NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - How do Organisms Reproduce? - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
The NCERT Solutions are always beneficial in your exam preparation and revision. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by master teachers. Science Students who are looking for Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions will also find the Solutions curated by our Master Teachers really Helpful.
An overview of Vedantu’s Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar for Chapter 8- How do Organisms Reproduce?
Multiple Choice Questions
1. In the list of organisms given below, those that reproduce by the asexual method are
(i)Banana
(ii)Dog
(iii)Yeast
(iv)Amoeba
(a) (ii) and (iv) (b) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv) (d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Ans: The correct answer is an option (b)
Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction which does not involves the fusion of gamete.In this kind of reproduction only one parent is involve.Being a mammal dog is always reproduce by the method of sexual reproduction.
2.In a flower, the parts that produce male and female gametes (germ cells) are
(a) Stamen and anther
(b) Filament and stigma
(c) Anther and ovary
(d) Stamen and style
Ans: The correct answer is option (c)
Flower is the main reproductive part of flowering plants.Anther is responsible for the production of pollen grains(male gamete) & ovary is responsible for the production of ova / egg(female gamete).
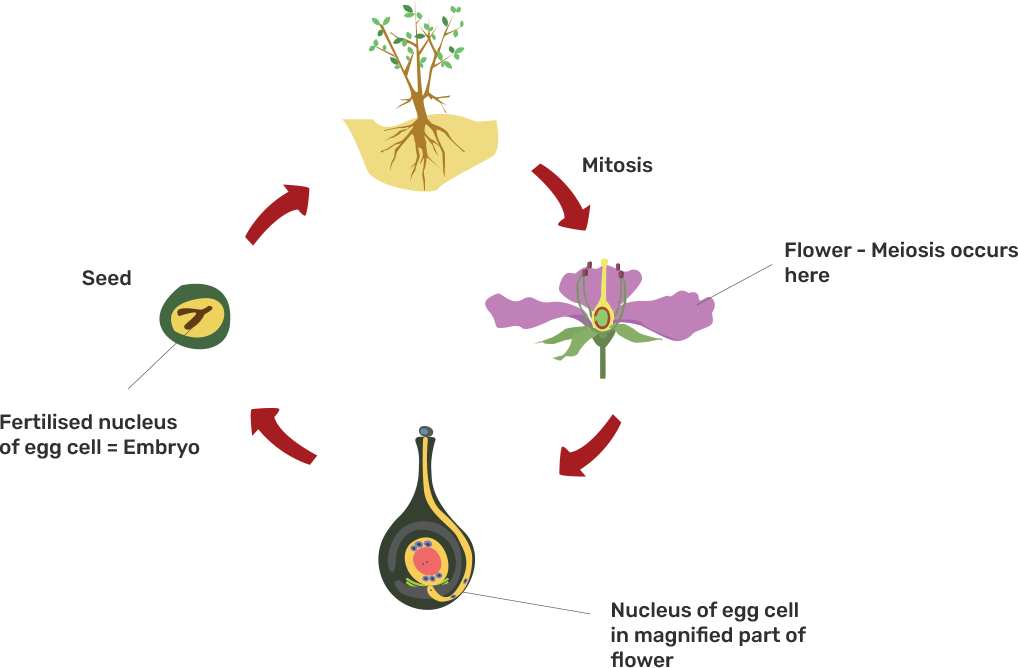
3.Which of the following is the correct sequence of events of sexual reproduction in a flower?
(a) pollination, fertilisation, seedling, embryo
(b) seedling, embryo, fertilisation, pollination
(c) pollination, fertilisation, embryo, seedling
(d) embryo, seedling, pollination, fertilisation
Ans: The correct answer is option (c)
Pollination→ Fertilisation→ Embryo→ Seedling
4. Offspring formed by the asexual method of reproduction has greater similarity among themselves because
(i)Asexual reproduction involves only one parent
(ii)Asexual reproduction does not involve gametes
(iii)Asexual reproduction occurs before sexual reproduction
(iv)Asexual reproduction occurs after sexual reproduction
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv) (d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: The correct answer is an option (a)
Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gamete. In this kind of reproduction, only one parent is involved. It is a less efficient & inferior kind of reproduction in comparison to the sexual one.
5. Characters transmitted from parents to offspring are present in
(a) cytoplasm
(b) ribosome
(c) golgi bodies
(d) genes
Ans: The correct answer is an option (d)
Genes are the unit of heredity.
6. Characters that are transmitted from parents to offspring during reproduction show
(a) only similarities with parents
(b) only variations with parents
(c) both similarities and variations with parents
(d) neither similarities nor variations
Ans: A correct answer is an option (c) both similarities and variations with parents.
This is because an offspring is the result of the fusion of gametes that comes from both the parent’s side & variation is because of crossing over.
7. A feature of reproduction that is common to Amoeba, Spirogyra and Yeast is that
(a) they reproduce asexually
(b) they are all unicellular
(c) they reproduce only sexually
(d) they are all multicellular
Ans: A correct answer is an option (a)
Amoeba, Spirogyra & Yeast reproduce by fission, fragmentation & budding respectively.
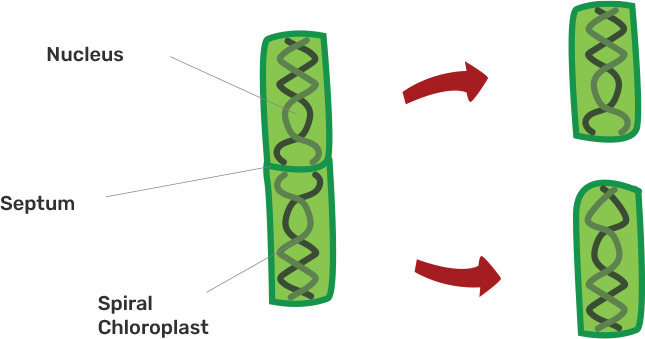
8. In Spirogyra, asexual reproduction takes place by
(a) breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
(b) division of a cell into two cells
(c) division of a cell into many cells
(d) formation of young cells from older cells.
Ans: The correct answer is an option (a)
This process of reproduction is called fragmentation.
9. The ability of a cell to divide into several cells during reproduction in Plasmodium is called
(a) budding
(b) reduction division
(c) binary fission
(d) multiple fission
Ans: A correct answer is an option (d).
It is the method of asexual reproduction. Plasmodium is the causative agent of Malaria.
10. The correct sequence of reproductive stages seen in flowering plants is
(a) gametes, zygote, embryo, seedling
(b) zygote, gametes, embryo, seedling
(c) seedling, embryo, zygote, gametes
(d) gametes, embryo, zygote, seedling
Ans: A correct answer is an option (a)
Gametes→ Zygote→ Embryo→ Seedling
11. The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a
particular species remains constant due to
(a) doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation
(b) the halving of chromosomes during gamete formation
(c) doubling of chromosomes after gamete formation
(d) the halving of chromosomes after gamete formation
Ans: A correct answer is an option (d)
During gamete formation, the no. of chromosomes become half due to reductional division. Both the parents contribute 50% each in the form of gamete ultimately gives rise to offspring that is provided with the same no. of chromosomes as the parents have.
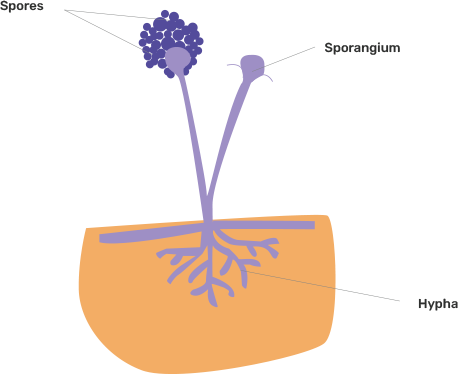
12. In Rhizopus, tubular thread-like structures bearing sporangia at their tips are called
(a) filaments
(b) hyphae
(c) rhizoids
(d) roots
Ans: The correct answer is an option (b).
13. Vegetative propagation refers to formation of new plants from
(a) stem, roots and flowers
(b) stem, roots and leaves
(c) stem, flowers and fruits
(d) stem, leaves and flowers
Ans: The correct answer is an option (b)
Vegetative propagation is the method of asexual reproduction that involves the vegetative parts of the plants such as roots, leaves & stems.
14. Factors responsible for the rapid spread of bread mould on slices of bread are
(i) a large number of spores
(ii) availability of moisture and nutrients in bread
(iii) presence of tubular branched hyphae
(iv) formation of round shaped sporangia
(a) (i) and (iii) (b) (ii) and iv)
(c) (i) and (ii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans: The correct answer is an option (c).
The presence of large no. of spores ensures survival in adverse conditions. Spores of bread mould require both moistures as well as nutrition for proper growth.
15. Length of pollen tube depends on the distance between
(a) pollen grain and the upper surface of stigma
(b) pollen grain on upper surface of stigma and ovule
(c) pollen grain in anther and upper surface of stigma
(d) upper surface of stigma and lower part of style
Ans: The correct answer is an option (d).
Pollen grain must be reached towards the ovary to ensure fertilization & this thing depends upon the length of the pollen tube.
16. Which of the following statements are true for flowers?
(i) Flowers are always bisexual
(ii) They are the sexual reproductive organs
(iii) They are produced in all groups of plants
(iv) After fertilization they give rise to fruits
(a) (i) and (iv) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii) (d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: A correct answer is an option (d).
It is not necessary that flowers are always bisexual. Flowers are produced by angiosperm plants only.
17. Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flowers possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
(a) (i) and (iv) (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Ans: A correct answer is an option (b).
Unisexual flowers are provided with stamen or pistil hence, cross-pollination occurs in them. Ovary matures to give rise to fruit, so unisexual flowers that exhibit stamens only can not produce fruits.
18. Which among the following statements are true for sexual
reproduction in flowering plants?
(i) It requires two types of gametes
(ii) Fertilisation is a compulsory event
(iii) It always results in formation of zygote
(iv) Offspring formed are clones
(a) (i) and (iv) (b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) (d) (i), (ii) and (iv)
Ans: The correct answer is option is (c)
Clones are the product of asexual reproduction, not sexual ones.
19. In Figure 8.1, the parts A, B and C are sequentially
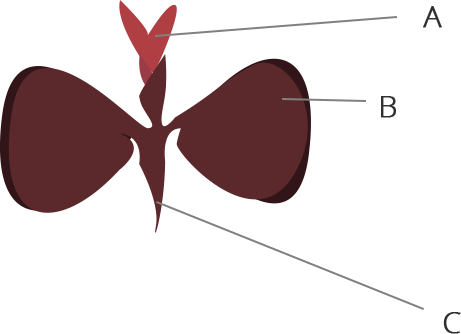
(a) cotyledon, plumule and radicle
(b) plumule, radicle and cotyledon
(c) plumule, cotyledon and radicle
(d) radicle, cotyledon and plumule
Ans: The correct answer is an option (c)
20. Offspring formed as a result of sexual reproduction exhibit more variations because
(a) sexual reproduction is a lengthy process
(b) genetic material comes from two parents of the same species
(c) genetic material comes from two parents of different species
(d) genetic material comes from many parents
Ans: The correct answer is an option (b)
During gamete formation, the no. of chromosomes become half due to the meiosis (reductional division). Both the parents contribute 50% each in the form of gamete ultimately gives rise to offspring that is provided with the same no. of chromosomes as the parents have as well the variation that is the result of crossing over.
21. Reproduction is essential for living organisms in order to
(a) keep the individual organism alive
(b) fulfill their energy requirement
(c) maintain growth
(d) continue the species generation after generation
Ans: A correct answer is an option (d).
Reproduction is defined as the production of offspring from the parents. As we know that every organism needs to fight for its survival & very few cope up with this which ultimately leads to a drastic decrease in the population. So, reproduction is the only way to maintain the stability of the population as well as the continuation of the human race.
22. During adolescence, several changes occur in the human body. Mark one change associated with sexual maturation in boys
(a) loss of milk teeth
(b) increase in height
(c) cracking of voice
(d) weight gain
Ans: A correct answer is an option (c).
The other changes that occur in males are-: i) Skin gets oilier, ii) emergence of facial hair, pubic hairs, and hair under the arms, iv) Larger size of penis and testes, v) development of muscles in chest, shoulders, and legs, etc.
23. In human females, an event that reflects the onset of the reproductive phase is-:
(a) growth of body
(b) changes in hair pattern
(c) change in voice
(d) menstruation
Ans: The correct answer is an option (d).
Other options that are mentioned in the given problem occur in male also. The onset of menstruation is called menarche.
24. In human males, the testes lie in the scrotum, because it helps in the
(a) process of mating
(b) formation of sperm
(c) easy transfer of gametes
(d) all the above
Ans: The correct answer is an option (b).
This is because it ensures the optimum temperature required for sperm production.
25. Which among the following is not the function of testes at puberty?
(i) formation of germ cells
(ii) secretion of testosterone
(iii) development of placenta
(iv) secretion of estrogen
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: The correct answer is an option (c)
This is because these events occur in the female body & the testis is the part of the male body.
26. The correct sequence of organs in the male reproductive system for the transport of sperms is
(a) testis → vas deferens → urethra
(b) testis → ureter → urethra
(c) testis → urethra → ureter
(d) testis → vas deferens → ureter
Ans: A correct answer is an option (a).
The ureter is associated with the kidney(excretory system).
27. Which of the following diseases is not sexually transmitted?
(a) Syphilis
(b) Hepatitis
(c) HIV - AIDS
(d) Gonorrhoea
Ans: The correct answer is an option (b).
STDs are such kinds of diseases that are spread from one person to another person by sexual intercourse. The medium of spread can be blood, semen, vaginal fluids, or any other body fluids. An example includes HIV, Herpes, Gonorrhea, etc.
Hepatitis is a viral infection that results in inflammation of the liver. It is not an STDs.
Short Answer Questions
28. In a bisexual flower in spite of the young stamens being removed artificially, the flower produces fruit. Provide a suitable explanation for the above situation.
Ans: Bisexual flowers are those that are provided with both the male as well female reproductive parts. Although the stamens of the bisexual flower is removed artificially in spite of this still the flowers produce fruits because of cross-pollination.
29. Can you consider cell division as a type of reproduction in unicellular organisms? Give one reason.
Ans: Yes, we can consider this. In unicellular organisms such as in Amoeba the division of cells gives rise to daughter cells that act as independent individuals.
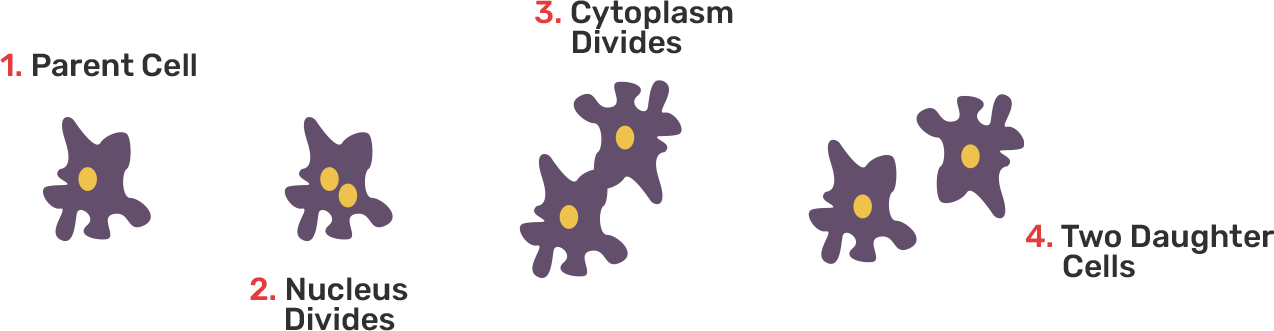
30. What is a clone? Why do offspring formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity?
Ans: Clone is defined as the photocopy of anything or any individual.
Asexual reproduction is the kind of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gamete. In this kind of reproduction, only one parent is involved. There is no event of variation or the crossing-over that creates the differences among the offspring. Hence, offsprings formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarities.
31. Explain how, offspring and parents of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes?
Ans: During gamete formation, the no. of chromosomes become half due to the meiosis (reductional division). Both the parents contribute 50% each in the form of gamete ultimately giving rise to offspring that is provided with the same no. of chromosomes as the parents have.
32. Colonies of yeast fail to multiply in water but multiply in sugar solution. Give one reason for this.
Ans: Yeast is a fungus that requires energy for growth & for maintaining homeostasis. Sugar fulfills this need hence, colonies of yeast multiply in sugar the solution only as water does not provide any energy.
33. Why does bread mould grow profusely on a moist slice of bread rather than on a dry slice of bread?
Ans: This is because the spores of bread mould require both moistures as well as nutrition for proper growth. A dry slice of bread can provide the nutrition but can’t provide the proper moisture while the moist slice provides both the nutrition as well as the moisture.
34. Give two reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction.
Ans: The reasons for the appearance of variations among the progeny formed by sexual reproduction are-:
1. Contribution of both the parents.
2. Crossing over during the meiosis.
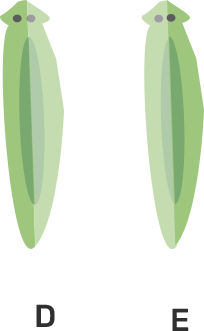
35. Would a Planaria cut vertically into two halves regenerate into two individuals? Complete Figure 8.2 D and E by indicating the regenerated regions.
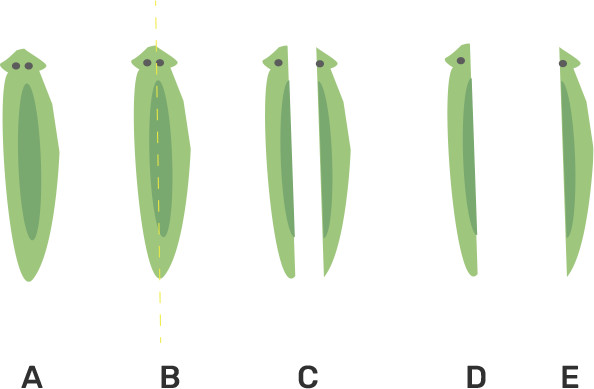
Ans: Planaria shows excellent regenerative capacity. They can give rise to new individuals whenever cut into pieces. The figure that represents the new individual from D & E is given below-:
36. From the internet, gather information about the chromosome numbers of five animals and five plants. Correlate the number with the size of the organism and answer the following questions.
Plant | No. of chromosome(2n) | Animal | No. of chromosome(2n) |
Black mulberry | 308 | Mouse | 40 |
Rattlesnake fern | 184 | Humans | 46 |
Pineapple | 50 | Gorilla | 48 |
Oat | 42 | Elephant | 56 |
Mango | 40 | Goat | 60 |
(a) Do larger organisms have more number of chromosomes/cells?
Ans: No, this is not true.
(b) Can organisms with fewer chromosomes reproduce more easily than organisms with more chromosomes?
Ans: No, this is because the process of reproduction follows a common pattern that is not dependent on the number of chromosomes.
(c) More the number of chromosomes/cells greater is the DNA content. Justify.
Ans: Yes, since the major component of chromosomes is DNA, if there are more chromosomes then the quantity of DNA will also be more in a cell.
37. In the tobacco plant, the male gametes have twenty-four chromosomes.
a) What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete?
Ans: Gametes are the result of reductional division. The chromosomal content will be the same in both cases. Hence, female gametes will also have twenty-four chromosomes.
b) What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote?
Ans: Zygote is the result of fertilization (fusion of gametes). Hence, the chromosomal content gets doubled i.e. forty-eight chromosomes.
38. Why cannot fertilization take place in flowers if pollination does not occur?
Ans: Pollination is defined as the dispersal of pollen grains. As soon as the pollen grains land on the stigma they germinate to produce pollen tubes that carry the male gamete towards the egg & facilitate the process of fertilization. Hence, fertilization can not take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
39. Is the chromosome number of the zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
Ans: Yes , no. of the chromosomes remain constant in all three stages. During gamete formation, the no. of chromosomes become half due to the meiosis (reductional division). Both the parents contribute 50% each in the form of gamete ultimately giving rise to offspring that is provided with the same no. of chromosomes as the parents have.
40. Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilization?
Ans: After the fertilization, the zygote is located in the ovary(swollen basal part of the female reproductive structure).
41. Reproduction is linked to stability of population of a species.Justify the statement.
Ans: Reproduction is defined as the production of offspring from the parents.As we know that every organism needs to fight for its survival & very few cope up with this which ultimately leads to a drastic decrease in the population.So, reproduction is the only way to maintain the stability of the population as well as the continuation of the human race.
42. How are general growth and sexual maturation different from each other?
Ans:
General growth | Sexual maturation |
1. It is defined as the increase in size of an organism because of an increase in no. of cells. | 1. It is defined as the attainment of sexual maturity of reproductive organs. |
2.It starts from the birth of an organism. | 2. It starts after attaining a particular age i.e. in adolescent stage. |
43. Trace the path of sperm during ejaculation and mention the gland and their functions associated with the male reproductive system.
Ans: Path of sperm during ejaculation:
Testis
↓
Epididymis
↓
Vas deferens
↓
Prostrate
↓
Urethra
Glands associated with the male reproductive system | Functions |
Testis | It secretes testosterone hormone |
Prostate gland | It add on the fluid content to the semen |
Seminal vesicle | It secretes fructose rich fluid that provides the energy to the sperms . |
Cowper’s gland | It lubricates the urethra & neutralize the acidity of traces of urine |
44. What changes are observed in the uterus if fertilization does not occur?
Ans: Changes observed in the uterus if fertilization does not occur are:
The extra lining of the uterus degenerates & comes out of the vagina in the form of menstrual fluid. Unfertilized eggs also comes out along with uterus lining. This event is mainly called menstruation that lasts for 2-7 days & occurs every month(28 days cycle).
45. What changes are observed in the uterus subsequent to implantation of a young embryo?
Ans: Changes observed in the uterus if implantation occurs are-:
Thickening of the uterus line takes place to support the pregnancy. The supply of blood vessels also increases to ensure the proper supply of nutrition to the developing embryos.
46. What are the benefits of using mechanical barriers during sexual acts?
Ans: Following are the advantages of using mechanical barriers during sexual acts are-:
1. Prevention of unwanted pregnancy.
2.Prevention of STDs (sexually transmitted diseases).
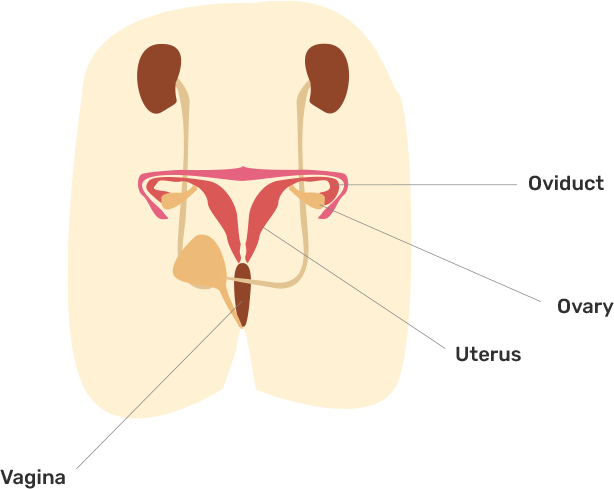
47. In the given Figure 8.3 label the parts and mention their functions-:
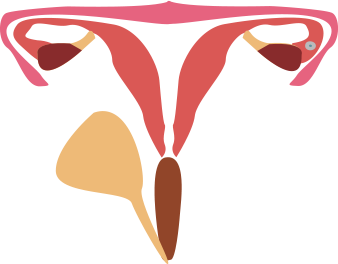
(a) Production of egg
Ans: The Production of eggs takes place in ovaries.
(b) Site of fertilisation
Ans: The site of fertilisation(fusion of gametes) is oviduct.
(c) Site of implantation
Ans: The site of implantation is the uterus.
(d) Entry of the sperms
Ans: Entry of the sperms occurs in vagina during the sexual intercouse.
48. What would be the ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote? How is the sperm genetically different from the egg?
Ans: The ratio of chromosome number between an egg and its zygote is 1:2 because an egg is the female gametes that produce due to reductional division & the zygote is the result of fusion of gametes (sperm & egg).
In human beings it is the male that decides the sex of devloping off-spring.
Sperm | Egg |
1.Sperm contains either X or Y chromosomes. | 1.Egg contains only an X chromosome. |
Long Answer Questions
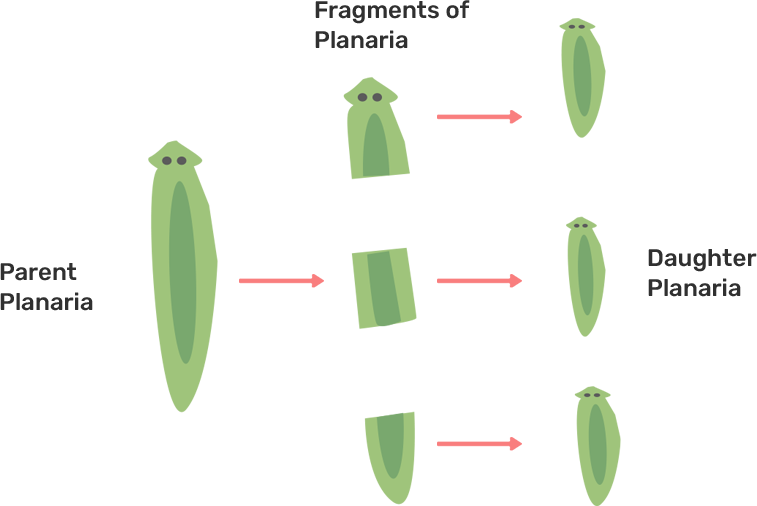
49. Why are budding, fragmentation and regeneration all considered as asexual types of reproduction? With neat diagrams explain the process of regeneration in Planaria.
Ans. This is because in all three cases single parent is involved as well as there is no gametes fusion.
Regeneration in planaria-: It is the capacity of any individual to restore the damaged parts.When ever the body of the planaria is divided into pieces then each piece is having the capacity to give rise to a new individual.
50. Write two points of difference between asexual and sexual types of reproduction. Describe why variations are observed in the offspring formed by sexual reproduction.
Ans:
Sexual reproduction | Asexual reproduction |
1. In this kind of reproduction two parents are involved. | 1.In this kind of reproduction single parent is involved & there is no fusion of gametes. |
2.Crossing over is there. | 2.Crossing over is not there. |
Variations are observed in the offspring formed by sexual reproduction because-:
1. Involvement of two parents.
2. Fusion of gametes.
3. Crossing over during the meiosis.
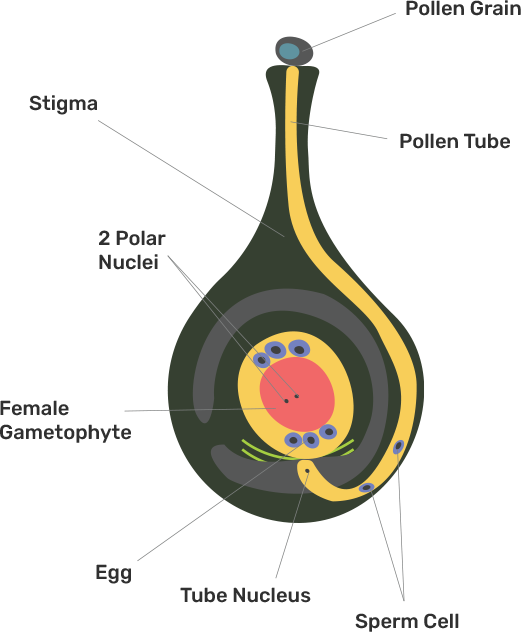
51. a)Distinguish between pollination and fertilization. Mention the site and product of fertilization in a flower.
Ans:
Pollination | Fertilization |
1. It is defined as the dispersal of pollen grains. | 1. It is defined as the fusion of gametes. |
2. It occurs outside the ovary. | 2. It occurs inside the ovary. |
3.It occurs in the early stages of sexual reproduction of flowering plants. | 3.It occurs after pollination. |
Site of fertilization in a flower - Ovary
Product of fertilization in a flower - Zygote
b)Draw a neat, labeled diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth and its entry into the ovule.
Ans:
52. Distinguish between a gamete and zygote. Explain their roles in
sexual reproduction.
Ans:
Gamete | Zygote |
1. It is the product of meiosis(reductional division). | 1. It is the product of fusion of gametes. |
2.It is provided with a single set of chromosomes. | 2. It has a diploid set of chromosomes. |
3. It is produced by male & female parts. | 3.There is no role of males in this case. |
Role in sexual reproduction-: Without the production gametes the process of fertilization can’t take place.Hence , there will be no production of offspring without this event. | Role in sexual reproduction-: It acts as the precursor for the production of embryos. |
53. Draw the diagram of a flower and label the four whorls. Write the names of gamete producing organs in the flower.
Ans:
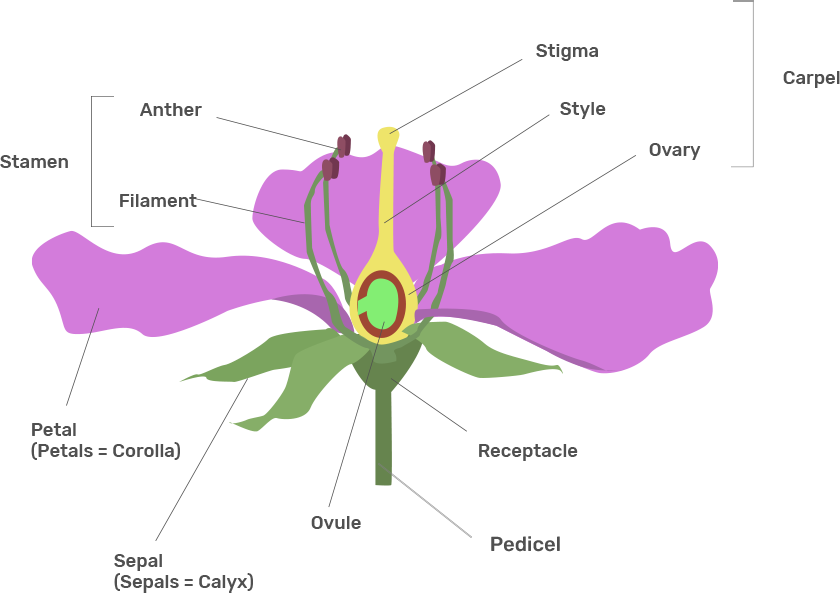
Gamete producing organs in the flower-:
Male gamete-:Ovary
Female gamete-:Anther
54. What is placenta? Mention its role during pregnancy?
Ans:
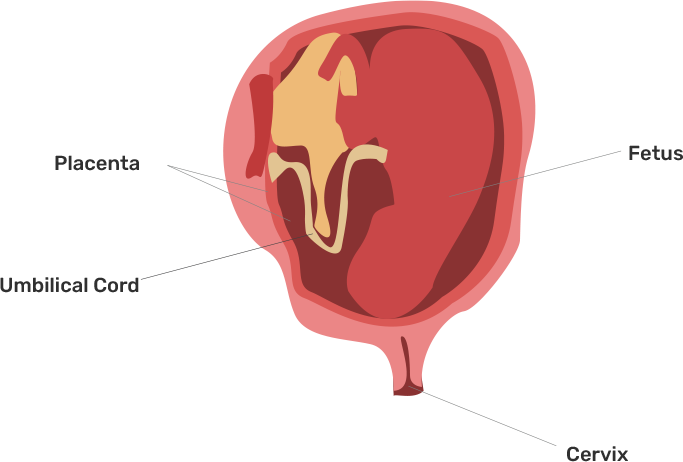
Placenta is the disc-like structure that is embedded in the uterine wall. It is the temporary organs that play variety of roles such as-:
1.It supplies nutrients to the baby.
2.It supplies oxygen to the baby.
3.It helps in elimination of waste products from foetus body.
4. It takes away carbon dioxide from the fetus' body.
55.What are various ways to avoid pregnancy? Elaborate any one method.
Ans: Birth control: It is defined as the way by which an unwanted pregnancy can be avoided.There are various method that are given below-:
Barrier Method: This kind of method involves putting up the barrier between the male & the female sex cells. It can be used by both genders. Contraceptive sponge, diaphragm, cervical shield & condoms come under this category.
Natural Birth Control: This method involves no intercourse or protected intercourse during the time when the woman is fertile.The fertile period in the womans starts 5 days before ovulation and continues for 3 days after ovulation.
Hormonal Method: This method dustrubs the hormonal balance in the woman's body in order to hamper fertilization, ovulation or fertilized egg implantation.It can be achieved by the help of contraceptive pills, estrogen and progestin-releasing patches or vaginal rings.
Intrauterine Devices (IUD’s): These are small T-shaped devices that are planted in the uterus. There are mainly two types of IUDs:
1. Copper-T: It releases a small amount of copper in the uterus which prevents sperm from reaching the ovary.
2.Hormonal IUD: It releases progestin in the body that prevents the formulation of eggs.
Surgical Methods: It is the permanent method of contraception.Both men and women can go for this. For women, the process is called Tubal ligation/tubectomy and for men, it is called Vasectomy.
56. How does fertilization take place? Fertilization occurs once in a month. Comment.
Ans: Human females release one egg each month. This egg is transferred to fallopian from the ovary. During the sexual intercourse male partner ejaculates the semen in the female reproductive part(vagina). There are about 40 millions to 300 millions of sperm in one milliliter of semen. From here the sperm swim up to the fallopian tube where it fuses with the egg & the event of fertilization takes place.
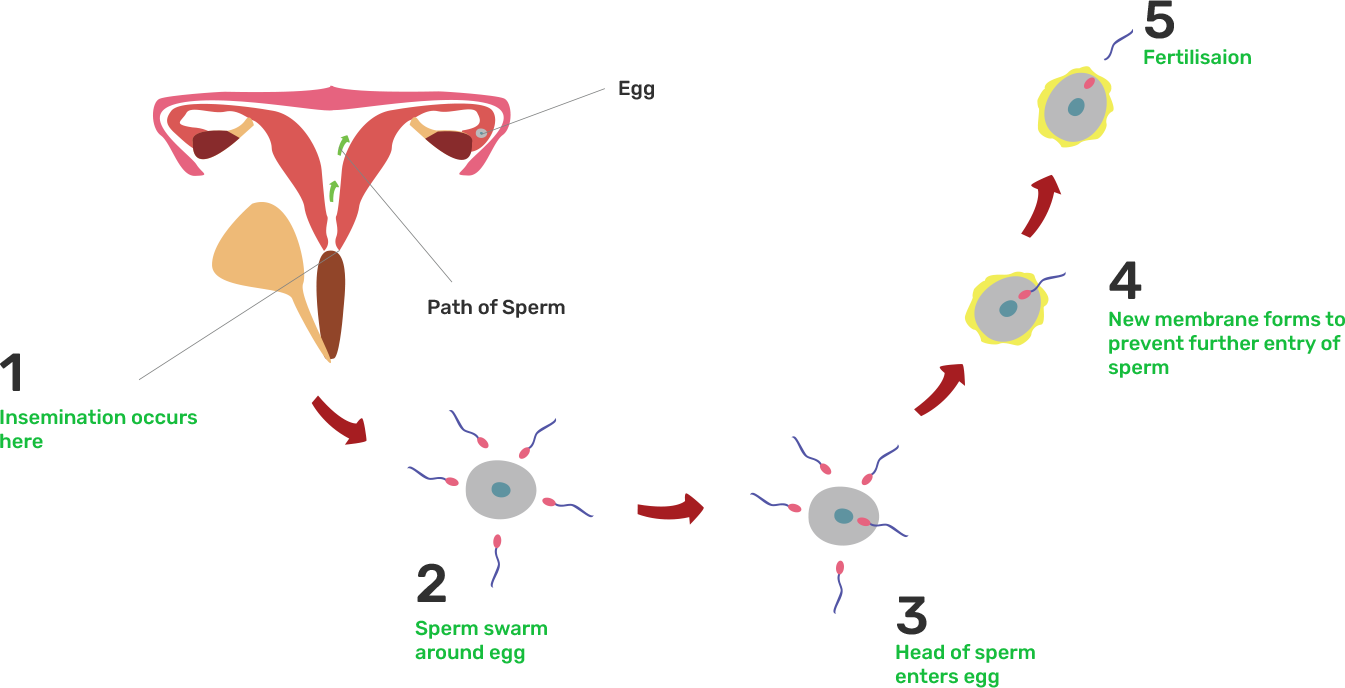
A menstrual cycle is composed of 28 days.This means that only one egg is available for fertilization in one menstrual cycle , hence it is said that fertilization can take place once a month.
57. Reproduction is essentially a phenomenon that is not for survival of an individual but for the stability of a species. Justify
Ans: The survival of an organism depends upon variety of factors such as:
1. Food & shelter
2. Not killed by predators.
3. Continuation of life processes.
Reproduction is defined as the production of offspring from the parents.As we know that every organism needs to fight for their survival & very few cope up with this which ultimately leads to drastic decrease in the population.So , reproduction is the only way to maintain the stability of the population as well as the continuation of human race.It does not play any role in the survival of an organism.
58. Describe sexually transmitted diseases and mention the ways to prevent them.
Ans: Such kind of diseases that are spread from one person to another person by sexual intercourse. The medium of spread can be blood, semen, vaginal fluids or any other body fluids.
The example includes HIV, Herpes, Gonorrhea etc. There are variety of ways one can prevent them to spread are:
1. By avoiding sexual intercourse with multiple or unknown partners.
2. By using physical barriers such as condoms.
3. By avoiding the sharing of clothes.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 - How do Organisms Reproduce? (Book Solutions)
Vedantu’s Chapter 8 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science covers some topics. They are listed below
Do Organisms Create Exact Copies Of Themselves?
The Importance Of Variation
Modes Of Reproduction Used By Single Organisms
Fission
Fragmentation
Regeneration
Budding
Vegetative Propagation
Spore Formation
Sexual Reproduction






































