NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Periodic Classification of Elements - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements exercise questions with solutions will help you to revise and complete the syllabus and score more marks in your examinations. Every NCERT Solution is provided to make the study simple and interesting on Vedantu. Subjects like Science, Maths, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 10 Science, Maths solutions and solutions of other subjects. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Access NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science(Chemistry) Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Upto which element, the law of Octaves was found to be applicable
(a) Oxygen
(b) Calcium
(c) Cobalt
(d) Potassium
Ans: b. Calcium
Upto calcium, the law of Octaves was found to be applicable. After calcium, (atomic number 20) every eighth element does not possess the similar property to that of the first element.
2. According to Mendeleev's Periodic Law, the elements were arranged in the periodic table In the order of
(a) increasing atomic number
(b) decreasing atomic number
(c) increasing atomic masses
(d) decreasing atomic masses
Ans: c. increasing atomic masses
According to Mendeleev's Periodic Law, the elements were arranged in the periodic table in the order of increasing atomic mass. So, according to Mendeleev, elements are the periodic function of their atomic masses.
3. In Mendeleev 's Periodic Table, gaps were left for the elements to be discovered later. Which of the following elements found a place in the periodic table later
(a) Germanium
(b) Chlorine
(c) Oxygen
(d) Silicon
Ans: a. Germanium
In Mendeleev's Periodic Table, gaps were left for the elements to be discovered later. Germanium was one of those elements, found a place in the periodic table later and shows the expected similarities.
4. Which of the following statement (s) about the Modern Periodic Table are incorrect
(i) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on the basis of their decreasing atomic number
(ii) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic masses
(iii) Isotopes are placed in adjoining group (s) in the Periodic Table
(iv) The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on
(a) (i) only
(b) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iv) only
Ans: (i), (ii) and (iii)
The elements in the Modern Periodic Table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic number hence, isotopes occupy the same position in the modern periodic table.
5. Which of the following statements about the Modern Periodic Table is correct:
(a) It has 18 horizontal rows known as Periods
(b) It has 7 vertical columns known as Periods
(c) It has 18 vertical columns known as Groups
(d) It has 7 horizontal rows known as Groups
Ans: c. It has 18 vertical columns known as Groups
The modern periodic table is the tabular arrangement of elements according to their increasing atomic numbers. There are 118 elements known and present in the periodic table which has 18 groups and 7 periods.
6. Which of the given elements A, B, C, D and E with atomic number 2, 3, 7, 10 and 30 respectively belong to the same period?
(a) A, B, C
(b) B, C, D
(c) A, D, E
(d) B, D, E
Ans: b. B, C, D
Element | Atomic Number | Electronic Configuration | Period |
A | 2 | (2) | 1 |
B | 3 | (2, 1) | 2 |
C | 7 | (2, 5) | 2 |
D | 10 | (2, 8) | 2 |
E | 30 | (2, 8, 18, 2) | 4 |
7. The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic number 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. Which pair of elements belong to the same group?
(a) A and B
(b) B and D
(c) A and C
(d) D and E
Ans:
Element | Atomic Number | Electronic Configuration | Group |
A | 9 | (2, 7) | 17 |
B | 11 | (2, 8, 1) | 1 |
C | 17 | (2, 8, 7) | 17 |
D | 12 | (2, 8, 2) | 2 |
E | 13 | (2, 8, 3) | 3 |
The elements that have the same valence electron belong to the same group, so elements A and C belong to the same group as they have 7 valence electrons.
8. Where would you locate the element with electronic configuration 2,8 in the Modern Periodic Table?
(a) Group 8
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 18
(d) Group 10
Ans: c. Group 18
The electronic configuration of the element is 2, 8. It has a total of 10 electrons. So, the atomic number is 10. The element is neon, an inert gas or noble group element. In the electronic configuration 2, 8 the octet is complete as the valence shell is having 8 electrons. This suggests a noble gas element. In the modern periodic table, noble gas elements are present in the group 18.
Hence, you would locate the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the Modern Periodic Table in the group 18.
9. An element which is an essential constituent of all organic compounds belongs to
(a) group 1
(b) group 14
(c) group 15
(d) group 16
Ans: b. group 14
Carbon is an essential constituent of all organic compounds due to its catenation property. It has atomic number 6, so electronic configuration is (2, 4). Valence electron present in carbon is 4 and hence, belongs to group 14.
10. Which of the following is the outermost shell for elements of period 2?
(a) K shell
(b) L shell
(c) M shell
(d) N shell
Ans: b. L shell
Period 2 contains two shells K shell and L shell. The outermost shell for the elements of period 2 is L shell.
11. Which one of the following elements exhibit maximum number of valence electrons?
(a) Na
(b) Al
(c) Si
(d) P
Ans: d. P
Element | Atomic Number | Electronic Configuration | Valence Electrons |
Na | 11 | (2,8,1) | 1 |
Al | 13 | (2,8,3) | 3 |
Si | 14 | (2,8,4) | 4 |
P | 15 | (2,8,5) | 5 |
Valence electrons are the total number of electrons present in the outermost shell. Phosphorus has 5 electrons in its valence shell which is the maximum among the given elements.
12. Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of the atomic radii of O, F and N?
(a) O, F, N
(b) N, F, O
(c) O, N, F
(d) F, O, N
Ans: d. F, O, N
Along the period the atomic radii decrease on moving left to right as the effective nuclear charge increases due to which the valence electrons suffer the more attractive effective nuclear charge.
13. Which among the following elements has the largest atomic radii?
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) K
(d) Ca
Ans: c. K
Along the period atomic size decreases due to increase in effective nuclear charge. And along the group, atomic size increases due to addition of new sub-shell. Addition of a new sub-shell is predominant over effective nuclear charge so.K has the largest atomic radii.
14. Which of the following elements would lose an electron easily?
(a) Mg
(b) Na
(c) K
(d) Ca
Ans: d. K
The element which has the largest size will lose electrons easily. K has the largest size among the given electrons (extreme left i.e. group 1 and period 4), so the effective nuclear charge on the valence electrons will be minimum and hence, would lose an electron easily.
15. Which of the following elements does not lose an electron easily?
(a) Na
(b) F
(c) Mg
(d) Al
Ans: b. F
The F element does not lose an electron easily as it has the smallest size among the given elements and hence maximum effective nuclear charge on the valence electron. So, it will require more energy to lose valence electrons.
16. Which of the following are the characteristics of isotopes of an element?
(i) Isotopes of an element have same atomic masses
(ii) Isotopes of an element have same atomic number
(iii) Isotopes of an element show same physical properties
(iv) Isotopes of an element show same chemical properties
(a) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: d. (ii) and (iv)
Isotopes have the same atomic number but different mass number. Chemical properties is a function of atomic number so, isotopes of an element show the same chemical properties.
17. Arrange the following elements in the order of their decreasing metallic character Na, Si, Cl, Mg, Al
(a) Cl > Si > Al > Mg > Na
(b) Na > Mg > Al > Si > Cl
(c) Na > Al > Mg > Cl > Si
(d) Al > Na > Si > Ca > Mg
Ans: b. Na > Mg > Al > Si > Cl
Metallic character decreases across the period from moving left to right as the effective nuclear charge increases due to which the tendency to lose the electron decreases and so, metallic character decreases.
18. Arrange the following elements in the order of their increasing non-metallic character
Li, O, C, Be, F
(a) F < O < C < Be < Li
(b) Li < Be < C < O < F
(c) F < O < C < Be < Li
(d) F < O < Be < C < Li
Ans: (a) F < O < C < Be < Li
Non-metallic character increases across the period from moving left to right due to an increase in force of attraction between the nucleus and valence electrons.
19. What type of oxide would Eka- aluminium form?
(a) EO3
(b) E3O2
(c) E2O3
(d) EO
Ans: (c) E2O3
Eka aluminium forms oxide as aluminium oxide as they exist in the same group. So, the type of oxide Eka- aluminium forms is E2O3.
20. Three elements B, Si and Ge are
(a) metals
(b) non-metals
(c) metalloids
(d) metal, non-metal and metalloid respectively
Ans: (d) metal, non-metal and metalloid respectively
The element B is metal, Si is non-metal and Ge is a metalloid. A metalloid is an element which shows the property of both metal and non-metal.
21. Which of the following elements will form an acidic oxide?
(a) An element with atomic number 7
(b) An element with atomic number 3
(c) An element with atomic number 12
(d) An element with atomic number 19
Ans: (a) An element with atomic number 7.
Non-metals form an acidic oxide element with atomic number 7 has electronic configuration as (2, 5) is a non-metal which can gain 3 electrons to attain the nearest noble gas configuration.
The elements with atomic number 3 has configuration as (2, 1), atomic number 12 has configuration (2, 8, 2) and with atomic number 19 has electronic configuration as (2, 8, 8, 1) can lose electron(s) easily to attain the nearest noble gas configuration and form basic oxide.
22. The element with atomic number 14 is hard and forms acidic oxide and a covalent halide. To which of the following categories does the element belong?
(a) Metal
(b) Metalloid
(c) Non-metal
(d) Left-hand side element
Ans: (b) Metalloid
The element with atomic number 14 is hard (metals are generally hard) and form acidic oxide (non-metals form acidic oxides) and a covalent halide (non-metal form covalent halide)is a metalloid. Metalloids are the elements which show the property of both metals and non-metals.
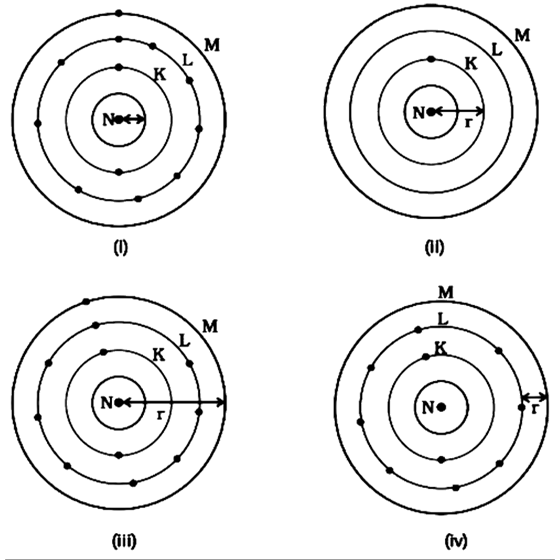
23. Which one of the following depict the correct representation of atomic radius(r) of an atom?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans: (c) (ii) and (iii)
Atomic radii is the distance from the centre of the nucleus to the outermost shell or valence shell. Valence shell is the outermost shell which has the valence electron that participate in the chemical bonding.
24. Which one of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?
(a) Atomic radius
(b) Metallic character
(c) Valence
(d) Number of shells in an element
Ans: (c) Valence
Valence electrons do not increase but remain the same on moving down the group of the periodic table.
Atomic radius increases due to the addition of a shell down the group. Metallic character increases due to increase of size of atom down the group.
25. On moving from left to right in a period in the periodic table, the size of the atom.
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) does not change appreciably
(d) first decreases and then increases
Ans: (b) decreases
On moving from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the size of the atom decreases as the effective nuclear charge increases due to which the force of attraction of the nucleus to the valence electron increases and hence the size of the atom decreases.
26. Which of the following set of elements is written in order of their increasing metallic character?
(a) Be Mg Ca
(b) Na Li K
(c) Mg Al Si
(d) C O N
Ans: (a) Be Mg Ca
In a modern periodic table, the atomic radii increases (a shell increases) due to which the effective nuclear charge on the valence shell decreases and the tendency to lose electrons increases, hence metallic character increases.
Short Answer Questions
27. The three elements A, B and C with similar properties have atomic masses X, Y and Z respectively. The mass of Y is approximately equal to the average mass of X and Z. What is such an arrangement of elements called as? Give one example of such a set of elements.
Ans: The arrangement of elements A, B and C is called triads. In Dobereiner triads, the three elements have similar properties in which the middle element has the atomic mass same as the average atomic mass of the other two elements.
Example:
Triad elements | Atomic mass |
Li | 7 |
Na | 23 |
K | 39 |
Atomic mass of Na = $\frac{7~+~39}{2}$ = 23
28. Elements have been arranged in the following sequence on the basis of their increasing atomic masses.
F, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K
(a) Pick two sets of elements which have similar properties.
Ans: (i) F and Cl
(ii) Na and K
The elements belonging to the same group have similar properties.
(b) The given sequence represents which law of classification of elements?
Ans: Newland’s law of octave is represented in the given sequence for the classification of elements which states that when the elements are arranged in their increasing atomic masses, every eighth element has the similar properties as the first element.
29. Can the following groups of elements be classified as Dobereiner's triad ? Atomic mass of Be 9; Na 23; Mg 24; Si 28; Cl 35; Ca 40
Explain by giving reason.
(a) Na, Si, Cl
Ans:
Elements | Atomic mass |
Na | 23 |
Si | $\frac{23~+~35}{2}$ = 29 |
Cl | 35 |
Atomic mass of Si is 28 which is not the average mean of atomic mass of Na and Cl so, it is not a Dobereiner's triad.
(b) Be, Mg, Ca
Ans:
Elements | Atomic mass |
Be | 9 |
Mg | $\frac{9~+~40}{2}$ = 24.5 |
Ca | 40 |
Atomic mass of Mg is 24 which is not same as the average mean of atomic mass of Be and Ca so, it is not a Dobereiner's triad.
30. In Mendeleev's Periodic Table the elements were arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses. However, cobalt with an atomic mass of 58.93 amu was placed before nickel having an atomic mass of 58.71 amu. Give reason for the same.
Ans: In Mendeleev 's Periodic Table, the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses but some elements such as cobalt with atomic mass of 58.93 amu was placed before nickel having an atomic mass of 58.71 amu because Mendeleev placed some elements with similar properties together in the periodic table.
31. “Hydrogen occupies a unique position in the Modern Periodic Table”. Justify the statement.
Ans: Hydrogen is a non-metal as it has one electron and can lose that to form stable H + ion. But it occupies a unique position in the Modern Periodic Table placed with the alkali metal as it can accept one electron to attain the nearest noble gas configuration and form hydrides.
32. Write the formulae of chlorides of Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium, the elements predicted by Mendeleev.
Ans: Eka-silicon forms chlorides of form- ECl4 and Eka-aluminium forms chlorides of form ECl3.
33. Three elements A, B and C have 3, 4 and 2 electrons respectively in their outermost shell. Give the group number to which they belong in the Modern Periodic Table. Also, give their valencies.
Ans:
Element | Valence electron | Group | Valency |
A | 3 | 13 | 3 |
B | 4 | 14 | 4 |
C | 2 | 2 | 2 |
Valency of an element is the combining capacity of the element with another element by losing or gaining the valence electrons..
34. If an element X is placed in group 14, what will be the formula and the nature of bonding of its chloride?
Ans: Element X is placed in group 14 it has 4 valence electrons and can share electrons (as losing or gaining 4 electrons will require a greater amount of energy than sharing) with chlorine element to form chlorides. So, the nature of the bonding of element X with chlorine is covalent bonding. Formula of the element X with chlorine is. XCl4.
35. Compare the radii of two species X and Y. Give reasons for your answer.
(a) X has 12 protons and 12 electrons
(b) Y has 12 protons and 10 electrons
Ans: Radius of element Y will be smaller than the radius of element X as element Y has more protons than electrons and will have more effective nuclear charge due to which the force of attraction on the valence electrons will be more in element Y than present in element X. As the force of attraction is more in element Y than in element X it has a smaller radius.
36. Arrange the following elements in increasing order of their atomic radii.
(a) Li, Be, F, N
Ans: The increasing order of atomic radii of the given elements:
Li < Be < N < F
Across the period from left to right effective nuclear charge increases due to which atomic radii decreases.
(b) Cl, At, Br, I
Ans: The increasing order of atomic radii of the given elements:
Cl < Br < I < At
Down the group atomic radii increases due to addition of a shell.
37. Identify and name the metals out of the following elements whose electron configurations are given below.
(a) 2, 8, 2
(b) 2, 8, 1
(c) 2, 8, 7
(d) 2, 1
Ans:
Element | Electronic configurations | Metal or Non-metal |
A | 2,8,2 | Metal |
B | 2,8,1 | Metal |
C | 2,8,7 | Non-Metal |
D | 2,8,1 | Metal |
The elements with configuration (2, 8, 2), (2, 8, 1) and (2, 1) are metals as they have 1 or 2 electrons that can be lost whereas the element with electron configuration (2, 8, 7) can gain 1 electron easily hence it is a non-metal.
38. Write the formula of the product formed when the element A (atomic number 19) combines with the element B (atomic number 17). Draw its electronic dot structure. What is the nature of the bond formed?
Ans:
Element | Atomic Number | Electronic configurations |
A | 19 | 2, 8, 8, 1 |
B | 17 | 2, 8, 7 |
Element A has 1 electron in its valence shell which can be lose to attain nearest noble gas configuration whereas element B has 7 electrons in its valence shell and can gain 1 electron to attain nearest noble gas configuration so one electron will transfer from element X to element Y to form ionic bond.
The electron dot structure of element X and Y is
Valency | |
A has electronic configuration = 2, 8, 8, 8 A has electronic configuration = 2, 8, 7 Formula is (Image will be uploaded soon) (A)+ \[{{(:\underset{.\,\,\,.}{\overset{.\,\,\,.}{\mathop{B}}}\,:)}^{-}}\] is electron dot diagram. The bond formed is ionic. | 1 1 |
39. Arrange the following elements in the increasing order of their metallic character.
Mg, Ca, K, Ge, Ga
Ans: The increasing order of the given metallic character is:
Ge < Ga < Mg < Ca < K
Alkali metals are the most electropositive metals and hence are the most metallic metals, alkaline earth metals show the next highest metallic character. Metallic character decreases across the period from left to right due to decrease in atomic size.
40. Identify the elements with the following property and arrange them in increasing order of their reactivity
(a) An element which is a soft and reactive metal
Ans: Sodium (Na) is a soft and reactive metal.
(b) The metal which is an important constituent of limestone
Ans: Calcium (Ca) is an important constituent of limestone.
(c) The metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature
Ans: Mercury (Hg) is a metal which exists in liquid state at room temperature.
Reactivity order: Hg < Ca < Na
In the reactivity series, sodium is placed above the given metals after which calcium is present and then near the bottom is the mercury.
41. Properties of the elements are given below. Where would you locate the following elements in the periodic table?
(a) A soft metal stored under kerosene.
Ans: Sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are highly reactive and soft metals placed under kerosene. Na is present in group 1 and period 3 whereas potassium is present in group 1 and period 4.
(b) An element with variable (more than one) valency stored under water.
Ans: Phosphorus (P) is an element with variable (more than one) valency stored under water. Phosphorus is a reactive non-metal hence stored under water and present in group 15 and period 3.
(c) An element which is tetravalent and forms the basis of organic chemistry.
Ans: Carbon (C) is an element which is tetravalent and forms the basis of organic chemistry which is present in group 14 and period 2.
(d) An element which is an inert gas with atomic number 2.
Ans: Helium (He) element is an inert gas with atomic number 2 and present in group 18 and period 1.
(e) An element whose thin oxide layer is used to make other elements corrosion resistant by the process of" anodising"
Ans: Aluminium (Al) elements form a thin oxide layer which is used to make other elements corrosion resistant by the process of" anodising". Al is present in group 13 and period 3.
Long Answer Questions
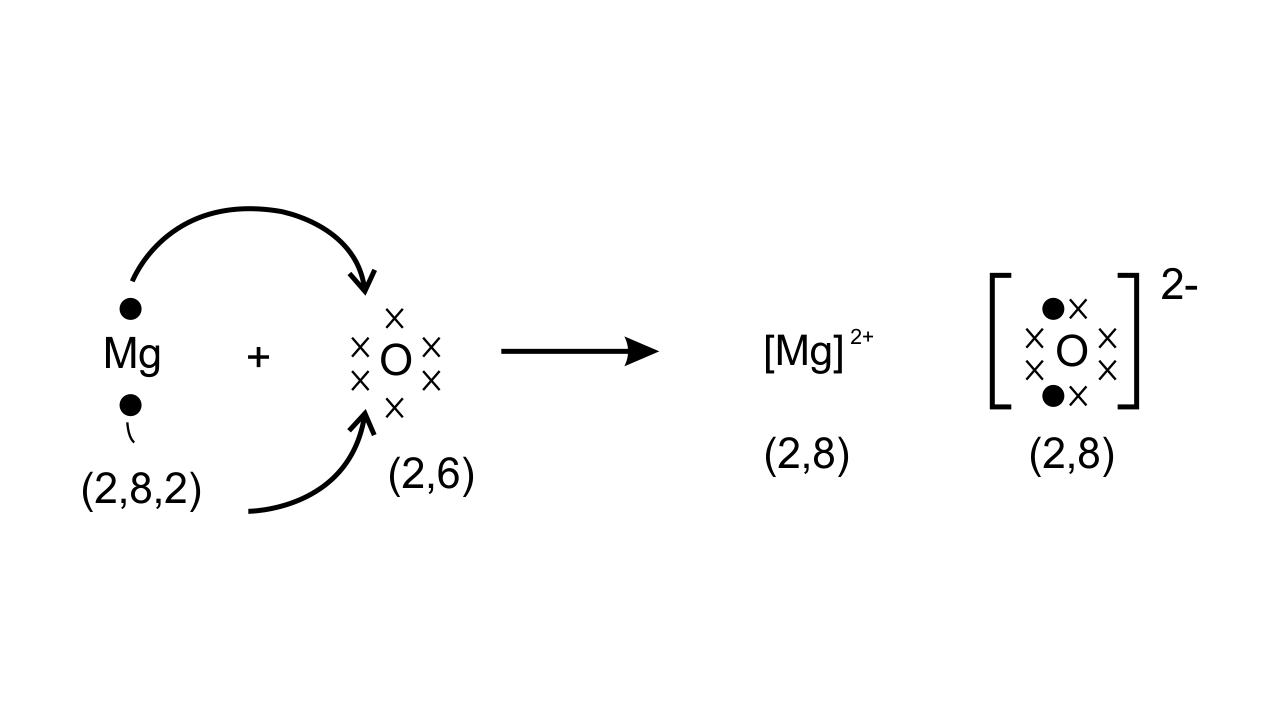
42. An element is placed in 2nd Group and 3rd Period of the Periodic Table, burns in presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(a) Identify the element
Ans: The element is magnesium which is placed in 2nd Group and 3rd Period of the Periodic Table, burns in presence of oxygen to form a basic oxide.
(b) Write the electronic configuration.
Ans: The electronic configuration of magnesium which has atomic number 12 is (2, 8, 2).
(c) Write the balanced equation when it burns in the presence of air.
Ans: The magnesium burns in air to form magnesium oxide the balanced equation is:
2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO
Magnesium Oxygen Magnesium oxide
(d) Write a balanced equation when this oxide is dissolved in water
Ans: The magnesium oxide dissolves in water to form alkali magnesium hydroxide
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)
Magnesium Oxide Water Magnesium hydroxide
(e) Draw the electron dot structure for the formation of this oxide
Ans:
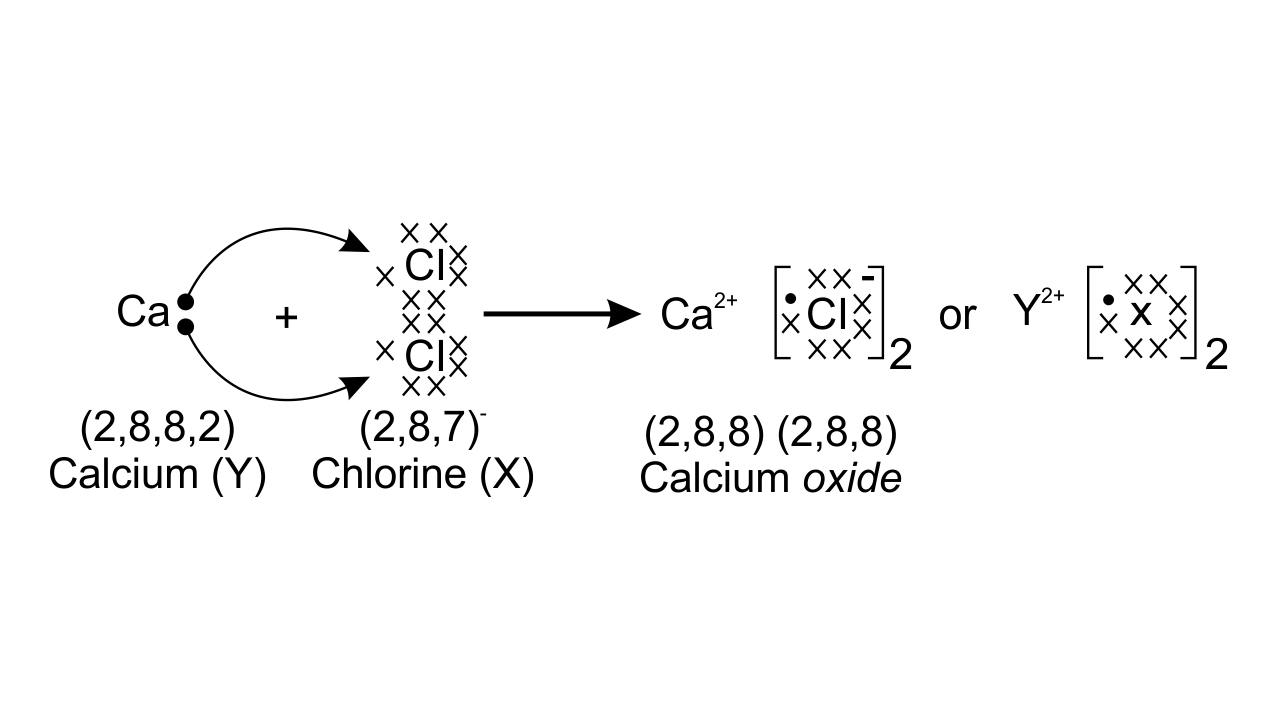
43. An element X (atomic number 17) reacts with an element Y (atomic number 20) to form a divalent halide.
(a) Where in the periodic table are elements X and Y placed?
Ans: Element X has atomic number 17 so the electronic configuration is (2, 8, 7) hence, it is placed in group 17 and period 3 in the periodic table.
Element Y has atomic number 20 so the electronic configuration is (2, 8, 8, 2) and placed in group 2 and period 4 in the periodic table.
(b) Classify X and Y as metal (s), non-metal (s) or metalloid (s).
Ans: Element X has 7 electrons in the valence shell and can accept 1 electron to attain nearest noble gas configuration. So element X is an electronegative element, and hence we can say that it is a non-metal.
Element Y has 2 electrons in its valence shell and can lose these 2 electrons to attain nearest noble gas configuration. So element Y is an electropositive element and hence we can say that it is a metal.
(c) What will be the nature of oxide of element Y? Identify the nature of bonding in the compound formed.
Ans: Element Y is a metal so it forms a basic oxide. The metal Y loses the 2 electrons and the oxygen gains these 2 electrons to form the basic oxide. As the compound formed by transfer of electrons, the nature of bonding in the compound is ionic compound.
(d) Draw the electron dot structure of the divalent halide
Ans: Calcium forms a divalent halide by losing 2 electrons. The electron dot structure of divalent halide is as follows:
44. Atomic number of a few elements are given below
10, 20, 7, 14
(a) Identify the elements
Ans: Atomic number 10: Neon
Atomic number 20: Calcium
Atomic number 7: Nitrogen
Atomic number 14: Silicon
(b) Identify the Group number of these elements in the Periodic Table
Ans: The group number of these elements in the periodic table is:
Neon - Group 18
Calcium - Group 2
Nitrogen - Group 15
Silicon - Group 14
(c) Identify the Periods of these elements in the Periodic Table.
Ans: The periods of these elements in the periodic table is:
Neon - Period 2
Calcium - Period 4
Nitrogen - Period 2
Silicon - Period 3
(d) What would be the electronic configuration for each of these elements?
Ans: The electronic configuration for each of these elements are:
Neon - Atomic Number 10 - Electronic configuration (2,8)
Calcium - Atomic Number 20 - Electronic configuration (2, 8, 8, 2)
Nitrogen - Atomic Number 7 - Electronic configuration (2, 5)
Silicon - Atomic Number 14 - Electronic configuration (2, 8, 4)
(e) Determine the valency of these elements
Ans: The valency of these elements are:
Neon - Valency 0
Calcium - Valency 2
Nitrogen - Valency 3
Silicon - Valency 4
45. Complete the following crossword puzzle (Figure 5.1)
1 | 7 | 2 | |||||||||
3 | 8 | 9 | 5 | ||||||||
4 | 6 | ||||||||||
Fig: 5.1
Across
(1) An element with atomic number 12.
Ans: Magnesium has atomic number 12.
(3) Metal used in making cans and members of Group 14.
Ans: Tin is a member of group 14 and used in making cans.
(4) A lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell.
Ans: Iodine is lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons in its outermost shell
Down
(2) Highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept in kerosene.
Ans: Sodium metal is a highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept in kerosene.
(5) The first element of second Period.
Ans: Lithium is the first element of second Period
(6) An element which is used in making fluorescent bulbs and is second member of Group 18 in the Modern Periodic Table
Ans: Neon is an element which is used in making fluorescent bulbs and is second member of Group 18 in the Modern Periodic Table.
(7) A radioactive element which is the last member of halogen family.
Ans: Astatine is a radioactive element which is the last member of halogen family.
(8) Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air.
Ans: Iron is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air.
(9) The first metalloid in Modern Periodic Table whose fibres are used in making bullet-proof vests
Ans: Boron is the first metalloid in Modern Periodic Table whose fibres are used in making bullet-proof vests
M 1 | A 7 | G | N | E | S 2 | I | U | M | |||
S | O | ||||||||||
T | I 8 | N | D | B 9 | 5 | ||||||
A | I 4 | O | D | I | N 6 | E | |||||
T | U | R | E | ||||||||
I | M | O | O | ||||||||
N | N | N | |||||||||
E | |||||||||||
46. (a) In this ladder (Figure 5.2) symbols of elements are Jumbled up. Rearrange these symbols of elements in the increasing order of their atomic number in the Periodic Table.
Ans: The increasing order of the atomic number is :
H, He, Li, Be, B, C, N O, F, Ne, Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, Ar, K, Ca.
(b) Arrange them in the order of their group also.
Ans:
Group 1 - H, Li, Na, K
Group 2 - Be, Mg, Ca
Group 13 - B, Al
Group 14 - C, Si
Group 15 - N, P
Group 16 - O, S
Group 17 - F, Cl
Group 18 - He, Ne, Ar
47. Mendeleev predicted the existence of certain elements not known at that time and named two of them as Eka-silicon and Eka-aluminium.
(a) Name the elements which have taken the place of these elements.
Ans: Gallium is the element which has taken the place of Eka-aluminium and Germanium is the element which has taken the place of Eka-silicon.
(b) Mention the group and the period of these elements in the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans: Gallium is placed in period 4 and group 13 and germanium is placed in period 4 and group 14.
(c) Classify these elements as metals, non-metals or metalloids.
Ans: Gallium is a metal whereas germanium is a metalloid.
(d) How many valence electrons are present in each one of them?
Ans: Gallium is present in group 13 has electron configuration as (2, 8, 3) so the number of valence electrons is 3. Germanium is present in group 14 has electronic configuration as (2, 8, 4) so the number of valence electrons is 4.
48. (a) Electropositive nature of the element(s) increases down the group and decreases across the period
(b) Electronegativity of the element decreases down the group and increases across the period
(c) Atomic size increases down the group and decreases across a period (left to right)
(d) Metallic character increases down t
On the basis of the above trends of the Periodic Table, answer the following about the elements with atomic numbers 3 to 9.
(a) Name the most electropositive element among them.
Ans: Lithium with atomic number 3 has electronic configuration as (2,1) is the most electropositive element among them.
(b) Name the most electronegative element.
Ans: Fluorine with atomic number 9 has electronic configuration as (2,7) is the most electronegative element.
(c) Name the element with smallest atomic size.
Ans: Fluorine is the element with the smallest atomic size among the given elements.
(d) Name the element which is a metalloid.
Ans: Boron is a metalloid which shows the property of both metals and nonmetals.
(e) Name the element which shows maximum valency.
Ans: Carbon is the element which shows maximum valency.
49. An element X which is a yellow solid at room temperature shows catenation and allotropy. X forms two oxides which are also formed during the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals and are the major air pollutants.
(a) Identify the element X
Ans: The element X is sulphur.
(b) Write the electronic configuration of X.
Ans: The electronic configuration of X is (2, 8, 6).
(c) Write the balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals?
Ans: The balanced chemical equation for the thermal decomposition of ferrous sulphate crystals is:
\[2FeS{{O}_{4}}\xrightarrow{\Delta}F{{e}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}+S{{O}_{2}}\uparrow +S{{O}_{3}}\uparrow \]
Ferrous Sulphate
(d) What would be the nature (acidic/ basic) of oxides formed?
Ans: The nature of oxides formed by sulphur are acidic oxides and turn the blue litmus red.
(e) Locate the position of the element in the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans: The sulphur is present in group 16 and period 3.
50. An element X of group 15 exists as a diatomic molecule and combines with hydrogen at 773 K in presence of the catalyst to form a compound, ammonia which has a characteristic pungent smell.
(a) Identify the element X. How many valence electrons does it have?
Ans: The element X is nitrogen and has 5 valence electrons.
(b) Draw the electron dot structure of the diatomic molecule of X. What type of bond is formed in it?
Ans: The electron dot structure of the diatomic molecule of X is:
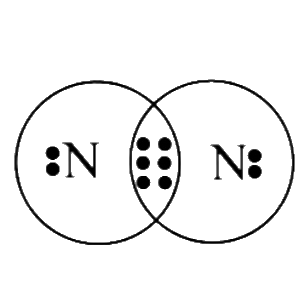
N2 is formed by sharing of electrons between two nitrogen atoms and hence the type of bonding is covalent bonding.
(c) Draw the electron dot structure for ammonia and what type of bond is formed in it?
Ans: The electron dot structure for ammonia:
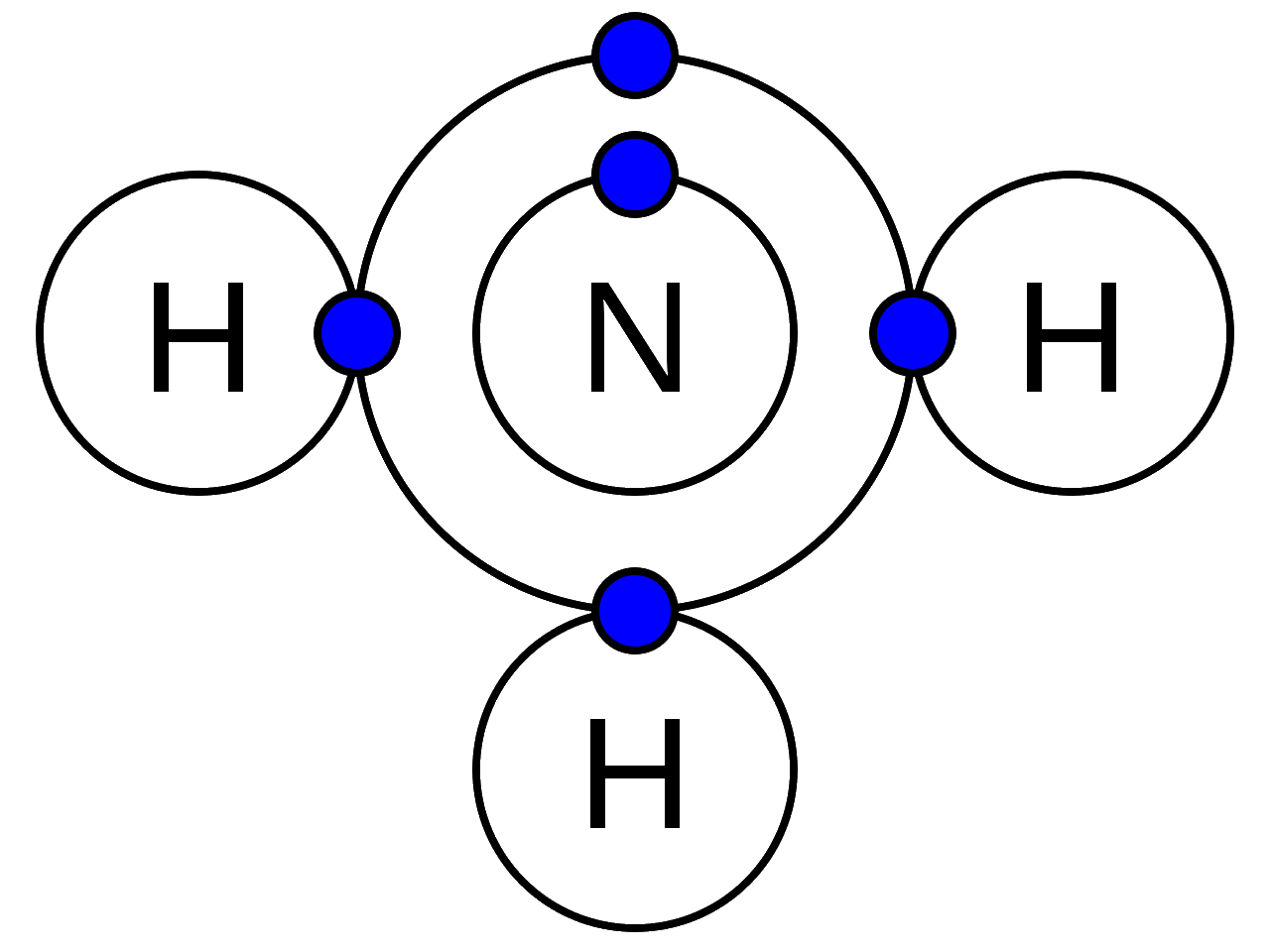
The three bonds are formed in NH3 by sharing of electrons between Nitrogen and hydrogen so the type of bonding is covalent bonding is formed in it.
51. Which group of elements could be placed in Mendeleev's Periodic Table without disturbing the original order? Give a reason.
Ans: Noble gases could be placed in Mendeleev's Periodic Table without disturbing the original order. Helium, neon, and argon are noble gases and were known by scientists much before Mendeleev. Mendeleev's Periodic Table contains only 63 elements as at that time only 63 elements were known however he left the spaces for the undiscovered elements. Noble gases were grouped much later than Mendeleev.
52. Give an account of the process adopted by Mendeleev for the classification of elements. How did he arrive at "Periodic Law"?
Ans: At the time of Mendeleev’s classification of elements, 63 elements were known. He examined the relationship of different elements having their particular atomic masses with their physical and chemical properties. For chemical properties, he examined the compounds formed with hydrogen and oxygen as they form compounds with most of the elements. Formulae of oxides and hydrides formed by the elements were treated as the basis for the classification of elements.
He grouped the elements with similar properties together and placed them in a periodic table. He observed that the elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses. He also observed that the elements that have similar properties occur periodically. This states the periodic law as ‘properties of elements are the periodic function of atomic masses.’
Periodic Classification of elements in NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5
In Chapter-5 of Class 10 Science, the periodic Classification of elements means arranging all the elements of the periodic table in such a way that they are aligned according to their properties. This should be done in such a way so that the elements with similar properties fall in one group. The students should note that however, each element is different from the other but they resemble each other in properties such as certain chemical reactions with a reactant and producing the same type of product.
By downloading and referring to this solution, you will get an idea of how to answer the questions related to this chapter. Focus on the ways the experts of Vedantu have framed the answers. Find out how they have used the concepts mentioned in the NCERT book to answer these questions easily. Learn how to save your time during an examination by answering these questions appropriately.
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements (Book Solutions)
1. What are the Concepts used in NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements (Book Solutions)?
The students of Class 10 in this chapter will learn about how the elements were Classified over the years such as Doberenier’s Triads, Newland’s law of Octaves-its assumptions and limitations, Mendeleev’s periodic tables - its limitations and achievements, The modern periodic table- trends and position of elements, the modern periodic law, periods in the modern periodic table, groups in the modern periodic table, Alkali metals, Alkali earth metals, Halogens, Noble gases, Classification of the modern periodic table and why there is the need for Classification of elements periodically.
2. Where can I find the NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements (Book Solutions)?
The students of Class 10 who want to prepare for their boards the right way can find everything they need at Vedantu.com. You can download a variety of study material like Important Questions for Class 10, Sample papers, Mock tests, Practice tests, NCERT Book, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions and so much more in PDF format for absolutely free. For this, the students can use the Vedantu website or app. All you have to do is sign in and enjoy the unlimited study material that Vedantu has curated just for you.
3. How can I understand NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements (Book Solutions)?
The students of Class 10 should give sufficient time to the concepts used in Class 10 Science Chapter-5 Periodic Classification of Elements solutions. Class 10 in itself is an important grade to be studying in and this chapter is also really important because the students will have to revisit these concepts in higher classes. Segmenting the concepts and understanding them with examples will help a lot. Refer to the solutions provided by Vedantu to figure out how these concepts are used for answering. Thus, it is advised that every single student studies, understands, and practices each concept of this chapter. In case of any doubts or queries arising, you can join our online tuitions to make sure you score well.
4. Why should I study from NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 5 - Periodic Classification of Elements (Book Solutions)?
Students who want to prepare for Class 10 board examinations in the best way possible to score the highest should use NCERT and NCERT Exemplar. The NCERT might have basic questions and that is why the examination paper also contains a lot of questions from NCERT Exemplar which can be considered a little more advanced as compared to the NCERT book questions. After completing NCERT, you can proceed to NCERT Exemplar for creating a stronger foundation of the chapters in science.






































