




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Ph Change Experiment
Chemistry Experiment - Experiments Based on pH Change
A pH of the solution is the concentration of hydronium ions in a given solution. It is mathematically represented by the negative logarithm of the concentration of hydronium ions in a solution: pH= -log[H3O+]. A pH scale helps to understand whether a given solution is acidic or basic. An acidic solution contains more H3O+ ions as compared to OH- ions; a basic solution contains more OH- ions as compared to H3O+ ions; a neutral solution contains equal amounts of H3O+ and OH- ions. Knowing the pH of a solution is very important, as various vital processes of many organisms are dependent on the pH.
Table of Contents
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Observations
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To determine the pH of various solutions using pH paper.
Apparatus Required
0.1 M H2SO4
0.1 M NaOH
0.1 M CH3COOH
0.1 M NH4OH
Soapy Water
Orange Juice
Test Tubes
Test Tube Stand
Dropper
pH Paper
pH Paper Colour Indicator.
Theory
pH is the amount of hydronium ions present in a given solution.
The pH of the solution determines whether a solution is acidic or basic.
The pH scale ranges between 0 and 14 from which 0-6 indicates that the solution is acidic, 8-14 indicates the solution is basic and 7 pH means the solution is neutral having an equal number of H3O+ and OH- ions.
The pH paper or Universal indicator can be used to determine the pH of a solution, which indicates the acidity or basicity of a solution based on colour change.
A pH indicator chart indicates colours and their corresponding pH.
Procedure
Take 6 test tubes and label them.
Add 1 ml of the given solution into each test tube.
Take pH paper and cut small strips of it.
Use forceps to catch the pH paper strips and dip them into test tubes containing solutions.
Observe the colour change of the pH paper strip.
Compare this colour change of the pH paper with the pH indicator chart.
Record your observations and note down the conclusion.
Observations and Result
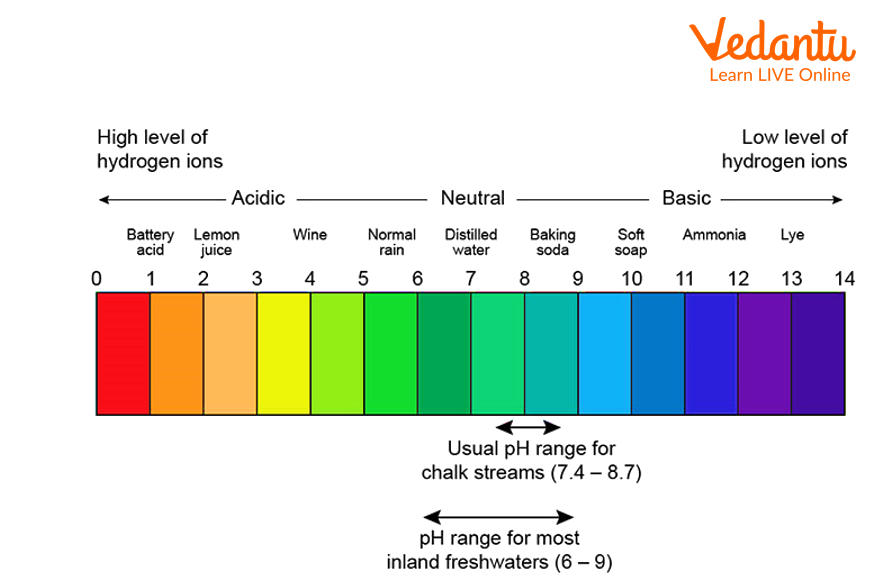
This diagram shows the pH range and their corresponding colours
Precautions
Be careful with the chemicals used.
Wear a lab coat while working in the lab.
Do not waste pH paper strips or chemicals used.
Lab Manual Questions
1. Give examples of strong acids and strong bases.
Ans: Strong acids are H2SO4, HCl and HNO3. Strong bases are NaOH, KOH and Ca(OH)2.
2. What is the difference between strong acids and weak bases?
Ans: The difference between strong acids and weak bases are given below:
3. What is the pH of a solution?
Ans: pH of a solution is known as the amount of H+ ions present in a given solution. It can be determined by using pH paper, universal indicator etc. Mathematically, it can be determined by pH = -log[H3O+].
4. What will be the colour change when pH paper is dipped in HCl, KOH and H2O?
Ans: The Following colour change is seen when pH paper is dipped in the above solutions:
HCl gives red colour since it is a strong acid.
KOH gives a violet colour since it is a strong base.
H2O gives green colour since it is neutral.
Viva Questions
1. The colour change is sharper at which pH?
Ans: The colour change is sharper when the pH is 10 as compared to other changes of colour in the pH observed through the pH paper.
2. Does the addition of water to a buffer or evaporation of water from a buffer solution change the pH of the buffer?
Ans: Upon the addition of water or elimination of water from the buffer solution, the pH of the buffer will not change.
3. In which case, pH will not change on dilution?
Ans: A buffer is an aqueous solution made between a weak acid and a weak base. The pH of such solutions does not change even if they are diluted. Hence, such solutions are used for preservation.
4. How is pH paper prepared?
Ans: pH paper is prepared by dipping a strip of paper into various basic and acidic indicators, followed by drying the paper.
5. What are other methods of determining the pH of a solution?
Ans: A universal indicator can be used for determining the pH of a solution, and it also shows the colour change based on the acidity or basicity of a solution.
6. What is a pH metre?
Ans: pH metre is an instrument which is used to measure the activity of hydrogen ions in a given solution. It is used to determine whether a given solution is acidic or basic.
7. Why does the NaCl solution show neutral pH?
Ans: Salts, which are formed from a combination of strong acid-HCl and strong base-NaOH, do not hydrolyse, but they form H2O molecules when dissolved in water. Therefore, their pH remains neutral.
8. What are pH indicators?
Ans: pH Indicators are chemical compounds used in minute quantities to determine the pH of a solution. These indicators, upon reaction with the solution, show colour change which helps in determining whether the solution is acidic or basic.
9. What are weak acids?
Ans: Weak acids are compounds which are weak electrolytes and partially dissociate in an aqueous solution, giving less amount of free Hydrogen ions. For example, H2S, CH3COOH, H2CO3 etc.
10. What is a weak base?
Ans: Weak bases are compounds which are weak electrolytes and partially dissociate in an aqueous solution, giving less amount of free Hydroxide ions. For example, Carbonates, Bicarbonate, NH4OH, etc.
Practical Based Questions (MCQs)
pH + pOH=______
15
16
14
17
Ans: 14
Which of the following will show resistance to change in pH?
Hydrochloric acid
Sodium Hydroxide
Acetic acid
A mixture of Acetic acid and Sodium Acetate
Ans: Mixture of Acetic acid and Sodium Acetate
A buffer solution resists changes in pH____
In addition, only acid
In addition, acid or base
In addition, only weak base
In addition, only strong acids and water
Ans: Upon the addition of acid or base
Experiments based on pH change do not involve which of the following:
Universal indicator
pH indicator chart
Burette
Dropper, test tube
Ans: Burette
What does ‘p’ in ‘pH’ indicate?
Price
Proportion
Power
Per
Ans: Power
Find the odd man out:
Sodium hydroxide
Sulphuric acid
Calcium hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide
Ans: Sulphuric acid
Phenolphthalein indicator is _____in acidic solution and____ in basic solution?
Colourless, Pink
White, Yellow
Pink, Colourless
Yellow, White
Ans: Colourless, Pink
Which of the following are pH indicators?
Bromophenol blue
Methyl orange
Phenolphthalein
All of the above
Ans: All of the above
Universal indicator is_____
A mixture of acidic indicators
A mixture of basic indicators
A mixture of both acidic and basic indicators
A mixture of strong acids
Ans: Mixture of both acidic and basic indicators
Find the odd man out:
Hydrogen sulphide
Nitric acid
Acetic acid
Carbonic acid
Ans: Nitric acid
Conclusion
The pH of a given solution indicates the presence of the amount of hydronium ions present in that solution. The pH helps us to understand whether a given solution is acidic or basic. Acidic solutions show a pH below 7 and basic solutions show a pH above 7, pH 7 is neutral. Indicators such as phenolphthalein, methyl orange etc. are used to determine the pH of a solution.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Ph Change Experiment
1. What are the key objectives of the Class 11 Chemistry experiment on pH change as per the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus?
The primary objectives of this important experiment are:
To determine the pH of various samples like fruit juices, and solutions of acids, bases, and salts using pH paper or a universal indicator.
To compare the pH of solutions of a strong acid and a weak acid of the same concentration.
To study the change in pH during the titration of a strong acid with a strong base.
To observe the pH change caused by the common-ion effect in solutions of weak acids and weak bases.
2. Define a buffer solution and provide an example. For how many marks is this concept typically asked in exams?
A buffer solution is a solution that resists a change in its pH upon the addition of a small amount of a strong acid or a strong base. This is a frequently asked question, often for 2 marks. An example of an acidic buffer is a mixture of acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and its salt, sodium acetate (CH₃COONa). An example of a basic buffer is a mixture of ammonium hydroxide (NH₄OH) and its salt, ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl).
3. What observations are expected when comparing the pH of 0.1M HCl and 0.1M CH₃COOH solutions using a universal indicator?
When comparing these two solutions, you will observe a significant difference in pH. This is an important question to test conceptual understanding.
0.1M HCl: Being a strong acid, it dissociates completely, leading to a high concentration of H⁺ ions. The universal indicator will show a colour corresponding to a very low pH, typically red (pH 1-2).
0.1M CH₃COOH: Being a weak acid, it dissociates only partially. This results in a lower concentration of H⁺ ions compared to HCl. The universal indicator will show a colour for a higher pH, typically orange or yellow (pH 3-4).
4. A student is asked to determine the pH of common salt (NaCl) and ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) solutions. What results should be expected and why?
This is a HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) question. The expected results are:
NaCl solution: The pH will be approximately 7 (neutral). This is because NaCl is a salt of a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH), so its ions do not undergo hydrolysis.
NH₄Cl solution: The pH will be less than 7 (acidic). This is because NH₄Cl is a salt of a weak base (NH₄OH) and a strong acid (HCl). The ammonium ion (NH₄⁺) undergoes hydrolysis to produce H⁺ ions, making the solution acidic.
5. Why does a buffer solution resist changes in pH? Explain the mechanism using an acidic buffer as an example.
A buffer solution resists pH change due to the presence of both an acidic component (to neutralize added base) and a basic component (to neutralize added acid). Consider an acidic buffer of acetic acid (CH₃COOH) and acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻ from sodium acetate).
- When a strong acid (H⁺) is added: The acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻) react with the added H⁺ to form weakly dissociated acetic acid: CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺ → CH₃COOH. This prevents a sharp drop in pH.
- When a strong base (OH⁻) is added: The acetic acid (CH₃COOH) neutralizes the added OH⁻ ions to form water and acetate ions: CH₃COOH + OH⁻ → CH₃COO⁻ + H₂O. This prevents a sharp rise in pH.
6. What important precautions must be taken while performing the pH change experiment to ensure reliable and accurate results in the board practical exam?
For scoring full marks in the practical exam, observing the following precautions is crucial:
Always use a clean and dry dropper for each different solution to avoid cross-contamination.
When using pH paper, do not dip the entire strip into the solution. Use a clean glass rod to transfer a drop of the solution onto the paper.
Compare the colour of the pH paper or universal indicator immediately with the standard colour chart, as the colour may fade over time.
Prepare fresh solutions of fruit juices as they can ferment or oxidise, which alters their pH.
7. What is the common ion effect and how is it a crucial principle for preparing a buffer solution?
The common ion effect is the suppression of the dissociation of a weak electrolyte by the addition of a strong electrolyte that has an ion in common with the weak electrolyte. This is a fundamental concept for understanding buffers. In an acetic acid solution (a weak electrolyte), adding sodium acetate (a strong electrolyte) introduces a high concentration of acetate ions (CH₃COO⁻), the common ion. According to Le Chatelier's principle, this excess acetate shifts the equilibrium of the acetic acid dissociation (CH₃COOH ⇌ H⁺ + CH₃COO⁻) to the left, reducing the concentration of H⁺ ions and suppressing further dissociation. This creates a reservoir of both the weak acid and its conjugate base, which is the essential condition for a solution to act as a buffer.
8. During the titration of a strong acid with a strong base, why is there a sudden and large jump in pH at the equivalence point?
This is a key analytical question. Before the equivalence point, there is an excess of strong acid, so the pH is low and changes slowly. After the equivalence point, there is an excess of strong base, so the pH is high and changes slowly. However, right at the equivalence point, the acid and base have completely neutralised each other. The addition of just one more drop of the strong base at this stage causes a massive change in the concentration of H⁺/OH⁻ ions in an unbuffered solution (now just salt and water), leading to a very sharp and large jump in the measured pH value.
























