
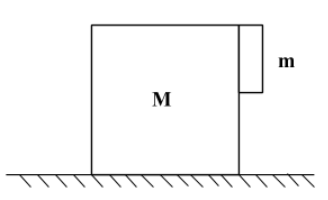
With what minimum acceleration, mass M must be moved on a frictionless surface so that m remains stuck to it as shown? The coefficient of friction between M and m is $\mu$.
A.$\dfrac {g} {\mu}$
B.$\mu g$
C.$2 \mu g$
D.$\dfrac {2g} {\mu}$

Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: Friction force is the force which is produced by two surfaces when they come in contact with each other and slide against each other. The maximum resistive force applied by the body against the applied force to remain in its state of motion is called the coefficient of friction. To solve this problem, use the formula for force of friction or friction force. Then, use the newton’s law of motion. Equate these two equations and calculate the minimum acceleration for the mass M.
Complete answer:
The force of friction is given by,
$F = \mu N$ …(1)
Where, N is the normal force of m on the surface of M
$\mu$ is the coefficient of friction
For mass m to stick to M while M is moving with acceleration, it has to move with the same acceleration with which M is moving.
Therefore, according to Newton’s second law of motion,
$F = mg$ …(2)
Equating equation. (1) and (2) we get,
$\mu N = ma$ …(3)
But, the normal force is given by,
$N= m.a$
Substituting this value in the equation. (3) we get,
$\mu \times m.a = mg$
$\Rightarrow \mu . a= g$
$\Rightarrow a= \dfrac {g}{\mu}$
Hence, the minimum acceleration should be $\dfrac {g}{\mu}$.
So, the correct answer is option A i.e. $\dfrac {g}{\mu}$.
Note:
Friction force can never be greater than the applied force. Whenever the frictional force is greater than the applied force, the friction force adjusts itself so that it becomes less as compared to the applied force. Friction force is dependent on the angle and the location of the object. The direction of force and friction force are always in opposite directions. Coefficient of friction is a dimensionless quantity.
Complete answer:
The force of friction is given by,
$F = \mu N$ …(1)
Where, N is the normal force of m on the surface of M
$\mu$ is the coefficient of friction
For mass m to stick to M while M is moving with acceleration, it has to move with the same acceleration with which M is moving.
Therefore, according to Newton’s second law of motion,
$F = mg$ …(2)
Equating equation. (1) and (2) we get,
$\mu N = ma$ …(3)
But, the normal force is given by,
$N= m.a$
Substituting this value in the equation. (3) we get,
$\mu \times m.a = mg$
$\Rightarrow \mu . a= g$
$\Rightarrow a= \dfrac {g}{\mu}$
Hence, the minimum acceleration should be $\dfrac {g}{\mu}$.
So, the correct answer is option A i.e. $\dfrac {g}{\mu}$.
Note:
Friction force can never be greater than the applied force. Whenever the frictional force is greater than the applied force, the friction force adjusts itself so that it becomes less as compared to the applied force. Friction force is dependent on the angle and the location of the object. The direction of force and friction force are always in opposite directions. Coefficient of friction is a dimensionless quantity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




