
${{x}^{2}}-\left( m-3 \right)x+m=0\left( m\in R \right)$ be a quadratic equation. Find the value of m for which, at least one root is greater than 2.
A. $\left[ -9,9 \right]$
B. $\left[ 9,\infty \right)$
C. $\left( -\infty ,9 \right]$
D. None of the above.
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint: We will use the concepts of quadratic functions to solve the problem. We will be using the fact that if both roots exist then the discriminant of the quadratic function is always greater than zero we will form another inequality by using the fact that we have given that one root is greater than 2 then we will use these two inequalities to find the range of m.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have to find the m for which $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-\left( m-3 \right)x+m$ has at least one root greater than 2. Now, here two cases arise. In the first case we have a number of greater than 2 is one. So, graph of this case is,
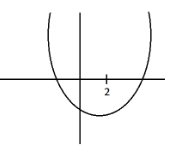
Now, from the graph we can see that $D\ge 0$and $f\left( e \right)<0$.
Now, solving $D\ge 0$for $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-\left( m-3 \right)x+m$.
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( m-3 \right)}^{2}}-4m\ge 0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}+9-6m-4m\ge 0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}-10m+9>0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}-9m-m+9\ge 0 \\
& m\left( m-9 \right)-1\left( m-9 \right)\ge 0 \\
& \left( m-1 \right)\left( m-9 \right)\ge 0 \\
\end{align}$
Now for $-\infty < x\le 1$ and $9 < x < \infty $we have $\left( m-1 \right)\left( m-9 \right)\ge 0$.
So,
$x\in \left( -\infty ,1 \right]\cup \left[ 9,\infty \right)...........\left( 1 \right)$
Also, $f\left( 2 \right)<0$ . So,
$\begin{align}
& 4-\left( m-3 \right)2+m < 0 \\
& 4-2m-6+m < 0 \\
& 10 < m \\
& m > 10.............\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Combining (1) & (2) we get;
$x\in \left( 10,\infty \right)$ for case 1;
We will similarly solve for case 2 in which both roots are greater than 2. So, graph of this case is,
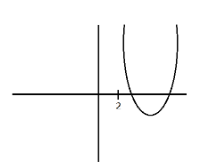
Now, from graph we have
$D\ge 0$ and $f\left( 2 \right)\ge 0$
$D\ge 0$is same as equation (1)
So, for $f\left( 2 \right)\ge 0$we have;
$\begin{align}
& 4-\left( m-3 \right)2+m\ge 0 \\
& 4-2m+6+m\ge 0 \\
& 10\ge m \\
& m\le 10..............\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, combining (1) and (3) we have;
$x\in \left( -\infty ,\left. 1 \right] \right.\cup \left[ 9,10 \right]...................\left( 4 \right)$
Now, we will be taking a union of solutions of both cases as both of them satisfy the given condition.
So,
$\begin{align}
& x\in \left( -\infty ,\left. 1 \right] \right.\cup \left[ 9,10 \right]\cup \left( 10,\infty \right) \\
& x\in \left( -\infty ,\left. 1 \right] \right.\cup \left[ 9,\left. \infty \right) \right. \\
\end{align}$
Option (B) is the correct option as it is the only correct subset of the solution.
Note: To solve these type of questions it is important to note that we have used the fact that if both roots of the quadratic equation are real and distinct then the discriminant of the quadratic equation is greater than zero also it has to be noticed that we have divided the question in cases and then solved for each cases for the condition that one root is greater than zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have to find the m for which $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-\left( m-3 \right)x+m$ has at least one root greater than 2. Now, here two cases arise. In the first case we have a number of greater than 2 is one. So, graph of this case is,

Now, from the graph we can see that $D\ge 0$and $f\left( e \right)<0$.
Now, solving $D\ge 0$for $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}-\left( m-3 \right)x+m$.
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( m-3 \right)}^{2}}-4m\ge 0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}+9-6m-4m\ge 0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}-10m+9>0 \\
& {{m}^{2}}-9m-m+9\ge 0 \\
& m\left( m-9 \right)-1\left( m-9 \right)\ge 0 \\
& \left( m-1 \right)\left( m-9 \right)\ge 0 \\
\end{align}$
Now for $-\infty < x\le 1$ and $9 < x < \infty $we have $\left( m-1 \right)\left( m-9 \right)\ge 0$.
So,
$x\in \left( -\infty ,1 \right]\cup \left[ 9,\infty \right)...........\left( 1 \right)$
Also, $f\left( 2 \right)<0$ . So,
$\begin{align}
& 4-\left( m-3 \right)2+m < 0 \\
& 4-2m-6+m < 0 \\
& 10 < m \\
& m > 10.............\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Combining (1) & (2) we get;
$x\in \left( 10,\infty \right)$ for case 1;
We will similarly solve for case 2 in which both roots are greater than 2. So, graph of this case is,

Now, from graph we have
$D\ge 0$ and $f\left( 2 \right)\ge 0$
$D\ge 0$is same as equation (1)
So, for $f\left( 2 \right)\ge 0$we have;
$\begin{align}
& 4-\left( m-3 \right)2+m\ge 0 \\
& 4-2m+6+m\ge 0 \\
& 10\ge m \\
& m\le 10..............\left( 3 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, combining (1) and (3) we have;
$x\in \left( -\infty ,\left. 1 \right] \right.\cup \left[ 9,10 \right]...................\left( 4 \right)$
Now, we will be taking a union of solutions of both cases as both of them satisfy the given condition.
So,
$\begin{align}
& x\in \left( -\infty ,\left. 1 \right] \right.\cup \left[ 9,10 \right]\cup \left( 10,\infty \right) \\
& x\in \left( -\infty ,\left. 1 \right] \right.\cup \left[ 9,\left. \infty \right) \right. \\
\end{align}$
Option (B) is the correct option as it is the only correct subset of the solution.
Note: To solve these type of questions it is important to note that we have used the fact that if both roots of the quadratic equation are real and distinct then the discriminant of the quadratic equation is greater than zero also it has to be noticed that we have divided the question in cases and then solved for each cases for the condition that one root is greater than zero.
Recently Updated Pages
While covering a distance of 30km Ajeet takes 2 ho-class-11-maths-CBSE

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




