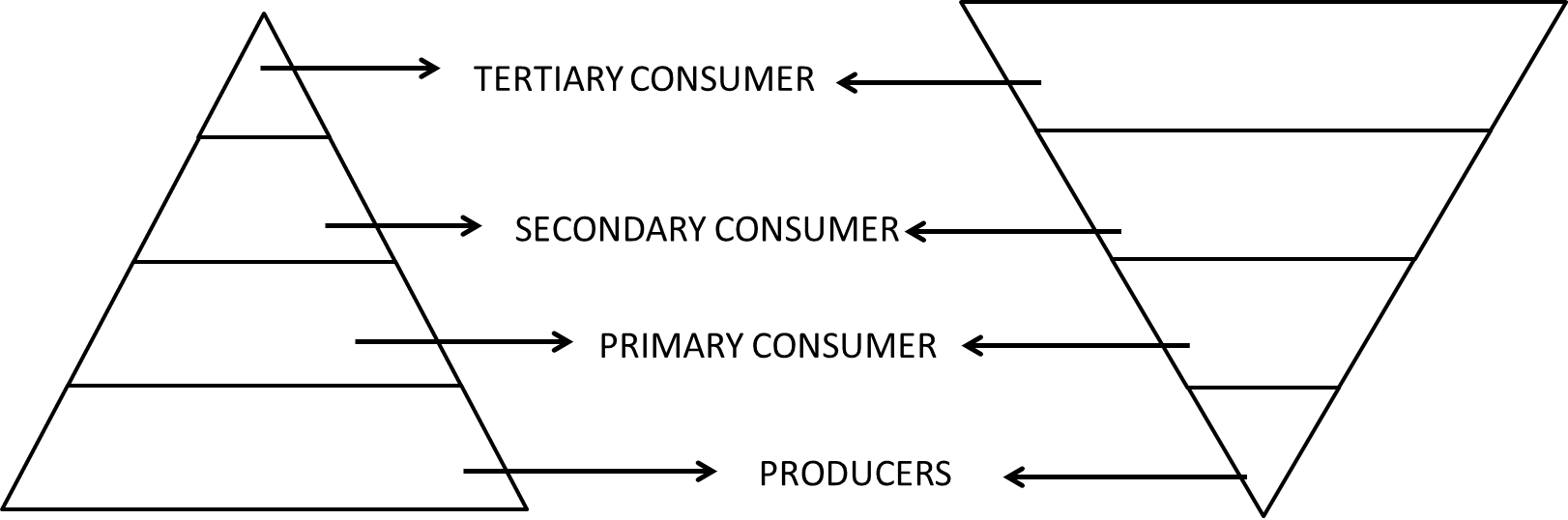
Ans: Figure A is correct.
In an ecosystem, the number of individuals at producer level is maximum. This number reduces at each successive level. Therefore, the shape is a pyramid with broader base and tapering apex.
On an average 10% of the food changes into body mass and is available for the next level of consumers.
33. It is the responsibility of the government to arrange for the management and disposal of waste. As an individual you have no role to play. Do you agree? Support your answers with two reasons.
Ans: I do not agree. As an individual, I also have the responsibility and can contribute in the following ways:
Practising 3 R’s.
Make compost pit for bio degradable waste.
Disposal of garbage only at appropriate places.
Cut down waste generation.
Recycle non-biodegradable waste.
Important Question of Our Environment Class 10 - Free PDF Download
The chapter on our environment is a very crucial chapter for students as it gives students insight into how the environment serves every organism in the animal kingdom. Students need to understand the chapter as it shows students the functioning of the food chain system in the environment. Students will also learn about the various functions of the ecosystem and how it serves various organisms. The differentiation between biotic and abiotic components of the ecosystem. Students will learn how to define an environment and all of its components. Chapter 13 of class 10 science can be found easily on the Vedantu website. The website allows for easy access to its important questions and also it is easily downloadable. Students will find these notes to be helpful during the preparation of their examinations, these important questions are easily downloadable in a pdf format. Students who find it difficult to study on the screen can also print this material so they don't waste too much time on the internet.
Chapter 13 Class 10 Science Important Concepts
This chapter on “our environment” holds importance in various aspects as it can help students understand the chapter as it shows students the functioning of the food chain system in the environment. There are some important concepts students should be familiar with when studying this subject and this includes the following
Photosynthesis
The process where green plants convert solar energy into chemical energy is known as photosynthesis. Inorganic molecules like carbon dioxide and water are used to synthesize food like starch. The process starts with the trapping of sunlight which is done by the chlorophyll present in green plants. Raw materials such as water and carbon dioxide are the prime ingredients for photosynthesis. Water is absorbed from the soil and carbon dioxide is taken from the atmosphere. The sunlight is the catalyst here in this process which converts the carbon dioxide and water into starch and oxygen. Starch is used up by the plant whereas the oxygen is left out to the atmosphere for other organisms to utilize.
Ozone Layer
The ozone layer is a layer that protects us from the extremely harmful rays of the sun. The ozone layer is a layer that is invisible in the atmosphere but can protect us from the harmful UV rays that the sun puts out. This chapter focuses on how the ozone layer protects us and what damages it. CFCs damage the ozone layer and create holes in the layer, this can only be avoided if we start taking better care of the environment and stop polluting so much. The more carbon dioxide there in the air the more it gets affected.
Energy Transfer is Said to Unidirectional
Energy transfer is said to be unidirectional because any energy that is lost to heat is said to the environment can’t be reutilized by plants for photosynthesis. Energy decreases from each trophic level by around 10 percent and thus it cannot be used again.
Significance of Food Chain
It means the transfer of food from one trophic level to another. It provides information about the various living components in our ecosystem. we can get a better understanding of the relation of different organisms that are present in our ecosystem. It is a pathway of flow from one ecosystem to another.
Harmful Effects of Acid Rain
It affects historical monuments and old buildings especially those made from marble. For example the taj mahal
There are certain bacteria that are good for maintaining soil fertility and this can be killed in acid rain.
It makes the water in lakes, ponds, and other water bodies bad for aquatic life.
Acid rain destroys the fertility of the soil which makes it hard to grow cereal crops and trees.
Life on Earth Depends on the Sun
For the earth, the sun is the ultimate source of energy. On various trophic levels, the plants convert the solar energy into chemical energy which is also transferred to various organisms. The energy that is also stored in various fossil fuels is basically transferred to solar energy because fossil fuel is made up of different plants and animals. Therefore we can see how solar energy is transferred into various forms of energy to consume.
Energy Received from Vegetarian Meals
Any organism that consumes vegetarian food is close to the product level that gets the maximum level of energy as compared to an organism of a higher trophic level because only 10 percent of the energy available is available at successive levels than any previous level.
Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Important Questions
Why do vegetarian food habits help us get more energy?
Write a food chain that has two trophic levels.
What percentage of solar energy is trapped and utilized by plants?
What are the harmful effects of acid rain?
Differentiate between biotic and abiotic components of the ecosystem.
Name the process that is a direct outcome of excessive burning of fuel.
Why is plastic not degraded by bacteria?
What is meant by the environment? Nam its components.
What is the 10% law? Name its components.
What is an artificial ecosystem? Name its components.
Why is there a need to ban polythene bags?
Diagrammatically represent the transfer of food chains
What are the two functions of the ecosystem?
Benefits of Important Question of Our Environment Class 10
Science is a very vast subject and can be quite difficult. So by using the right guide material like the ones found in Vedantu students can utilize it to their maximum and score the best marks possible.
Students studying this chapter on the environment will find that it helps in higher studies and help them understand the basics in any bio-based subject in the future.
Students can utilize and practice the important questions so that they can ace their examinations.
This is a fundamental subject for high school kids and plays an important role in higher studies
.It provides students with a structure with which they will study for his or her upcoming examinations.
Students don’t need to worry about the relevance of these questions as they're all cross-checked and updated consistently with the newest CBSE guidelines and rules. therefore the information in Vedantu is genuine and reliable.
Students can use this text to use their time wisely, it helps boost their confidence after consistent practice and students can plan their preparation accordingly.
Conclusion
This chapter takes into account various components of the ecosystem. It starts from how the food chain works and how the various organisms in the environment help each other, the chapter talks about all the harms in the environment and all the energy that can be consumed from the sun. This article on chapter 13 class 10 science important questions will help guide students through their preparations. Students will be able to study more efficiently by using these important questions. These questions will help students to understand the topics that have more weightage than others and thus students will find that they don't have to waste time studying irrelevant topics. This article is important for students to understand the various concepts in the chapter. Students can work more diligently towards their goals and strive for higher marks as well. These important questions make sure that students are aware of the various topics in the chapter and with constant practice students will learn to tackle the difficult questions in the examinations.
Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 13
S. No | Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 |
1 | |
2 |
Important Questions Chapter-wise Links for Class 10 Science
S. No | CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Links |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | Chapter 10 - The Human Eye and the Colourful World Questions |
11 | |
12 |
Related Study Material Links for Class 10 Science
S. No | Important Links for Science Class 10 |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. |
FAQs on Important Questions For Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Our Environment - 2025-26
1. What are the most frequently asked questions from Chapter 13, Our Environment, for the CBSE Class 10 board exam 2025-26?
For the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam, important questions from 'Our Environment' frequently revolve around a few key areas. Expect questions worth 3 to 5 marks on:
The structure of food chains and food webs, including the flow of energy.
The 10% law of energy transfer, often with a numerical problem.
The concept of biomagnification and its effect on top carnivores.
The causes and effects of ozone layer depletion.
Differentiation between biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes with examples.
2. What is the 10% law of energy transfer, and how are questions on this topic typically framed for 3 marks in the board exam?
The 10% law states that during the transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next, only about 10% of the energy is stored in the body of the organism at the next level. The rest is lost to the environment as heat or used in metabolic processes. For a 3-mark question, you might be asked to first define the law and then solve a problem. For example: 'If 20,000 J of energy is available at the producer level (plants), calculate the energy transferred to the lion in this food chain: Plants → Deer → Lion.' You would show the calculation step-by-step for full marks.
3. Why is a food web considered a more realistic and stable model of an ecosystem than a simple food chain?
A food web is considered more realistic because it shows the complex and interconnected network of multiple food chains within an ecosystem. Unlike a linear food chain, where each organism has a single source of food, a food web illustrates that most organisms have multiple food sources. This provides greater stability to the ecosystem. For instance, if one prey species' population declines, the predator can switch to an alternative food source, preventing the predator's extinction and the collapse of the entire energy flow system.
4. What would be the consequences for an ecosystem if all decomposers were suddenly eliminated?
This is a classic Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) question. If all decomposers like bacteria and fungi were eliminated, the ecosystem would face severe consequences:
Accumulation of Waste: Dead plants, animals, and waste products would pile up, as there would be no organisms to break them down.
Halt in Nutrient Recycling: The flow of essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the soil, water, and air would stop. This process, called decomposition, is vital for life.
Depletion of Soil Fertility: Without nutrient replenishment, the soil would become infertile, and producers (plants) would not be able to grow. This would lead to the collapse of all food chains and the entire ecosystem.
5. How are marks typically distributed for questions on biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes in the Science exam?
Questions on waste management are a staple in board exams. Typically, you can expect this topic to appear as:
A 2-mark question asking for two points of differentiation between biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes.
A 3-mark question asking for the definition of each with two relevant examples (e.g., paper and cotton for biodegradable; plastic and glass for non-biodegradable).
Part of a 5-mark question on waste disposal methods, where you might have to suggest why segregating these two types of waste is the first crucial step in effective garbage management.
6. How does the concept of biomagnification explain why top carnivores are most affected by pesticides like DDT?
Biomagnification is the process where the concentration of harmful, non-biodegradable chemicals increases at successive trophic levels in a food chain. Here's how it affects top carnivores:
Pesticides like DDT are not metabolised or excreted and thus accumulate in an organism's fatty tissues. When a primary consumer eats a producer, it ingests all the DDT from many plants. A secondary consumer then eats many primary consumers, accumulating the DDT from all of them. This process continues up the food chain. As a result, the organism at the highest trophic level (the top carnivore) ends up with the maximum concentration of the toxin, which can lead to diseases, reproductive failure, and death.
7. What key points about the ozone layer are important for the Class 10 Board Exam 2025-26?
For the board exam, you must know these key points about the ozone (O₃) layer:
Function: The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, acts as a protective shield by absorbing most of the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
Depletion Cause: The primary cause of its depletion is the release of man-made chemicals called Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which were used in refrigerants and aerosol sprays.
Harmful Effects: UV radiation can cause skin cancer, cataracts, and damage to the immune system in humans, and also harm plants and aquatic life.
International Action: The Montreal Protocol is a significant international treaty that successfully phased out the production of CFCs, helping the ozone layer to recover.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video
















