
Explain sex determination in humans with the help of a flow- chart.
Answer
526.7k+ views
Hint: Among the 23 pairs of chromosomes, the 23rd pair are sex chromosomes (which determine whether the offspring will be male or female), XX for females, or XY for males. They participate in sex determination.
Complete answer:
In a human being, the sex of a child is determined depending upon which type of male gamete fertilizes with the female gamete. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of the mother and the father. Out of 23 pairs, 22 pairs are said to be autosomes and one pair is called sex chromosomes (in male XY and female XX). At the time of fertilization, the sperm fertilizes the egg cell to form the zygote. If the sperm carrying X- chromosome fertilizes an ovum carrying an X chromosome, then the child born will be a girl. If the sperm carrying Y- chromosome fertilizes an ovum carrying X- chromosome, the child born will be a boy.
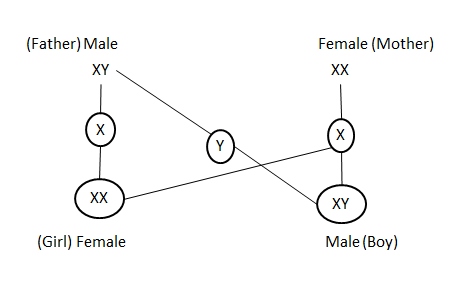
Figure: Sex determination
Additional Information:
- Sex is the hereditary difference between two individuals of the same species.
- X- chromosomes were first identified by Wilson and Stevens in 1905.
- Autosomes are chromosomes that are the same in both types of sexes.
- Sex chromosomes are also known as allosomes.
- Males are known as heterogametic because they possess the Y- chromosome.
- Two short arms (p arms), two longer arms (q arms), and a centromere at the center are present in each chromosome.
Note:
- At the time of spermatogenesis, there will be two types of sperm cells produced in equal numbers, one containing an X- chromosome and the other containing a Y chromosome.
- Since in males, one sex chromosome is X and the other is Y, they are called heterogametic while the females are homogametic because of two X chromosomes.
Complete answer:
In a human being, the sex of a child is determined depending upon which type of male gamete fertilizes with the female gamete. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in each of the mother and the father. Out of 23 pairs, 22 pairs are said to be autosomes and one pair is called sex chromosomes (in male XY and female XX). At the time of fertilization, the sperm fertilizes the egg cell to form the zygote. If the sperm carrying X- chromosome fertilizes an ovum carrying an X chromosome, then the child born will be a girl. If the sperm carrying Y- chromosome fertilizes an ovum carrying X- chromosome, the child born will be a boy.

Figure: Sex determination
Additional Information:
- Sex is the hereditary difference between two individuals of the same species.
- X- chromosomes were first identified by Wilson and Stevens in 1905.
- Autosomes are chromosomes that are the same in both types of sexes.
- Sex chromosomes are also known as allosomes.
- Males are known as heterogametic because they possess the Y- chromosome.
- Two short arms (p arms), two longer arms (q arms), and a centromere at the center are present in each chromosome.
Note:
- At the time of spermatogenesis, there will be two types of sperm cells produced in equal numbers, one containing an X- chromosome and the other containing a Y chromosome.
- Since in males, one sex chromosome is X and the other is Y, they are called heterogametic while the females are homogametic because of two X chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




