
Write short note on:
Mesomeric effect
Answer
516.9k+ views
Hint: the displacement of covalent bonds in any compound can result in various types of effects that affect the reacting capability of that compound. Mesomeric effect is the delocalization of electrons in a system having variable electron densities. The mesomeric effect is also known as resonance effect and is of +M and – M types.
Complete answer:
The flow of electrons from the bonded pair of electrons like a covalent bond can give rise to various effects. Mesomeric effect or the M effect is the flow of electrons from one part of the system to the other in a conjugated system that consists of double and single bonds. This flow of electrons can give rise to centers of low and high electron densities. This is the effect that has an interaction between the pi – bonds or between the pi – bonds and lone pair of electrons that is present on the adjacent atoms.
There are 2 types of M effect:
+M effect is shown when the attached groups on the system tend to donate electrons into the conjugated system. These groups create areas of high electron densities. Examples OH, OR, OCOR, NHR, $N{{H}_{2}},N{{R}_{2}}$, etc.
– M effect is the effect when the attached groups withdraw electrons from the system creating electron deficiency in the system. The examples of such groups are COOH, COCl, CHO, CO, CN, etc.
Mesomeric effect can be depicted by various canonical forms that show the delocalization (flow) of electrons. Example of M effect in a phenoxide ion is shown:
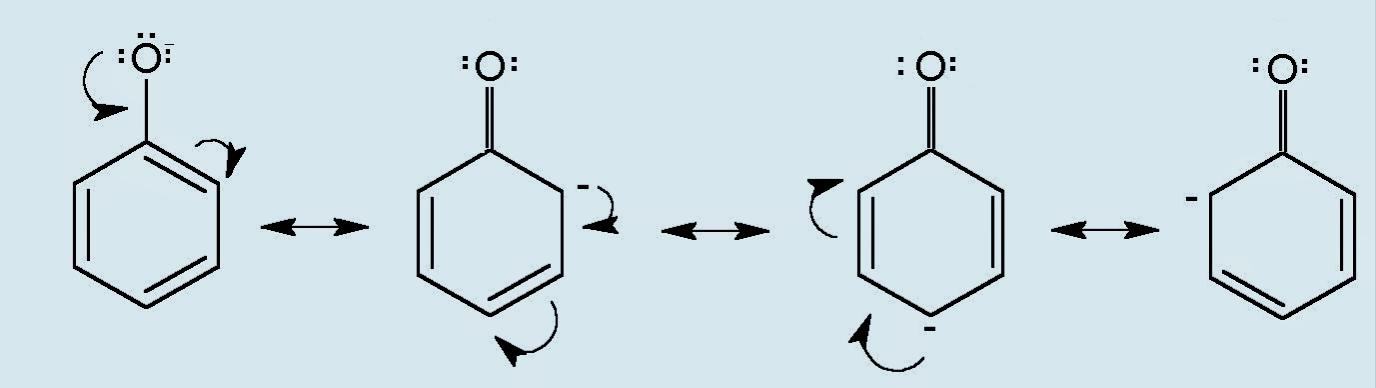
Note:
Mesomeric effect is also called the resonance effect that can be denoted as – R or + R, this involves the canonical structures just like the resonating structures. There are various other effects also like inductive effect, hyper conjugation, electromeric effect (E effect) etc. They all specify the reactivity of the substances towards various reactions.
Complete answer:
The flow of electrons from the bonded pair of electrons like a covalent bond can give rise to various effects. Mesomeric effect or the M effect is the flow of electrons from one part of the system to the other in a conjugated system that consists of double and single bonds. This flow of electrons can give rise to centers of low and high electron densities. This is the effect that has an interaction between the pi – bonds or between the pi – bonds and lone pair of electrons that is present on the adjacent atoms.
There are 2 types of M effect:
+M effect is shown when the attached groups on the system tend to donate electrons into the conjugated system. These groups create areas of high electron densities. Examples OH, OR, OCOR, NHR, $N{{H}_{2}},N{{R}_{2}}$, etc.
– M effect is the effect when the attached groups withdraw electrons from the system creating electron deficiency in the system. The examples of such groups are COOH, COCl, CHO, CO, CN, etc.
Mesomeric effect can be depicted by various canonical forms that show the delocalization (flow) of electrons. Example of M effect in a phenoxide ion is shown:

Note:
Mesomeric effect is also called the resonance effect that can be denoted as – R or + R, this involves the canonical structures just like the resonating structures. There are various other effects also like inductive effect, hyper conjugation, electromeric effect (E effect) etc. They all specify the reactivity of the substances towards various reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




