
Write the IUPAC name of ${{\left[ Co{{\left( en \right)}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}} \right]}^{+}}$ion and draw the structure of its geometrical isomers.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The given compound is a coordination compound. Such compounds are different from other compounds. They retain their identity in the solution. Its naming will be done by the rules of nomenclature of coordination compounds. Isomerism is possible in this due to the presence of 2 different ligands associated with the central atom.
Complete step by step solution:
-Coordination compounds consist of the central atom and ligands associated with it. Ligands are the species which are directly linked to the central tom. They can be neutral, anion or cation. Coordination compounds are named based on certain rules for their naming.
- The rules for naming these types of compounds are:
1. Always the cations are written first and then the anions in the compounds.
2. Ligands are always written alphabetically before the central atom/ion. 2 ligands are present here and so chlorine will come prior to ethylenediamine.
3. Names of anionic ligands end in –o and cationic ligands end in –ium. This rule is not followed by neutral ligands like CO, CS, NO, water and ammonia. So in this question, chlorine will be written as chloro and no suffix is added in other ligands as it is neutral.
4. If there are more than 1 ligands of the same type, prefixes are used to indicate the numbers like di, tri, tetra, etc. For polydentate ligands, prefixes used are –bis, -tris, etc is used. 2 chlorine ligands are present and so we write dichloro and bis for ethylenediamine.
5. Oxidation state of the central atom is always indicated in naming these compounds and is written in roman numerals after the metal name in parenthesis. Here the oxidation number is 3 and so we write cobalt(III).
6. Name of metal is written the same as that of the element if the compound is cationic. If the complex is anion, then the metal name ends with suffix –ate. Latin names are used for this. The given ion is cationic and so we do not use any suffix in cobalt.
7. Neutral complex is named similar to the cations.
8. If the complex shows geometrical isomerism, then the prefix cis- and trans- is used before the name of the compound.
So, keeping in mind the following rules, we can see that the IUPAC name of the compound is Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine) cobalt(III) ion.
-Now coming to the second part of the question. We are asked to draw the structures of the isomers of this complex compound.There are basically 2 types of isomerism in such compounds which are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
-Structural isomerism is subdivided into ionization, hydrate, linkage, coordination, ligands and polymerization isomerism. Stereoisomerism is subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
-Now looking at the compounds given, we can see that it has 2 different types of ligands and so can show geometrical isomers of two forms- cis and trans which can be shown as
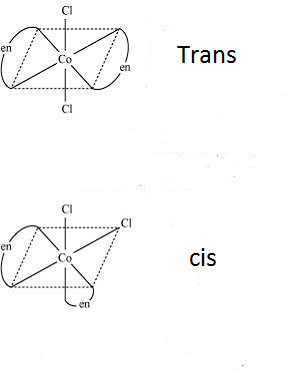
Note: We should know that geometrical isomerism is not possible in tetrahedral compounds as all the 4 different positions are considered to be identical in a tetrahedral structure. Geometrical isomerism occurs in square planar compounds of coordination number 4 and in the compounds with the coordination number 6.
Complete step by step solution:
-Coordination compounds consist of the central atom and ligands associated with it. Ligands are the species which are directly linked to the central tom. They can be neutral, anion or cation. Coordination compounds are named based on certain rules for their naming.
- The rules for naming these types of compounds are:
1. Always the cations are written first and then the anions in the compounds.
2. Ligands are always written alphabetically before the central atom/ion. 2 ligands are present here and so chlorine will come prior to ethylenediamine.
3. Names of anionic ligands end in –o and cationic ligands end in –ium. This rule is not followed by neutral ligands like CO, CS, NO, water and ammonia. So in this question, chlorine will be written as chloro and no suffix is added in other ligands as it is neutral.
4. If there are more than 1 ligands of the same type, prefixes are used to indicate the numbers like di, tri, tetra, etc. For polydentate ligands, prefixes used are –bis, -tris, etc is used. 2 chlorine ligands are present and so we write dichloro and bis for ethylenediamine.
5. Oxidation state of the central atom is always indicated in naming these compounds and is written in roman numerals after the metal name in parenthesis. Here the oxidation number is 3 and so we write cobalt(III).
6. Name of metal is written the same as that of the element if the compound is cationic. If the complex is anion, then the metal name ends with suffix –ate. Latin names are used for this. The given ion is cationic and so we do not use any suffix in cobalt.
7. Neutral complex is named similar to the cations.
8. If the complex shows geometrical isomerism, then the prefix cis- and trans- is used before the name of the compound.
So, keeping in mind the following rules, we can see that the IUPAC name of the compound is Dichlorobis(ethylenediamine) cobalt(III) ion.
-Now coming to the second part of the question. We are asked to draw the structures of the isomers of this complex compound.There are basically 2 types of isomerism in such compounds which are structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
-Structural isomerism is subdivided into ionization, hydrate, linkage, coordination, ligands and polymerization isomerism. Stereoisomerism is subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
-Now looking at the compounds given, we can see that it has 2 different types of ligands and so can show geometrical isomers of two forms- cis and trans which can be shown as

Note: We should know that geometrical isomerism is not possible in tetrahedral compounds as all the 4 different positions are considered to be identical in a tetrahedral structure. Geometrical isomerism occurs in square planar compounds of coordination number 4 and in the compounds with the coordination number 6.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




