
Write short notes on synergic bonding.
Answer
600.9k+ views
Hint: We must know that It is usually used in the context of organometallic chemistry where there is a transition metal center and good pi-acceptor ligands.
Complete step by step answer:
- The back donation reinforces the sigma bond and vice versa. This type of bonding has been called synergic bonding.
- Pi back bonding is very common in organometallic chemistry, where transition elements form coordinate covalent bonds with polyatomic ligands (examples of which include carbon monoxide and ethylene).
- Reason: This effect is observed when a pi-back donation of electron density occurs from an atomic orbital of one atom to the antibonding pi-orbital of another. The antibonding pi-orbital of a pi-acceptor ligand.
The interaction involved in the formation of a metal-carbonyl bond:
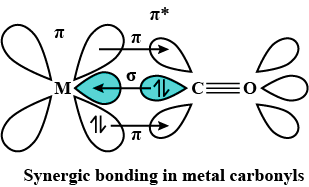
> Firstly donation of electrons from the ligand to an empty orbital on the metal which gives the typical ligand-metal interaction.
> A second interaction can occur if the metal has filled d orbitals. The electrons are donated from the filled d orbitals on the metal to an empty orbital of the ligand.
Together, these two interactions make up synergic bonding.
> Effects of synergistic bonds are:
(1) It strengthens the M-C bond while weakening the C-O bond.
(2) It also leads to a shortening of the M-C-O bond length.
Note: Synergistic bonds in organ-metallic chemistry are affected by various factors:
(1) Charge on the metal - To increase the strength of the synergic bonds, the central metal atom in the coordination complex should be electron rich.
(2) Contribution of other ligands on the metal center - Electron donating ligands increase the back-bonding process while the electron-withdrawing reduces the back-bonding process.
Complete step by step answer:
- The back donation reinforces the sigma bond and vice versa. This type of bonding has been called synergic bonding.
- Pi back bonding is very common in organometallic chemistry, where transition elements form coordinate covalent bonds with polyatomic ligands (examples of which include carbon monoxide and ethylene).
- Reason: This effect is observed when a pi-back donation of electron density occurs from an atomic orbital of one atom to the antibonding pi-orbital of another. The antibonding pi-orbital of a pi-acceptor ligand.
The interaction involved in the formation of a metal-carbonyl bond:

> Firstly donation of electrons from the ligand to an empty orbital on the metal which gives the typical ligand-metal interaction.
> A second interaction can occur if the metal has filled d orbitals. The electrons are donated from the filled d orbitals on the metal to an empty orbital of the ligand.
Together, these two interactions make up synergic bonding.
> Effects of synergistic bonds are:
(1) It strengthens the M-C bond while weakening the C-O bond.
(2) It also leads to a shortening of the M-C-O bond length.
Note: Synergistic bonds in organ-metallic chemistry are affected by various factors:
(1) Charge on the metal - To increase the strength of the synergic bonds, the central metal atom in the coordination complex should be electron rich.
(2) Contribution of other ligands on the metal center - Electron donating ligands increase the back-bonding process while the electron-withdrawing reduces the back-bonding process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




