Vedantu’s Solutions for Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms, Science Class 9
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. Subjects like Science, Maths, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 9 Science, Maths solutions and solutions of other subjects. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science(Biology) Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Protista includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms
(b) Whittaker considered cell structure, mode and source of nutrition for classifying the organisms in five kingdoms
(c) Both Monera and Protista may be autotrophic and heterotrophic
(d) Monerans have well defined nucleus
Ans: Monerans are unicellular prokaryotic,i.e., they do not have well defined nucleus. Protists are unicellular and eukaryotic. i.e they have well defined nuclei.
Therefore; option (d), ‘Monerans have well defined nucleus’ is the incorrect sentence.
2. Which among the following has specialized tissue for conduction of water?
(i) Thallophyta
(ii) Bryophyta
(iii) Pteridophyta
(iv) Gymnosperms
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: Plant kingdom is classified into subgroups; Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperm, Angiosperm on the basis of plant body, vascular system, seed formation.
Specialised conducting tissues first appear in Pteridophyta and it gets modified in Gymnosperm and well developed in Angiosperms.
Therefore; option (c), (iii) and (iv) is the correct answer.
3. Which among the following produce seeds?
(a) Thallophyta
(b) Bryophyta
(c) Pteridophyta
(d) Gymnosperms
Ans: Plant kingdom is classified into subgroups; Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta, Gymnosperm, Angiosperm on the basis of plant body, vascular system, seed formation. Among the above given groups Gymnosperms (Gymno- naked, sperm- seed) produce seeds.
Therefore; option (d) is the correct choice.
4. Which one is a true fish?
(a) Jellyfish
(b) Starfish
(c) Dogfish
(d) Silverfish
Ans: The characteristics of true fish are the presence of gills, fins, vertebrae.
Jellyfish belong to phylum Cnidaria, Silverfish belong to phylum Arthropoda, Starfish belong to phylum Echinodermata and these phyla belong to Invertebrata.
Therefore; among the given options (c) Dogfish is a true fish.
5. Which among the following is exclusively marine?
(a) Porifera
(b) Echinodermata
(c) Mollusca
(d) Pisces
Ans: Among the above-given options Echinodermata is exclusively marine, others are aquatic as well as marine both.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
6. Which among the following have open circulatory system?
(i) Arthropoda
(ii) Mollusca
(iii) Annelida
(iv) Coelenterata
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: Open circulatory system is a system in which blood flows freely throughout the body cavity as blood vessels are not present.
Therefore; among the given options, Annelids have a closed circulatory system, and Coelenterates do not have any circulatory system.
Hence, options (a), (i), and (ii) i.e., Arthropoda and Mollusca are the correct choice.
7. In which group of animals, coelom is filled with blood?
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Annelida
(c) Nematoda
(d) Echinodermata
Ans: Coelom is the cavity in the body that is filled with blood. Among the given options Arthropods will have their coelom filled with blood. Annelids have blood vessels in their body. Nematodes do not have a circulatory system and in Echinoderms have a water vascular system through which blood is pumped throughout the body.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
8. Elephantiasis is caused by
(a) Wuchereria
(b) Pinworm
(c) Planarians
(d) Liver flukes
Ans: Elephantiasis is a disease in which limbs or body parts get enlarged due to swelling. It is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti.
9. Which one is the most striking or (common) character of the vertebrates?
(a) Presence of notochord
(b) Presence of triploblastic condition
(c) Presence of gill pouches
(d) Presence of coelom
Ans: The presence of notochord is the striking characteristic of the vertebrates. Other characteristics such as triploblastic condition, presence of gill pouches and presence of coelom are common among both vertebrates and invertebrates.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
10. Which among the following have scales?
(i) Amphibians
(ii) Pisces
(iii) Reptiles
(iv) Mammals
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (ii)
Ans: Among the given options Pisces and Reptiles have scales while amphibians and mammals do not have scales.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
11. Find out the false statement
(a) Aves are warm blooded, egg laying and have four chambered heart
(b) Aves have feather covered body, fore limbs are modified as wing and breathe through lungs
(c) Most of the mammals are viviparous
(d) Fishes, amphibians and reptiles are oviparous
Ans: Among the given options, option (d) is the correct choice because the statement is false as there are some fishes, amphibians and reptiles that are viviparous.
12. Pteridophyta do not have
(a) root
(b) stem
(c) flowers
(d) leaves
Ans: Pteridophytes are first vascular land plants. They produce spores for reproduction. They do not bear flowers.
Hence, option (c) is the correct choice.
13. Identify a member of porifera
(a) Spongilla
(b) Euglena
(c) Penicillium
(d) Hydra
Ans: Porifera is the phylum of invertebrates. Members of the phylum porifera have a porous body. Among the given options Spongilla is a member of porifera, Euglena is a protozoa, Penicillium is a fungi and Hydra is a coelenterata.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
14. Which is not an aquatic animal?
(a) Hydra
(b) Jellyfish
(c) Corals
(d) Filaria
Ans: Filaria is not an aquatic animal, it is a worm which is also known as Wuchereria bancrofti.
15. Amphibians do not have the following
(a) Three chambered heart
(b) Gills or lungs
(c) Scales
(d) Mucus glands
Ans: Amphibians do not have scales. Their skin is free from scales and is mucusy which helps them in respiration by means of diffusion. They have three chambered heart and gills and lungs both are present as they are aquatic and terrestrial both.
16. Organisms without nucleus and cell organelles belong to
(i) fungi
(ii) protista
(iii) cyanobacteria
(iv) archaebacteria
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans: Organisms without nucleus and cell organelles belong to kingdom Monera, i.e., they are prokaryotes. Organisms that belong to the kingdom Protista have well-developed nuclei and are known as eukaryotes.
Cyanobacteria and Archaebacteria are prokaryotes, they are without nucleus and cell organelles. Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
17. Which of the following is not a criterion for the classification of living organisms?
(a) Body design of the organism
(b) Ability to produce one’s own food
(c) Membrane bound nucleus and cell organelles
(d) Height of the plant
Ans: Height of a plant is not a criteria for the classification of living organisms. Body design of the organism, ability to produce one’s own food, membrane-bound nucleus and cell organelles are the criterion for the classification of living organisms.
18. The feature that is not a characteristic of protochordata?
(a) Presence of notochord
(b) Bilateral symmetry and coelom
(c) Jointed legs
(d) Presence of circulatory system
Ans: Protochordata is known as lower chordata. a notochord is present at the larval stage. Their body is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, and coelomate. The jointed leg is the characteristic of Arthropods.
19. The locomotory organs of Echinodermata are
(a) tube feet
(b) muscular feet
(c) jointed legs
(d) parapodia
Ans: Echinodermata has a contrasting characteristic of the water vascular system. All the functions in their body are performed by this system. Echinoderms move with the help of this water vascular system known as tube feet.
20. Corals are
(a) Poriferans attached to some solid support
(b) Cnidarians, that are solitary living
(c) Poriferans present at the sea bed
(d) Cnidarians that live in colonies
Ans: Corals belong to the phylum Cnidaria. They live in marine water and are known as colonial organisms, they are dependent on one another for survival. Adults are attached to substratum (rocks) and larvae are free-swimming.
Hence, option (d) is the correct choice.
21. Who introduced the system of scientific nomenclature of organisms
(a) Robert Whittaker
(b) Carolus Linnaeus
(c) Robert Hooke
(d) Ernst Haeckel
Ans: Carolus Linnaeus is known as the father of taxonomy. He introduced the system of scientific nomenclature of organisms in the year 1758.
22. Two chambered heart occurs in
(a) crocodiles
(b) fish
(c) aves
(d) amphibians
Ans: Two chambered heart have one auricle and one ventricle. It occurs in fish. Amphibians have three chambered heart. Crocodiles and aves have a four-chambered heart.
23. Skeleton is made entirely of cartilage in
(a) Sharks
(b) Tuna
(c) Rohu
(d) None of these
Ans: Skeleton is made entirely of cartilage in Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fishes) i.e., in sharks. Tuna, Rohu are osteichthyes.
24. One of the following is not an Annelid
(a) Nereis
(b) Earthworm
(c) Leech
(d) Urchins
Ans: Annelids are also known as ringworm/ segmented worms.
Urchins (hedgehogs) belong to the phylum Echinodermata. Nereis, Earthworm, and Leech are examples of Annelid.
25. The book Systema Naturae was written by
(a) Linnaeus
(b) Haeckel
(c) Whittaker
(d) Robert Brown
Ans: Carolus Linnaeus in the year written the book Systema Naturae which was published in the year 1735.
26. Karl Von Linne was involved with which branch of science?
(a) Morphology
(b) Taxonomy
(c) Physiology
(d) Medicine
Ans: Carl von Linne is commonly known as Carl Linnaeus. He is the father of taxonomy. One of their main contributions was in the development of a hierarchical system of classification of living organisms and had proposed binomial nomenclature.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
27. Real organs are absent in
(a) Mollusca
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Echinodermata
Ans: Real organs are absent in Coelenterata as they show tissue level of organisation. Mollusca, Arthropoda, Echinodermata show organ level of organisation.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
28. Hard calcium carbonate structures are used as skeleton by
(a) Echinodermata
(b) Protochordata
(c) Arthropoda
(d) Nematoda
Ans: Body of echinoderms are covered with spiny, hard calcareous plates. These calcareous plates are made up of calcium carbonate. Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
29. Differentiation in segmental fashion occurs in
(a) Leech
(b) Starfish
(c) Snails
(d) Ascaris
Ans: Differentiation in segmental fashion occurs in leech. Leech belongs to phylum Annelida, they show metameric segmentation which means their body is divided into segments and all the segments are identical and each segment bears a set of organs.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
30. In taxonomic hierarchy family comes between
(a) Class and Order
(b) Order and Genus
(c) Genus and Species
(d) Division and Class
Ans: Taxonomic hierarchy is a rank in the classification of organisms into 7 levels of taxonomy. i.e., Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species. Therefore, in the taxonomic hierarchy family comes between order and genus.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
31. 5-Kingdom classification has given by
(a) Morgan
(b) R. Whittaker
(c) Linnaeus
(d) Haeckel
Ans: Five kingdom classification was given by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. In this system of classification living beings are divided into five kingdoms, i.e., Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
32. Well defined nucleus is absent in
(a) blue green algae
(b) diatoms
(c) algae
(d) yeast
Ans: The organisms which have well defined nuclei are called eukaryotes and the organisms which do not have well developed nuclei are called prokaryotes. Therefore, from the given options Blue green algae is prokaryotic and diatoms, algae and yeast are eukaryotes.
Hence, option (a) is the correct choice.
33. The ‘Origin of Species’ is written by
(a) Linnaeus
(b) Darwin
(c) Hackel
(d) Whittaker
Ans: The ‘Origin of Species’ is written by Charles Darwin which was published in the year 1859.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
34. Meena and Hari observed an animal in their garden. Hari called it an insect while Meena said it was an earthworm. Choose the character from the following which confirms that it is an insect.
(a) Bilateral symmetrical body
(b) Body with jointed legs
(c) Cylindrical body
(d) Body with little segmentation
Ans: Insects belong to class insecta which come under the phylum Arthropoda (arthron - jointed, poda - legs). Therefore, presence of jointed legs is the basic characteristic of insects.
Hence, option (b) is the correct choice.
Short Answer Questions
35. Write true (T) or false (F)
(a) Whittaker proposed five kingdom classification.
Ans: True
Explanation: Five kingdom classification was given by R.H. Whittaker in 1969. In this system of classification living beings are divided into five kingdoms, i.e., Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia.
(b) Monera is divided into Archaebacteria and Eubacteria.
Ans: True
Explanation: Organisms are classified into five kingdoms in which monera is further divided into archaebacteria and eubacteria.
(c) Starting from Class, Species comes before the Genus.
Ans: False
Explanation: Living organisms are classified according to taxonomic hierarchy. Taxonomic hierarchy is a rank in the classification of organisms into 7 levels of taxonomy. i.e., Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
(d) Anabaena belongs to the kingdom Monera.
Ans: True
Explanation: Anabaena comes under the genus of cyanobacteria and it belongs to the kingdom Monera.
(e) Blue green algae belongs to the kingdom Protista.
Ans: False
Explanation: Blue green algae (BGA) is prokaryotic and according to five kingdom classification prokaryotic unicellular organisms are placed under kingdom monera.
(f) All prokaryotes are classified under Monera.
Ans: True
Explanation: According to five kingdom classification living organisms are classified into monera, protista, fungi, plantae and animalia. All prokaryotic unicellular organisms are placed under kingdom monera, all eukaryotic unicellular/multicellular organisms are placed under kingdom protista.
36. Fill in the blanks
(a) Fungi shows__________mode of nutrition.
Ans: Fungi shows saprophytic mode of nutrition.
(b) Cell wall of fungi is made up of _______.
Ans: Cell wall of fungi is made up of chitin.
(c) Association between blue green algae and fungi is called as_______.
Ans: Association between blue green algae and fungi is called as symbiosis
(d) Chemical nature of chitin is _______.
Ans: Chemical nature of chitin is nitrogen-containing polysaccharide.
(e) ________has smallest number of organisms with maximum number of similar characters
Ans: Species has smallest number of organisms with maximum number of similar characters
(f) Plants without well differentiated stem, root and leaf are kept in ________.
Ans: Plants without well differentiated stem, root and leaf are kept in thallophyta
(g) _________are called as amphibians of the plant kingdom.
Ans: Bryophytes are called as amphibians of the plant kingdom.
37. You are provided with the seeds of gram, wheat, rice, pumpkin, maize and pea. Classify them whether they are monocot or dicot.
Ans: Monocot- Gram, pea, Pumpkin
Dicot- Wheat, Rice
38. Match items of column (A) with items of column (B)
Column (A) | Column (B) |
(a) Naked seed | (A) Angiosperms |
(b) Covered seed | (B) Gymnosperms |
(c) Flagella | (C) Bryophytes |
(d) Marchantia | (D) Euglena |
(e) Marsilea | (E) Thallophyta |
(f) Cladophora | (F) Pteridophyta |
(g) Penicillium | (G) Fungi |
Ans:
Column (A) | Column (B) |
(a) Naked seed | (B) Gymnosperms |
(b) Covered seed | (A) Angiosperms |
(c) Flagella | (D) Euglena |
(d) Marchantia | (C) Bryophytes |
(e) Marsilea | (F) Pteridophyta |
(f) Cladophora | (E) Thallophyta |
(g) Penicillium | (G) Fungi |
39. Match items of column (A) with items of column (B)
Column (A) | Column (B) |
(a) Pore bearing animals | (A) Arthropoda |
(b) Diploblastic | (B) Coelenterata |
(c) Metameric segmentation | (C) Porifera |
(d) Jointed legs | (D) Echinodermata |
(e) Soft bodied animals | (E) Mollusca |
(f) Spiny skinned animals | (F) Annelida |
Ans:
Column (A) | Column (B) |
(a) Pore bearing animals | (C) Porifera |
(b) Diploblastic | (B) Coelenterata |
(c) Metameric segmentation | (F) Annelida |
(d) Jointed legs | (A) Arthropoda |
(e) Soft bodied animals | (E) Mollusca |
(f) Spiny skinned animals | (D) Echinodermata |
40. Classify the following organisms based on the absence/presence of true coelom (i.e., acoelomate, pseudocoelomate and coelomate)
Spongilla, Sea anemone, Planaria, Liver fluke, Wuchereria, Ascaris, Nereis, Earthworm, Scorpion, Birds, Fishes, Horse.
Ans: Acoelomate- Spongilla, Sea anemone, Planaria, Liver fluke
Pseudocoelomate- Wuchereria, Ascaris
Coelomate- Nereis, Earthworm, Scorpion, Birds, Fishes, Horse
41. Endoskeleton of fishes are made up of cartilage and bone; classify the following fishes as cartilaginous or bony
Torpedo, Sting ray, Dog fish, Rohu, Angler fish, Exocoetus.
Ans: Cartilaginous- Torpedo, Sting ray, Dog fish
Bony- Rohu, Angler fish, Exocoetus
42. Classify the following based on number of chambers in their heart.
Rohu, Scoliodon, Frog, Salamander, Flying lizard, King Cobra, Crocodile, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale
Ans: Two-chambered- Rohu, Scoliodon
Three-chambered- Frog, Salamander, Flying lizard, King Cobra
Four-chambered- Crocodile, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale
43. Classify Rohu, Scoliodon, Flying lizard, King Kobra, Frog, Salamander, Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Crocodile and Whale into the cold blooded/warm blooded animals.
Ans: Cold blooded: Rohu, Scoliodon, Flying lizard, King Kobra, Frog, Salamander, Crocodile
Warm blooded: Ostrich, Pigeon, Bat, Whale
44. Name two egg laying mammals.
Ans: The two egg laying mammals are:
(i) Platypus
(ii) Echidna
45. Fill in the blanks
(a) Five kingdom classification of living organisms is given by ________.
Ans: Five kingdom classification of living organisms is given by R.H. Whittaker
(b) Basic smallest unit of classification is ________.
Ans: Basic smallest unit of classification is species
(c) Prokaryotes are grouped in Kingdom_________.
Ans: Prokaryotes are grouped in Kingdom Monera
(d) Paramecium is a protista because of its _______.
Ans: Paramecium is a protista because of its nucleus
(e) Fungi do not contain _______.
Ans: Fungi do not contain chlorophyll
(f) A fungus _______ can be seen without microscope.
Ans: A fungus mushroom can be seen without microscope.
(g) Common fungi used in preparing the bread is ________.
Ans: Common fungi used in preparing the bread is Saccharomyces cerevisiae
(h) Algae and fungi form a symbiotic association called _________.
Ans: Algae and fungi form symbiotic association called lichens.
46. Give True (T) and False (F)
(a) Gymnosperms differ from Angiosperms in having covered seeds.
Ans: False, (Gymno means naked, sperm means seed), (Angeion means vessel, sperm means seed).
(b) Non flowering plants are called Cryptogamae.
Ans: True, Cryptogams are the plants that reproduce by spores, they do not bear flowers and seeds and their reproductive organs are hidden or inconspicuous such as Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta.
(c) Bryophytes have conducting tissue.
Ans: False,Bryophytes have no vascular tissues. True leaves, stems and roots are absent.
(d) Funaria is a moss.
Ans: True, Funaria is a moss. It is derived from a latin word funis which means a rope. It belongs to the class bryopsida.
(e) Compound leaves are found in many ferns.
Ans: True, Compound leaves are those leaves whose leaf blade is divided into two or more distinct leaflets, such leaves are also called fronds which are found in ferns.
(f) Seeds contain embryos.
Ans: True, Seeds are covered with seed coats to survive in unfavourable conditions and inside the seed embryo and cotyledons are present. When seed germinates then two parts come out from the embryo one is called shoot another is called root.
47. Give examples for the following
(a) Bilateral, dorsiventral symmetry is found in__________.
Ans: Bilateral, dorsiventral symmetry is found in liver fluke.
(b) Worms causing disease elephantiasis is_______.
Ans: Worms causing disease elephantiasis is filarial worm.
(c) Open circulatory system is found in_______where the coelomic cavity is filled with blood.
Ans: Open circulatory system is found in arthropods where coelomic cavity is filled with blood.
(d) ________are known to have pseudocoelom.
Ans: Nematodes are known to have pseudocoelom.
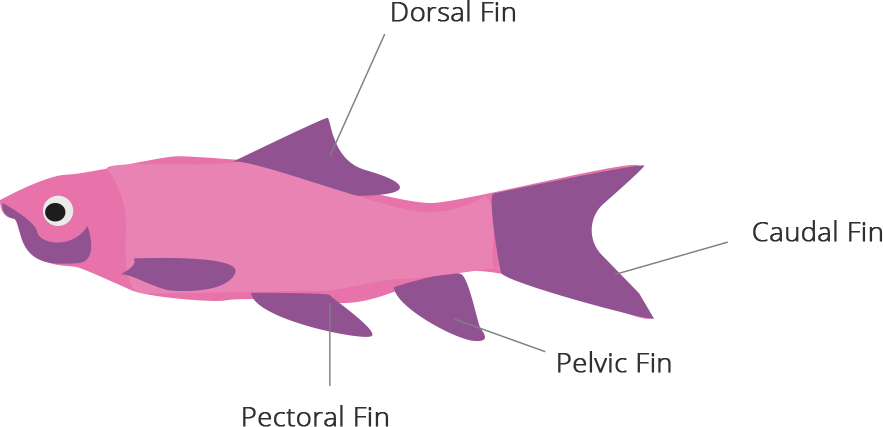
48. Label a,b,c and d. given in Fig. 7.1 Give the function of (b)
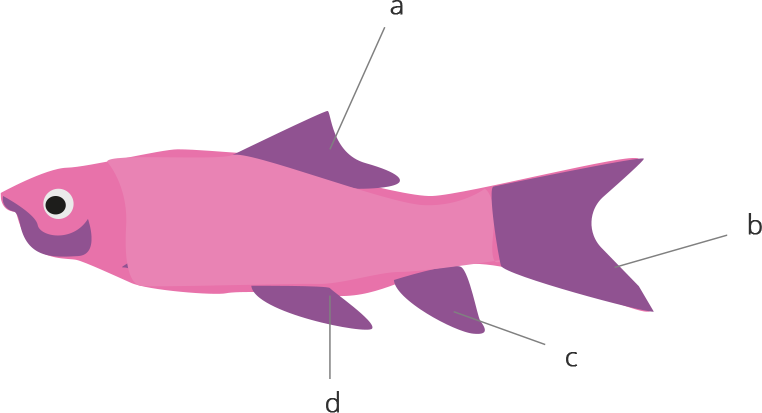
Ans:
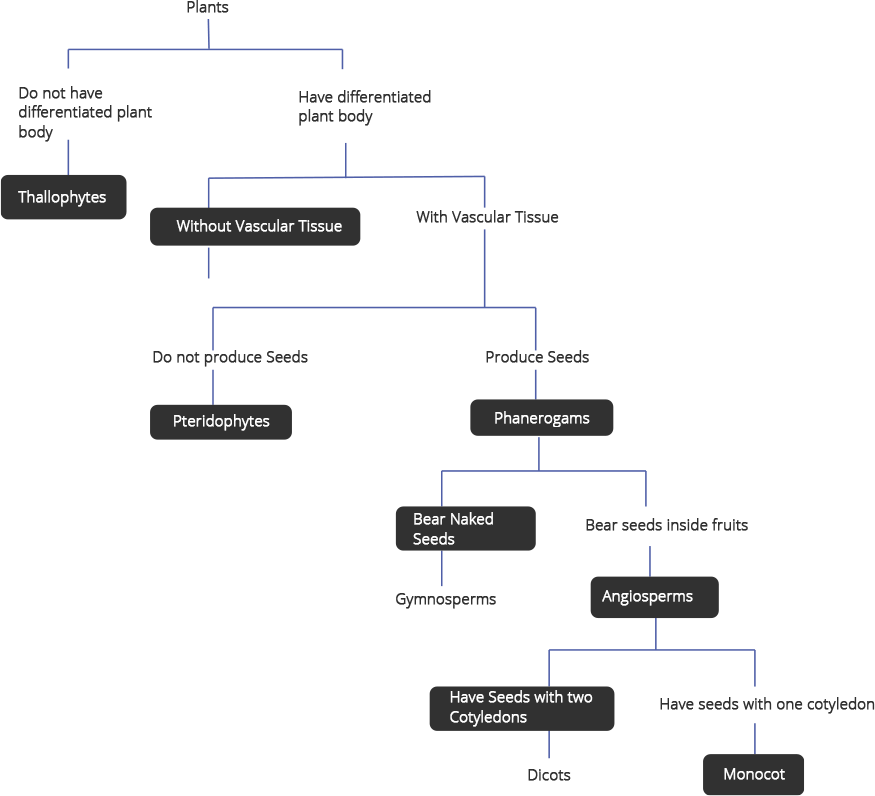
49. Fill in the boxes given in Fig. 7.2 with appropriate characteristics/plant group (s)
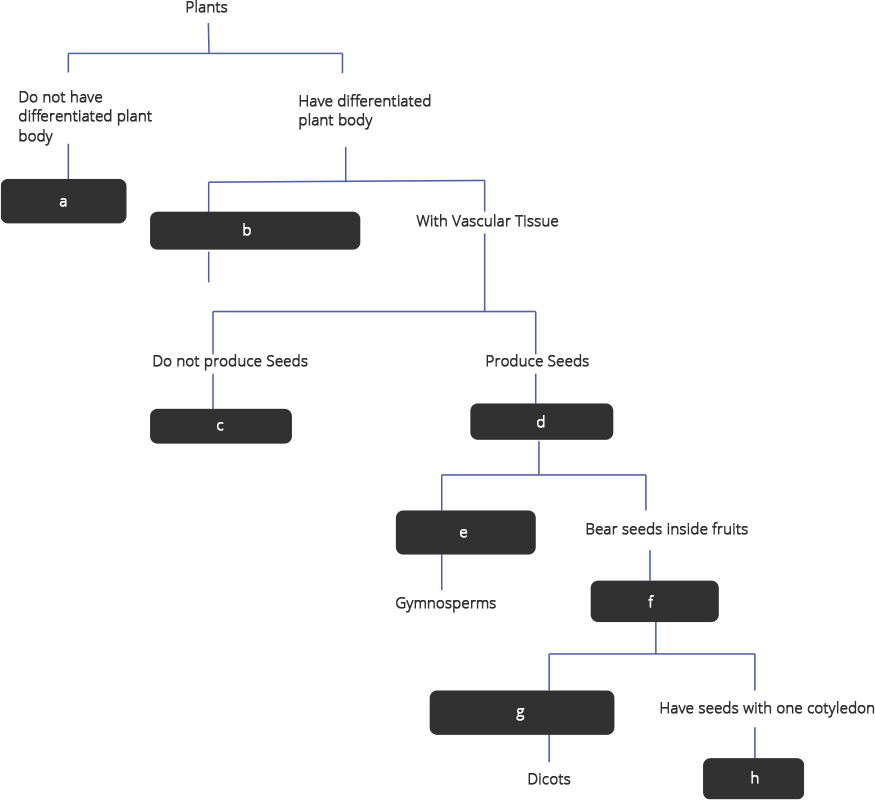
Ans:
Long Answer Questions
50. Write names of a few thallophytes. Draw a labelled diagram of Spirogyra.
Ans: Any group of plants that do not have true stems, leaves and roots are grouped under thallophyta. Example; Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Cladophora, Ulva, Chara.
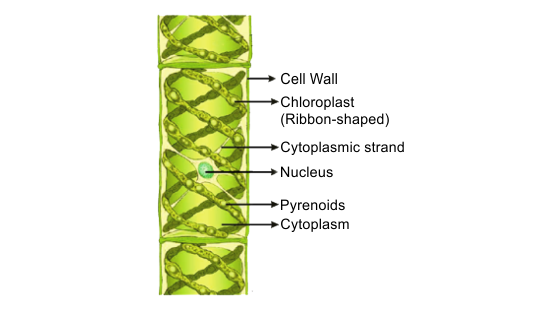
Spirogyra
51. Thallophyta, bryophyta and pteridophyta are called ‘Cryptogams’. Gymnosperms and Angiosperms are called ‘phanerogams’. Discuss why? Draw one example of Gymnosperm.
Ans: Cryptogams are the plants that reproduce by spores, they do not bear flowers and seeds and their reproductive organs are hidden or inconspicuous such as Thallophyta, Bryophyta, Pteridophyta. while phanerogams are the plants that bear flowers and seeds such as Gymnosperms and Angiosperms in which we can see well differentiated reproductive parts.
52. Define the terms and give one example of each
(a) Bilateral symmetry
Ans: Bilateral symmetry is a form of symmetry in which the body of an organism can be divided into left and right right sides when passing along a plane. Example; Humans
(b) Coelom
Ans: Coelom is a body cavity which is hollow and fluid filled which acts as a protective cushion for internal organs. Example; Coelom between the body wall and digestive tract.
(c) Triploblastic
Ans: Triploblastic- Triploblastic is a condition in which gastrula has three germ layers which are ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm from which differentiated tissue can be made. Example; Humans
53. You are given leech, Nereis, Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion; and all have segmented body organisation. Will you classify them in one group? If no, give the important characters based on which you will separate these organisms into different groups.
Ans: No, all the organisms given in the question do not belong to the same group. As Leech and Nereis belong to phylum Annelida because their body is metamerically segmented but Scolopendra, Prawn and scorpion belong to phylum Arthropoda as they have jointed legs.
54. Which organism is more complex and evolved among Bacteria, Mushroom and Mango trees? Give reasons.
Ans: Bacteria is unicellular and prokaryotic, mushroom is a fungi which is saprophytic and Mango tree is more complex and evolved than bacteria and mushroom, it is eukaryotic, autotrophic.
55. Differentiate between flying lizard and bird. Draw the diagram.
Flying Lizard | Bird |
It belongs to class Reptilia. | It belongs to class Aves. |
It is cold blooded. | It is warm blooded. |
Their bodies are covered with scales. | Their bodies are covered with feathers. |
They have three chambered heart. | They have four chambered heart. |
56. List out some common features in cat, rat and bat.
Ans: Common features in cat, rat and bat are:
(i) They belong to class Mammalia.
(ii) They all have notochord at some stage of life.
(iii) They all are warm blooded.
(iv) They all have four chambered heart.
(v) Their skin is covered with hair, sweat and oil glands.
57. Why do we keep both snake and turtle in the same class?
Ans: We keep both snake and turtle in the same class because:
(a) They both are cold blooded
(b) They both have scales on their body.
(c) They both breathe through their lungs.
(d) They both have three chambered hearts.
(e) They both lay eggs with tough covering.
Advantages of Referring to NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science- Diversity in Living Organisms
The right approach of answering difficult questions will be picked up by the students.
The NCERT Exemplar serves as an ideal model for revision before examinations.
Solving those exercises by timing oneself will teach the students about time management and thereby ensure that they complete their papers on time.
Making notes through referring to the book will get much smoother.
Students will know which areas to specifically pay attention to.
Solving these exercises regularly will also instill discipline among the students.
These books will also help one in competitive examinations as they cover all the vital topics.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science - Diversity in Living Organisms - Free PDF Download
1. What are the characteristics of species belonging to reptilia?
Cold-blooded animals who breathe through their lungs and have scales are termed reptilia. They reproduce by laying eggs. Some examples would be snakes, lizards, turtles and crocodiles. NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms made by well-known teachers have all this information available on Reptilia. The explanations are pretty lucid and the exercises equip one with the right amount of knowledge. Solving them before appearing for tests will guarantee higher marks in students who would otherwise find these topics boring.
2. Which book do I solve to get a better understanding of Class 9 Science Chapter 7- Diversity in Living Organisms?
You must refer to NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms on Vedantu.
The book has an array of questions to choose from although it would be probably best if the students were to solve every question and exercise that’s there in the book. The questions have been carefully curated by science teachers and so, they have made sure to include all the essential portions which are necessary to know about. Students must solve them consistently.
3. How do I know about the question paper pattern for NCERT Class 9 Science?
You can familiarize yourself with the question paper pattern for NCERT Class 9 Science by solving NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science on Vedantu.
The book has been made in keeping with the NCERT and CBSE board guidelines and so, will guide the students regarding the sort of questions that they may have to encounter during tests. They must go through the book and each of the exercises well to familiarize themselves and not fret before the tests take place.
4. What are some of the features of a mammal?
Mammals are warm-blooded and have a four-chambered heart. Their glands, especially the hair and sweat glands assist them in regulating their body temperature. They give birth to their children and they also feed their children milk from the mammary glands that are present in them.
Information on mammals and relevant questions about them which might come for examinations are present in NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms. The book has lots of questions that are related to mammals and is an ideal guide for students.
5. How do I make notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 7- Diversity in Living Organisms?
You can refer to NCERT Exemplar for Class 9 Science Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms available on Vedantu.
The book has considerable material that’s needed for you to prepare for tests and is also great for compiling notes for self-studying. By solving the questions posed, you will understand the concepts much better and be able to make notes that will come in handy before assessments. Making notes is an effective method of preparing for examinations as they help you understand the topics through your perspective.





































