NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Chapter 18 Free PDF Available on Vedantu
Students can download the free PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry - Environmental Chemistry from the Vedantu website. Our subject experts have carefully made the solutions keeping in mind the difficulties students usually face while preparing for this subject. The solutions are very easy to understand and concise which makes them a great addition to your study routine. Students can benefit greatly by going through the Class 11 Chemistry - Environmental Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Questions.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Science(Biology) Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation
Multiple-Choice Questions
1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytosis activity?
a. Monocyte
b. Neutrophil
c. Basophil
d. Macrophage
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin, etc., and are involved in inflammatory reactions.
2. One of the common symptoms observed in people infected with Dengue fever is
a. Significant decrease in RBC count
b. Significant decrease in WBC count
c. Significant decrease in platelets count
d. Significant increase in platelets count
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. One of the common symptoms observed in people infected with Dengue fever is a significant decrease in platelets count.
3. Which of the following is correct during each cardiac cycle?
a. The volume of blood pumped out by the Rt and Lt ventricles is the same.
b. The volume of blood pumped out by the Rt and Lt ventricles is different
c. The volume of blood received by each atrium is different
d. The volume of blood received by the aorta and pulmonary artery is different
Ans: Option (a) is the answer.
The volume of blood entering the lungs is the same as the volume leaving the lungs after oxygenation. Otherwise, it will lead to congestive heart failure due to varying pressure.
4. The cardiac activity could be moderated by the autonomous neural system. Tick the correct answer:
a. The parasympathetic system stimulates the heart rate and stroke volume
b. The sympathetic system stimulates the heart rate and stroke volume
c. The parasympathetic system decreases the heart rate but increases stroke volume
d. The sympathetic system decreases the heart rate but increases stroke volume
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. Through the autonomic nervous system, a particular neural unit in the medulla oblongata may modulate heart function (ANS). The sympathetic nerves (a component of the autonomic nervous system) can raise the pace of heartbeat, the strength of ventricular contraction, and hence the cardiac output. Parasympathetic neural signals (another component of the ANS) reduce the rate of heartbeat, the speed of action potential conduction, and hence the cardiac output.
5. Mark the pair of substances among the following which is essential for coagulation of blood.
a. Heparin and calcium ions
b. Calcium ions and platelet factors
c. Oxalates and citrates
d. Platelet factors and heparin
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. Calcium ions help in the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin so that blood can be coagulated.
6. ECG depicts the depolarisation and repolarisation processes during the cardiac cycle. In the ECG of a normal healthy individual one of the following waves is not represented.
a. Depolarisation of atria
b. Repolarization of atria
c. Depolarisation of ventricles
d. Repolarization of ventricles
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. During the cardiac cycle, the ECG illustrates the depolarization and repolarization processes. Repolarization of the atria is not seen in the ECG of a typical healthy person.
7. Which one of the following types of cells lacks a nucleus in humans?
a. Erythrocytes
b. Neutrophils
c. Eosinophils
d. Monocytes
Ans: Option a is correct. Erythrocytes lack a nucleus in humans.
8. Which one of the following blood cells are involved in antibody production?
a. B-Lymphocytes
b. T-Lymphocytes
c. RBC
d. Neutrophils
Ans: Option (a) is the answer. B - lymphocytes assisted by T-Lymphocytes.
9. The cardiac impulse is initiated and conducted further up to the ventricle. The correct sequence of conduction of impulse is
a. S A Node, A V Node, Purkinje fibre, A V Bundle
b. S A Node, Purkinje fibre, A V Node, A V Bundle
c. S A Node, A V Node, A V Bundle, Purkinje fibre
d. S A Node, Purkinje fibre, A V Bundle, A V Node
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. The correct sequence of the cardiac impulse is SA Node, AV Node, AV Bundle, Purkinje fibre
10. The cells involved in inflammatory reactions are
a. Basophils
b. Neutrophils
c. Eosinophils
d. Lymphocytes
Ans: Option (d) is the answer. Lymphocytes are responsible for immune response by producing antibodies.
11. The second heart sound (dubb) is associated with the closure of
a. Tricuspid valve
b. Semilunar valves
c. Bicuspid valve
d. Tricuspid and bicuspid valves.
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. The second heart sound (dubb) is associated with the closure of Semilunar valves.
12. Which of the following correctly explains a phase/ event in the cardiac cycle in a standard electrocardiogram?
a. QRS complex indicates atrial contraction.
b. QRS complex indicates ventricular contraction.
c. The time between S and T represents atrial systole.
d. P-wave indicates the beginning of ventricular contraction.
Ans: Option (b) is the answer.
• P-wave—Atrial depolarisation (atrial systole/contraction)
• QRScomplex—Ventricular depolarisation(ventricular systole/contraction)
• T-wave—Ventricular repolarization (ventricular relaxation
13. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a. A person of ‘O’ blood group has anti ‘A’ and anti ‘B’ antibodies in his blood plasma.
b. A person of ‘B’ blood group can’t donate blood to a person of ‘A’ blood group.
c. Blood group is designated based on the presence of antibodies in the blood plasma.
d. A person of the AB blood group is a universal recipient.
Ans: Option (c) is the answer. Blood group is designated on the basis of the antigen is present on the RBCs surface
14. What would be the cardiac output of a person having 72 heartbeats per minute and a stroke volume of 50 ml?
a. 360 mL
b. 3600 mL
c. 7200 mL
d. 5000 mL
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. Cardiac output = Stroke volume x Heart rate = 50 x 72 = 3600 mL/min.
15. Match the terms given under Column ‘A’ with their functions given under Column ‘B’ and select the answer from the options given below:
Column I | Column II |
A. Lymphatic System | i. Carries oxygenated blood |
B. Pulmonary vein | ii. Immune Response |
C. Thrombocytes | iii. To drain back the tissue fluid to the circulatory system |
D. Lymphocytes | iv. Coagulation of blood |
Options:
a. A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
b. A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-ii
c. A-iii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
d. A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
Ans: Option (b) is the answer- A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-ii
Column I | Column II |
A. Lymphatic System | iii. To drain back the tissue fluid to the circulatory system |
B. Pulmonary vein | i. Carries oxygenated blood |
C. Thrombocytes | iv. Coagulation of blood |
D. Lymphocytes | ii. Immune Response |
16. Read the following statements and choose the correct option
Statement 1: Atria receive blood from all parts of the body which subsequently flows to ventricles.
Statement 2: Action potential generated at the sino-atrial node passes from atria to ventricles.
a. Action mentioned in Statement 1 is dependent on action mentioned in Statement 2
b. Action mentioned in Statement 2 is dependent on action mentioned in Statement 1
c. Action mentioned in Statements 1 and 2 is independent of each other.
d. Action mentioned in Statements 1 and 2 is synchronous.
Ans: Option (b) is the answer. Statement 1: The atria receive blood from all of the body's organs, which then flows to the ventricles.
Statement 2: The action potential generated at the sino-atrial node travels via the atria and into the ventricles.
The action in Statement 2 is dependent on the action in Statement 1.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. Name the blood component which is viscous and straw-coloured fluid.
Ans: Plasma, a viscous and straw-coloured fluid that makes up 55 per cent of the blood, is a viscous and straw-coloured fluid.
2. Complete the missing word in the statement given below:
a. Plasma without _________ factors is called serum.
Ans: Plasma without blood clotting factors is called serum. The serum is the liquid that remains after the clotting of blood
b. ___________ and monocytes are phagocytic cells.
Ans: Neutrophils and monocytes are phagocytic cells. A type of white blood cell that is an important part of the immune system.
c. Eosinophils are associated with _____ reactions.
Ans: Eosinophils are associated with allergic reactions.
d. _______ ions play a significant role in clotting.
Ans: Calcium ions play a vital role in blood clotting, with an elevated calcium concentration assisting in the activation of proteins in platelets, which is required for blood clotting.
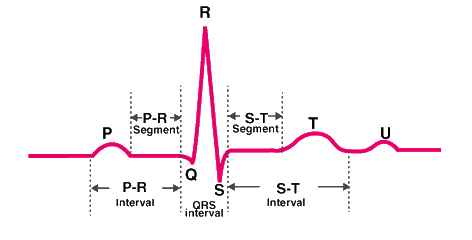
e. One can determine the heartbeat rate by counting the number of _________ in an ECG.
Ans: One can determine the heartbeat rate by counting the number of ORS complexes in an ECG.
3. Given below is the diagrammatic representation of a standard ECG. Label its different peaks.

Ans: The diagrammatic representation of a standard ECG is-
4. Name the vascular connection that exists between the digestive tract and liver.
Ans: The vascular connection that exists between the digestive tract and liver is known as Hepatic Portal System.
5. Given below are the abnormal conditions related to blood circulation. Name the disorders.
a. Acute chest pain due to failure of O2 supply to heart muscles
Ans: The disorder caused due to acute chest pain due to failure of O2 supply to heart muscles is known as angina pectoris.
b. Increased systolic pressure
Ans: Increased systolic pressure causes hypertension. It is a condition in which the blood vessels have persistently raised pressure
6. Which coronary artery disease is caused due to narrowing of the lumen of arteries?
Ans: Atherosclerosis is a coronary artery disease caused due to narrowing of the lumen of arteries.
7. Define the following terms and give their location?
a. Purkinje fibre
Ans: Purkinje fibre: It is present in the Myocardium of the ventricle and is formed by the branching of the right and left bundle. It carries impulses from S.A node
b. Bundle of His
Ans: Bundle of His: The Purkinje fibres along with left and right bundles are known as Bundle of His. These are fibres that originate from the AV node present in the wall of the right atrium.
8. State the functions of the following in blood
a. Fibrinogen
Ans: Fibrinogen is involved in the clotting of blood. When you start bleeding, your body starts the coagulation cascade, also known as the clotting cascade. Coagulation components mix in this process, resulting in a clot that stops bleeding.
b. Globulin
Ans: Globulin functions in the immune responses. They play an important role in the immune response by detecting and attaching to certain antigens, such as germs or viruses.
c. Neutrophils
Ans: Neutrophils are phagocytic and these are the first cell that reaches the site and engulf the microbes when an infection occurs
d. Lymphocytes
Ans: Lymphocytes are involved in the immune response in the blood. Lymphocytes are immune system cells that circulate through the bloodstream. T cells and B cells are the two primary kinds of lymphocytes.
9. What physiological circumstances lead to erythroblastosis foetal?
Ans: Erythroblastosis foetalis develops during pregnancy as a result of Rh incompatibility between the mother and the foetus, which can result in the foetus' mortality or severe anaemia.
10. Explain the consequences of a situation in which blood does not coagulate.
Ans: If blood clotting does not take place excessive bleeding would take place which might lead to death.
11. What is the significance of the time gap in the passage of action potential from the sino-atrial node to the ventricle?
Ans: The time gap in the passage of action potential from the SA node to the ventricle allows relaxation to the ventricles. This causes ventricular pressure to fall leading to the closure of semilunar valves which prevents the backflow of blood into the ventricles.
12. How will you interpret an electrocardiogram (ECG) in which time taken in the QRS complex is higher?
Ans: The QRS complex normally lasts less than or equal to 0.10 seconds. If the QRS complex lasts longer than 0.10 seconds and the wave is expanded, the person is suffering from a heart attack or myocardial infarction.
Short Answer Type Questions
1. The walls of ventricles are much thicker than atria. Explain.
Ans: The role of the ventricles is to pump blood to all organs, causing them to exert increased pressure. The atria get blood, thus their walls are thinner since they have fewer loads to carry.
2. Differentiate between
a. Blood and Lymph
Ans: The difference between Blood and Lymph is-
Blood | Lymph |
1. It contains plasma, RBCs, WBCs and platelets | 1. It contains plasma and lymphocytes |
2. It is red in colour | 2. It is colourless |
3. Haemoglobin is present | 3. Haemoglobin is absent |
4. It transports nutrients and gases from the heart to tissues and vice-versa | 4. It transports infection-fighting white blood cells from tissues to lymph nodes |
b. Basophils and Eosinophils
Ans: The difference between Basophils and eosinophils is-
Basophils | Eosinophils |
1. They constitute about 0.5-1% of WBCs | 1. They constitute about 2-3% of WBCs |
2. They secrete heparin, histamine and serotonin | 2. They resist infection |
3. They are involved in inflammatory reaction | 3. These are associated with allergic reactions |
c. Tricuspid and bicuspid valve
Ans: The difference between tricuspid and the bicuspid valves is
Tricuspid Valve | Bicuspid Valve |
1. It has three cusps. | 1. It has two cusps. |
2. It is present between the right atrium and right ventricle | 2. It is present between the left atrium and left ventricle. |
3. Briefly describe the following:
a. Anaemia
Ans: Anaemia is a condition in which the number of red blood cells (RBCs) or the quantity of haemoglobin in the blood is lower than normal.
b. Angina Pectoris
Ans: When enough oxygen does not reach the heart muscles, angina pectoris develops, causing chest pain and discomfort.
c. Atherosclerosis
Ans: Atherosclerosis is a condition that occurs when fat deposits on the arterial walls.
d. Hypertension
Ans: Hypertension is a condition in which the normal blood pressure, which is 120/80 mm Hg, continues to rise
e. Heart failure
Ans: Heart failure occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to satisfy the body's needs.
f. Erythroblastosis foetal
Ans: Erythroblastosis foetal is a disorder in which the foetal RBCs are destroyed owing to a Rh factor incompatibility between the mother and the foetus.
4. Explain the advantage of the complete partition of ventricle among birds and mammals and hence leading to double circulation.
Ans: The interventricular septum separates the two ventricles in birds and mammals. The left atria receive oxygenated blood, which goes to the left ventricle, while the right atria receive deoxygenated blood, which goes to the right ventricle. Blood that has been deoxygenated and blood that has been oxygenated remain separate and do not mix.
5. What is the significance of the hepatic portal system in the circulatory system?
Ans: The hepatic portal system transports deoxygenated blood from the gastrointestinal tract to the liver, where it is then transported to the heart. This gives metabolic substrates to the liver.
6. Explain the functional significance of the lymphatic system?
Ans: Lymph fluid transports hormones and nutrients while also maintaining a fluid balance between the blood and tissues. Fat is absorbed through the lymphatic system.
7. Write the features that distinguish between the two
a. Plasma and Serum
Ans: Plasma is a liquid form of blood that has no cells and is treated with an anticoagulant similar to EDTA, whereas serum is a liquid form of blood that has been coagulated.
b. Open and closed circulatory system
Ans: Blood travels via vast arteries into sinuses in an open circulatory system, whereas blood flows through a closed network of blood vessels in a closed circulatory system.
c. Sino-atrial node and atrioventricular node
Ans: The Sino-atrial node is located at the entry of the superior vena cava in the right atrium, whereas the atria-ventricular node is located near the base of the interatrial septum in the right atrium.
8. Thrombocytes are essential for the coagulation of blood. Comment.
Ans: Thrombocytes are also known as platelets which are found in the blood. Thrombocytes are formed in the bone marrow. When an injury occurs, for example, bleeding begins and platelets dissolve. They secrete thromboplastin, a clotting factor III. In the presence of calcium ions, thromboplastin activates prothrombokinase, which sets off a chain of events that results in a blood clot.
9. Answer the following
a. Name the major site where RBCs are formed.
Ans: In the early embryonic stage, RBC’s are produced in Yolk Sac. In the later embryonic stage, RBC’s are produced in the Liver and Spleen. In mature adults, RBC’s are produced in Bone Marrow
b. Which part of the heart is responsible for initiating and maintaining its rhythmic activity?
Ans: SA node or Sino Atrial Node is responsible for the rhythmic activity. The SA (sinoatrial) node sends an electrical signal to the upper chambers of the heart (atria). The signal then travels to the lower heart chambers (ventricles) through the AV (atrioventricular) node, which causes them to contract, or pump. The heart's pacemaker is known as the SA node.
c. What is specific in the heart of crocodiles among reptilians?
Ans: Crocodiles have a four-chambered heart (2 atria and 2 ventricles) with no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, whereas reptiles have a three-chambered heart (2 atria and 1 ventricle).
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Explain Rh-incompatibility in humans.
Ans: There are several blood types that are well-known. Another form of blood group is the Rh factor, sometimes known as the Rhesus monkey factor, which is a hereditary factor. Rh-negative folks are those who do not have the Rh factor (Rh-ve). If the foetus is Rh+ve and the mother is Rh-ve and the blood from the foetus enters the mother's system, antibodies against the foetal blood are produced, resulting in Erythroblastosis foetal. This is unaffected during the first pregnancy, but if the baby is RH+ve, antibodies generated against Rh+ve blood during the first pregnancy may reach the foetus through the placenta during subsequent pregnancies. This leads to the destruction of pregnancy.
2. Describe the events in the cardiac cycle. Explain “double circulation”.
Ans: The events in the cardiac cycle is-
1. Atrial Systole (0.7 sec): When the SA node initiates a wave of contraction, the atria contracts. Because the two valves are open, blood flows through the ventricles.
2. Ventricle Systole (0.5 sec): Following this, the AV node initiates a wave of contraction, which causes the ventricles to contract. As a result, the two valves close and the first heart sound, 'lub,' is created.
3. Complete Ventricular Systole: The semilunar valves open after ventricular contraction, allowing blood to pass into the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
4. Ventricular Diastole: In this condition, the ventricles relax and the semilunar valves shut, resulting in a 'dub' heart sound.
5. Complete Ventricular Diastole: As the pressure in the ventricles decreases and blood flows from the atria to the ventricles, the bicuspid and tricuspid valves open. The cycle will take 0.8 seconds to complete.
Deoxygenated and oxygenated blood stay separate and do not combine in double circulation.
3. Explain different types of blood groups and donor compatibility by making a table.
Ans: The different types of blood groups are-
Blood group | Alleles | Antigenon RBC surface | Antibodies against | Donate blood to | Received blood from |
A | IA IA or IA IO | A | B | A & AB | A & O |
B | IB IB or IB IO | B | A | B & AB | B & O |
AB | IAIB | A & B | None | AB | AB, A, B & O |
O | IOIO | None | A & B | A, B & AB | O |
4. Write a short note on the following
a. Hypertension:
Ans: a. Hypertension is a condition in which normal blood pressure (120/80 mm Hg) is constantly elevated. Hypertension is defined as a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mm Hg or above. Hypertension is divided into two categories. Primary hypertension and secondary hypertension are the two types of hypertension. The former is referred to as idiopathic hypertension since the cause of the elevated blood pressure is unknown, whereas the latter is referred to as hypertension with a known cause.
b. Coronary Artery Disease:
Ans: Coronary Artery Disease is a condition in which the artery lumen narrows owing to the build up of lipids and cholesterol, reducing the oxygen flow to the body's organs. It might potentially result in cardiac muscle damage. It can be caused by smoking, obesity, or inherited factors. Regular exercise and a good diet can help to avoid it.
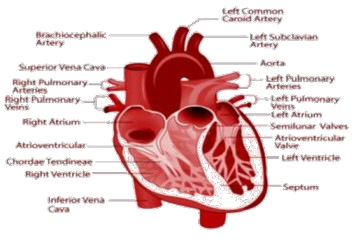
5. In the diagrammatic presentation of heart given below, mark and label, SAN, AVN, AV bundles, a bundle of His and Purkinje fibres
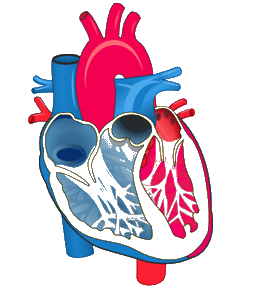
Ans: The diagrammatic presentation of the heart is given below-
Benefits of Solving Class 11 Biology - Body Fluids and Circulation
The benefits are numerous. The thing is, many students solve their NCERT textbook numerous times but they forget to refer to the NCERT Exemplar. It is a very good book for students who want to enhance their preparation and aim for excellence. The questions are of a good level. Anyone who is able to solve them will gain confidence about their preparation.
We recommend students first study their NCERT textbook at least twice before progressing to additional material. They can then solve their examples and exercises. Once they are done with the NCERT textbook, they can take their preparation to the next level by going through the NCERT Exemplar.
For exams like NEET and JEE, even board exams, students need to solve many questions. The more questions they practice, the more familiar they become about the question pattern and marking scheme. Rather than spending a huge amount on buying expensive books, students can solve questions from NCERT Exemplar for free by downloading their PDF from Vedantu.
Some of the topics which have been discussed in the Body Fluids and Circulation chapter are as follows:
Plasma
Formed Elements
Groups of Blood
The ABO Blood Grouping System
Diagram of Blood Groups and Antigen on Red Blood Cells
Rhomboid Classification
Coagulation of Blood
Lymph
Pathways of Circulation
The Circulatory System of the Human Body
Cycle of the Heart
The Sound of the Heart
Circulatory System Disorders
The chapter consists of the description of the blood and its components. They can also learn about the blood grouping system along with Rhomboid Classification. The chapter covers the coagulation of blood where students learn about how blood gets clotted. Apart from this, they learn about the pathways of circulation and the cycle of the heart. The chapter also explains circulatory system disorders in a very easy manner.
Why Should you Join Vedantu?
If you are someone who actually wants to enjoy studying, then join Vedantu. Here, our teachers make sure to keep students as their first priority. We have revolutionized the process of online learning through our interactive Classes. You can attend the Classes online, watch their recordings at your own pace or even download the videos for offline watching.
We make use of learning methods that actually work so that students are able to see themselves improving. We have a collection of NCERT- based questions, PYQs, online tests, etc., to ensure you don't miss the crucial practice. If you have any doubts, you can ask our subject experts too. So, wait no more and join Vedantu today whether you are preparing for NEET, JEE, boards, or school exams.
There is no shortcut to success. In order to shine in exams, you need to practice as many questions as you can. NCERT Exemplar can be a good source for some good-level questions for students who are done with their main textbook and are looking for some other books to solve.
Here we have provided all the NCERT Exemplar questions along with their solutions in a detailed manner. The solutions have been provided in a PDF format which is free to download.
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 11 Biology Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation solved by expert Biology teachers on Vedantu as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 18 - Body Fluids and Circulation exercise questions with solutions will help you to revise and complete the syllabus to score more marks in your examinations. Download it today from Vedantu to resolve your queries right away.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 11 Biology - Body Fluids and Circulation - Free PDF Download
1. How to remember all the examples in Biology?
In order to remember all the examples in Biology, revise them as many times as you can. You can write all the examples in one place and go through them whenever you feel like you are forgetting them.
You can also try solving questions from NCERT Exemplar for more questions practice. You can download them from Vedantu for free.
2. What are the best books to score well in Biology?
The best book to score well in Biology is NCERT. Be it for school exams, boards, or NEET, a good grasp of NCERT is sure to guarantee you a good score. If you want to further boost your marks, solving the NCERT Exemplar will help. You can download the solutions of all NCERT Exemplar questions at Vedantu in PDF format for free.
3. Is NCERT enough for NEET Biology?
Yes, the majority of the questions asked in NEET are NCERT based. If you have studied the NCERT properly and have solved all the exercises along with its questions, you can score good marks in NEET. For an extra edge over others, you can solve the NCERT Exemplar. To get the NCERT Exemplar questions along with their solutions for free download them from here. They are available in PDF format.
4. What are the benefits of solving the NCERT Exemplar?
The benefits of solving NCERT Exemplar questions for practice in Biology are many. The questions of NCERT Exemplar are of a very good level. Solving them will make the student's concepts strong and will prepare them for entrance tests that begin soon for students in Class 11. All the NCERT Exemplar questions can be found here for free along with their solutions for free.
5. Who should solve the NCERT Exemplar?
Anyone can solve the NCERT Exemplar whether you are preparing for boards or competitive exams. Questions similar to the ones in NCERT Exemplar have been asked both in boards and competitive examinations. School teachers base their questions on the NCERT Exemplar too. So, anyone can benefit from them.

























